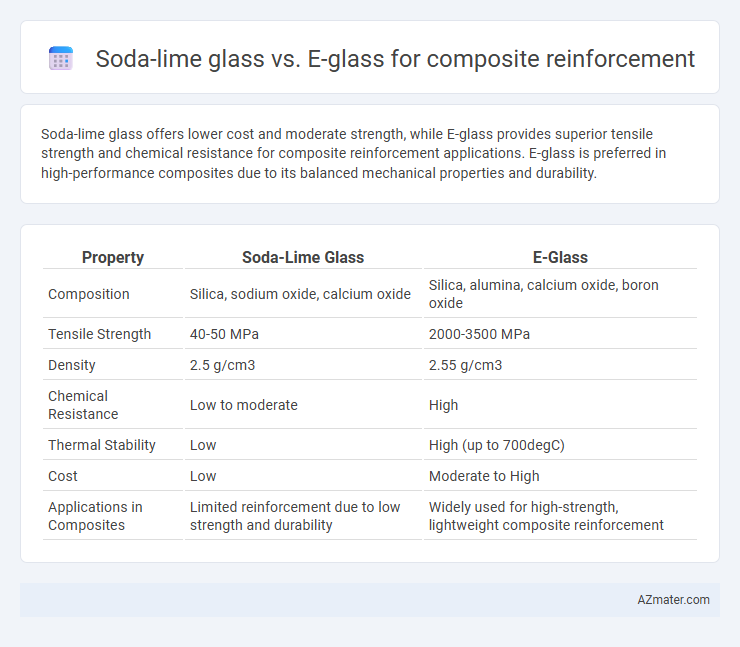
Soda-lime glass offers lower cost and moderate strength, while E-glass provides superior tensile strength and chemical resistance for composite reinforcement applications. E-glass is preferred in high-performance composites due to its balanced mechanical properties and durability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Soda-Lime Glass | E-Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Silica, sodium oxide, calcium oxide | Silica, alumina, calcium oxide, boron oxide |
| Tensile Strength | 40-50 MPa | 2000-3500 MPa |
| Density | 2.5 g/cm3 | 2.55 g/cm3 |
| Chemical Resistance | Low to moderate | High |
| Thermal Stability | Low | High (up to 700degC) |
| Cost | Low | Moderate to High |
| Applications in Composites | Limited reinforcement due to low strength and durability | Widely used for high-strength, lightweight composite reinforcement |
Introduction to Composite Reinforcement
Soda-lime glass and E-glass are widely used as reinforcement fibers in composite materials due to their distinct mechanical and chemical properties. Soda-lime glass offers cost-effective reinforcement with moderate strength and durability, while E-glass provides superior tensile strength, electrical insulation, and resistance to moisture and chemicals, making it ideal for high-performance composite applications. The selection between soda-lime glass and E-glass depends on the required composite material properties such as strength, durability, and environmental resistance.
Overview of Soda-Lime Glass
Soda-lime glass, the most common glass type used for composite reinforcement, consists primarily of silica (SiO2), soda (Na2O), and lime (CaO), providing cost-effective and versatile material properties. It offers moderate chemical resistance, good mechanical strength, and ease of processing, making it suitable for a wide range of applications including automotive and building materials. While less resistant to alkali environments than E-glass, soda-lime glass remains a popular choice for composites where budget and general performance are key factors.
Overview of E-Glass
E-glass, a type of fiberglass composed mainly of silica, alumina, and calcium oxide, offers superior tensile strength and excellent electrical insulating properties, making it ideal for composite reinforcement. Compared to soda-lime glass, E-glass exhibits higher chemical durability and better resistance to moisture, enhancing the longevity and structural integrity of composite materials. Its consistent fiber diameter and high modulus contribute to improved mechanical performance in aerospace, automotive, and construction applications.
Chemical Composition Comparison
Soda-lime glass primarily consists of approximately 70-74% silica (SiO2), 12-16% sodium oxide (Na2O), and 5-11% calcium oxide (CaO), which makes it less chemically resistant and more prone to moisture-related degradation. E-glass contains about 53-56% silica (SiO2), 14-16% alumina (Al2O3), 16-25% calcium oxide (CaO), and low alkali content, providing enhanced chemical durability and electrical insulation properties. The higher alumina content in E-glass contributes to improved mechanical strength and corrosion resistance, making it more suitable for composite reinforcement applications.
Mechanical Properties Analysis
Soda-lime glass exhibits moderate mechanical properties with tensile strength around 45-60 MPa and a lower modulus of elasticity compared to E-glass, which typically features tensile strength exceeding 2000 MPa and a higher elastic modulus near 70 GPa. E-glass's superior impact resistance, higher fatigue endurance, and better chemical durability make it the preferred reinforcement for high-performance composite materials. Mechanical properties analysis consistently shows E-glass composites deliver enhanced load-bearing capacity and improved structural stability over soda-lime glass composites in demanding engineering applications.
Thermal Performance Differences
Soda-lime glass exhibits lower thermal stability compared to E-glass, making it less suitable for high-temperature composite applications. E-glass demonstrates superior thermal resistance and maintains mechanical properties at elevated temperatures up to 600degC, which ensures greater composite durability. The enhanced thermal performance of E-glass reduces thermal expansion mismatch and improves composite dimensional stability under thermal cycling.
Durability and Environmental Resistance
Soda-lime glass offers moderate durability and environmental resistance with limited moisture and chemical stability, making it less suitable for harsh or long-term composite reinforcement applications. E-glass, engineered with enhanced silica and alumina content, provides superior durability and outstanding resistance to moisture, UV radiation, and alkali conditions, ensuring longevity and reliability in composites exposed to aggressive environments. The enhanced chemical composition of E-glass significantly improves its performance in marine, automotive, and construction industries compared to soda-lime glass.
Cost and Availability Factors
Soda-lime glass is significantly cheaper and more widely available than E-glass, making it a cost-effective option for composite reinforcement in large-scale applications. While E-glass offers superior mechanical properties and chemical resistance, its higher production costs and limited supply increase the overall expense of composite manufacturing. Cost-sensitive industries often favor soda-lime glass due to its abundant raw materials and established global supply chain, despite performance trade-offs.
Applications in Composite Materials
E-glass exhibits superior tensile strength and chemical resistance, making it the preferred choice for high-performance composite reinforcement in aerospace and automotive industries. Soda-lime glass, while more cost-effective, is primarily utilized in non-structural composite applications such as insulation and decorative panels where mechanical demands are lower. The optimized combination of mechanical properties in E-glass enhances composite durability and load-bearing capacity in demanding environments.
Choosing the Right Glass for Reinforcement
Soda-lime glass offers cost-effective reinforcement with moderate mechanical strength and chemical durability, making it suitable for general-purpose composites. E-glass provides higher tensile strength, better electrical insulation, and enhanced corrosion resistance, ideal for demanding structural applications. Selecting the right glass reinforcement requires balancing mechanical performance, environmental resistance, and budget constraints to optimize composite material properties.
Infographic: Soda-lime glass vs E-glass for Composite reinforcement
 azmater.com
azmater.com