Bulletproof glass provides enhanced ballistic protection with multiple layers of polycarbonate and glass, making it ideal for high-security vehicles. Laminated glass features a safety interlayer that prevents shattering, offering standard impact resistance and improved occupant safety for everyday windshields.
Table of Comparison
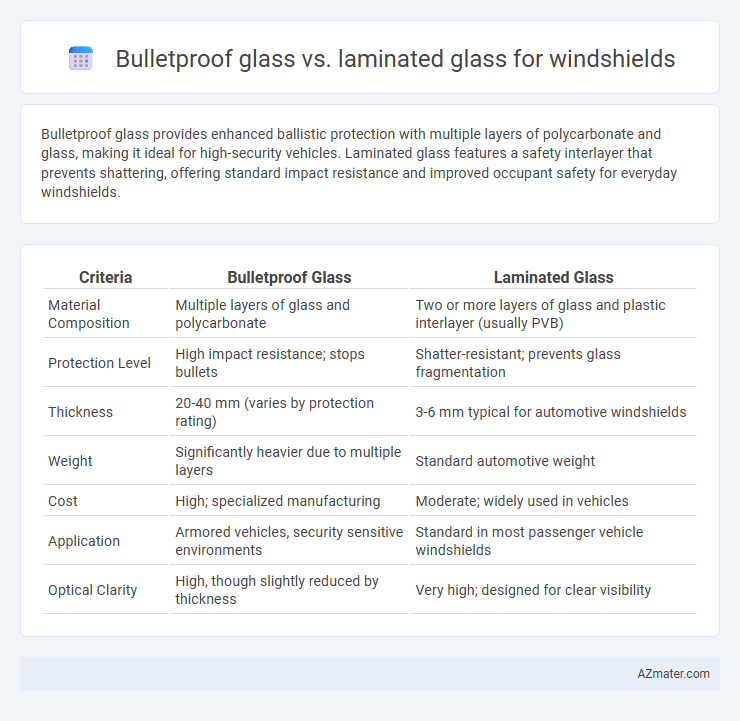
| Criteria | Bulletproof Glass | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Multiple layers of glass and polycarbonate | Two or more layers of glass and plastic interlayer (usually PVB) |
| Protection Level | High impact resistance; stops bullets | Shatter-resistant; prevents glass fragmentation |
| Thickness | 20-40 mm (varies by protection rating) | 3-6 mm typical for automotive windshields |
| Weight | Significantly heavier due to multiple layers | Standard automotive weight |
| Cost | High; specialized manufacturing | Moderate; widely used in vehicles |
| Application | Armored vehicles, security sensitive environments | Standard in most passenger vehicle windshields |
| Optical Clarity | High, though slightly reduced by thickness | Very high; designed for clear visibility |
Introduction to Automotive Glass Technologies
Bulletproof glass and laminated glass serve as critical advancements in automotive glass technologies, enhancing safety and durability for vehicle windshields. Laminated glass consists of multiple layers of glass and a plastic interlayer, providing shatter resistance and improved impact absorption. Bulletproof glass incorporates thicker, multi-layered materials, including polycarbonate and glass composites, designed to withstand high-velocity projectiles while maintaining visibility and structural integrity.
What is Bulletproof Glass?
Bulletproof glass, also known as ballistic glass, is a multi-layered material specifically engineered to resist high-velocity impacts and penetration from bullets. It typically combines layers of laminated glass and polycarbonate or other transparent plastics, providing superior strength compared to traditional laminated glass used in windshields. This specialized glass is essential for military vehicles, armored cars, and security applications, ensuring enhanced protection against ballistic threats while maintaining visibility.
What is Laminated Glass?
Laminated glass consists of two or more layers of glass bonded together with an interlayer, usually made of polyvinyl butyral (PVB), which holds the layers in place when shattered, providing enhanced safety and impact resistance. This type of glass is commonly used in windshields because it prevents shards from scattering upon impact, maintaining structural integrity and protecting vehicle occupants. Compared to bulletproof glass, laminated glass offers sufficient protection for everyday driving conditions while being lighter and more cost-effective.
Composition and Structure Comparison
Bulletproof glass consists of multiple layers of laminated glass and polycarbonate materials designed to absorb and disperse impact energy, providing high-level ballistic protection. Laminated glass for windshields typically features two or more layers of glass bonded with a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer, ensuring shatter resistance and clarity without the enhanced bullet-resistance of bulletproof variants. The structural difference lies in bulletproof glass having thicker, more complex layering and stronger interlayers to withstand ballistic threats, while laminated glass primarily focuses on impact resistance and passenger safety during collisions.
Protection and Safety Features
Bulletproof glass offers superior protection against high-velocity impacts and gunfire due to its multi-layered construction of polycarbonate and glass, making it ideal for maximum security needs. Laminated glass, commonly used in windshields, provides excellent shatter resistance and prevents glass shards from dispersing upon impact, enhancing occupant safety during collisions. Both materials improve safety, but bulletproof glass is designed for ballistic threats, whereas laminated glass prioritizes impact absorption and maintaining structural integrity in everyday driving scenarios.
Impact Resistance and Durability
Bulletproof glass outperforms laminated glass in impact resistance due to its multi-layered construction of polycarbonate and glass, effectively absorbing and dispersing high-velocity impacts from ballistic threats. Laminated glass, composed of two or more glass layers bonded with a plastic interlayer, offers reliable resistance against common road hazards but is less durable under extreme force or repeated impacts. The durability of bulletproof glass ensures long-term protection in security-sensitive applications, while laminated glass provides sufficient strength and shatter resistance suitable for everyday automotive use.
Cost Analysis: Bulletproof vs Laminated Glass
Bulletproof glass typically costs three to five times more than laminated glass due to its multi-layered construction combining polycarbonate and glass for enhanced ballistic protection. Laminated glass, consisting of two or more layers of glass bonded with a plastic interlayer, offers basic safety at a fraction of the price, averaging $100 to $400 per windshield replacement. Bulletproof glass installations can exceed $1,000, making laminated glass a more budget-friendly option for standard windshield protection without the need for ballistic resistance.
Weight and Vehicle Performance Implications
Bulletproof glass is significantly heavier than laminated glass due to its multiple layers of polycarbonate and tempered glass, which impacts vehicle acceleration and fuel efficiency. Laminated glass, being lighter, enhances overall vehicle performance by reducing weight and improving handling dynamics. The increased weight of bulletproof glass may require suspension upgrades to maintain ride quality and stability.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Bulletproof glass for windshields must comply with stringent safety standards such as UL 752 or NIJ Level certifications, while laminated glass typically adheres to federal motor vehicle safety standards (FMVSS 205) for glazing materials. Legal regulations often restrict the thickness and tinting of bulletproof glass to ensure visibility and occupant safety, whereas laminated glass is widely accepted under existing vehicle safety laws. Vehicle manufacturers and retrofitters must navigate state-specific laws regarding the use of bulletproof glass, particularly concerning weight limits and crash impact requirements.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Windshield
Bulletproof glass offers enhanced protection by combining multiple layers of polycarbonate and glass, ideal for high-risk environments requiring maximum security. Laminated glass, constructed by bonding two or more glass layers with a plastic interlayer, excels in impact resistance and passenger safety during everyday driving conditions. Selecting the right windshield glass depends on assessing security needs, vehicle type, budget, and legal regulations to ensure optimal protection and durability.
Infographic: Bulletproof glass vs Laminated glass for Windshield
 azmater.com
azmater.com