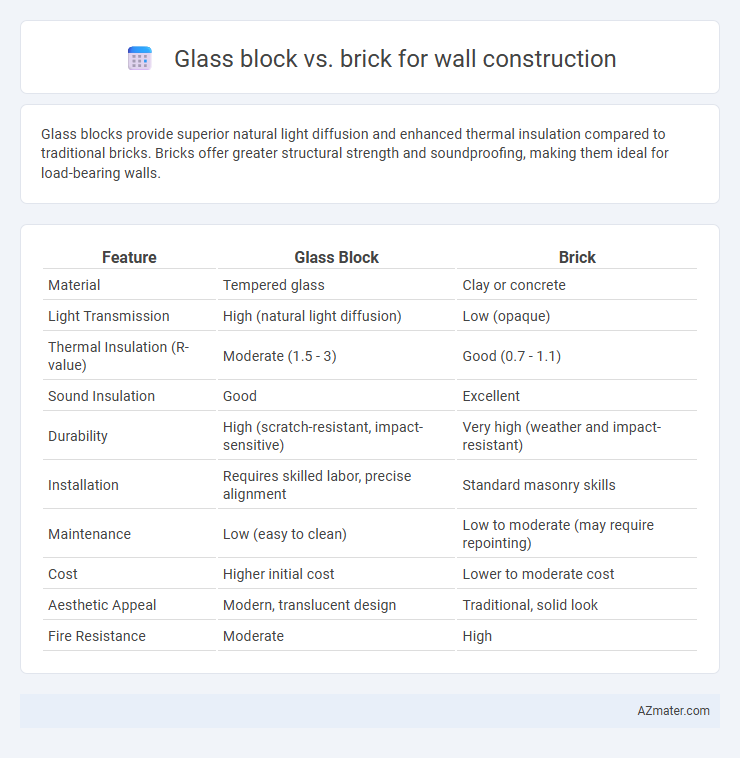
Glass blocks provide superior natural light diffusion and enhanced thermal insulation compared to traditional bricks. Bricks offer greater structural strength and soundproofing, making them ideal for load-bearing walls.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Glass Block | Brick |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Tempered glass | Clay or concrete |
| Light Transmission | High (natural light diffusion) | Low (opaque) |
| Thermal Insulation (R-value) | Moderate (1.5 - 3) | Good (0.7 - 1.1) |
| Sound Insulation | Good | Excellent |
| Durability | High (scratch-resistant, impact-sensitive) | Very high (weather and impact-resistant) |
| Installation | Requires skilled labor, precise alignment | Standard masonry skills |
| Maintenance | Low (easy to clean) | Low to moderate (may require repointing) |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower to moderate cost |
| Aesthetic Appeal | Modern, translucent design | Traditional, solid look |
| Fire Resistance | Moderate | High |
Introduction to Glass Block and Brick Walls
Glass block walls offer enhanced natural light transmission, thermal insulation, and aesthetic appeal, making them popular in modern architectural designs. Brick walls provide superior structural strength, durability, and fire resistance, commonly used in traditional and load-bearing constructions. Both materials serve distinct purposes, with glass blocks prioritized for light and design, while bricks emphasize robustness and longevity.
Material Composition and Properties
Glass blocks are composed primarily of silica-based glass with air or sand-filled cavities, providing natural light transmission and excellent insulation. Bricks consist of clay or shale, fired at high temperatures, offering superior compressive strength, fire resistance, and thermal mass. Glass blocks are non-porous and moisture-resistant but less load-bearing, whereas bricks provide durability and structural support suitable for walls in various climatic conditions.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Flexibility
Glass blocks offer a modern, sleek aesthetic that allows natural light to penetrate while maintaining privacy, ideal for creating visually striking, luminous walls. Brick provides a timeless, classic look with rich textures and color variations, offering versatile design options for both traditional and contemporary architecture. Glass blocks enable creative patterns and transparency effects, whereas bricks afford structural robustness and a wide range of finishes to suit diverse architectural styles.
Structural Strength and Durability
Glass blocks offer moderate structural strength, ideal for non-load-bearing walls, and provide excellent resistance to weather and corrosion, enhancing durability in moist environments. Bricks deliver superior compressive strength suitable for load-bearing walls and exhibit exceptional long-term durability against environmental stresses, including freeze-thaw cycles and impact. Both materials require proper installation techniques to maximize structural integrity and lifespan, with bricks generally favored for high-strength requirements and glass blocks preferred for aesthetic light transmission and moisture resistance.
Thermal Insulation Capabilities
Glass block walls provide moderate thermal insulation with their hollow cavities trapping air, resulting in an R-value typically around 1.75 to 2.0 per inch, making them suitable for light insulation needs. Brick walls, especially when combined with proper cavity insulation, offer higher thermal resistance with R-values ranging from 3.0 to 5.0 or more, providing better energy efficiency and durability in various climates. The choice between glass block and brick for wall construction should consider insulation performance alongside aesthetics and natural light transmission requirements.
Light Transmission and Privacy
Glass blocks provide superior light transmission compared to bricks, allowing natural light to penetrate while maintaining a level of privacy due to their translucent surface. Brick walls offer minimal light transmission, creating opaque barriers ideal for total privacy but reducing natural illumination. Choosing between glass block and brick depends on balancing the need for daylight access with privacy requirements in wall construction.
Sound Insulation Comparison
Glass blocks offer moderate sound insulation with a typical sound transmission class (STC) rating between 30 and 40, making them suitable for reducing noise in residential spaces but less effective against high-frequency sounds compared to bricks. Brick walls provide superior soundproofing due to their dense, solid structure, often achieving STC ratings exceeding 50, which effectively blocks airborne noise for urban or industrial environments. For optimum sound insulation, combining bricks with sound-dampening materials outperforms glass blocks, especially in settings requiring enhanced acoustic privacy.
Installation Process and Complexity
Glass block installation requires precise alignment and sealing techniques to ensure structural integrity and water resistance, often involving mortar setting between blocks, which can be time-consuming and demands skilled labor. Brick walls, while also requiring careful mortar application and leveling, typically benefit from a more straightforward and widely familiar process due to standard brick sizes and traditional masonry practices. The complexity of glass block installation is higher compared to brick, as it involves specialized handling to maintain transparency and prevent damage, impacting project duration and labor costs.
Cost Analysis and Maintenance
Glass blocks typically cost more per square foot than traditional bricks due to specialized manufacturing and installation requirements, but they offer better insulation and natural light benefits. Brick walls have lower upfront material and labor costs, require minimal maintenance, and offer long-term durability with periodic cleaning and occasional repointing. Maintenance for glass blocks involves careful cleaning to prevent damage and occasional seal replacement to maintain waterproofing, which can result in higher lifecycle expenses compared to brick walls.
Best Applications and Use Cases
Glass blocks are ideal for areas requiring natural light diffusion and privacy, such as bathroom walls, shower enclosures, and decorative partitions, offering both aesthetic appeal and thermal insulation. Bricks suit structural walls, exterior facades, and high-load-bearing constructions due to their durability, strength, and excellent weather resistance. Choosing between glass blocks and bricks depends on balancing transparency, light transmission, and structural requirements for specific architectural needs.
Infographic: Glass block vs Brick for Wall construction
 azmater.com
azmater.com