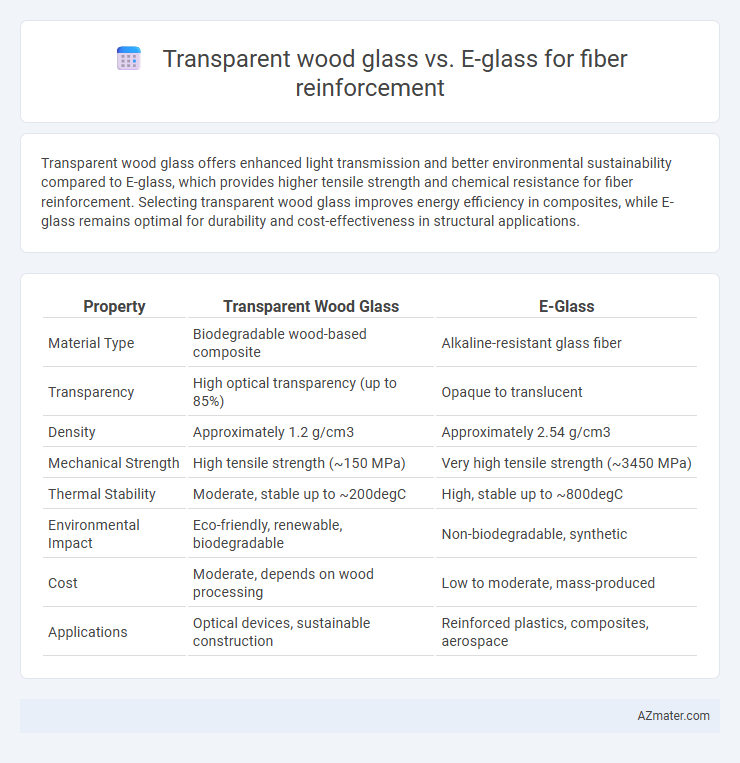
Transparent wood glass offers enhanced light transmission and better environmental sustainability compared to E-glass, which provides higher tensile strength and chemical resistance for fiber reinforcement. Selecting transparent wood glass improves energy efficiency in composites, while E-glass remains optimal for durability and cost-effectiveness in structural applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Transparent Wood Glass | E-Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Biodegradable wood-based composite | Alkaline-resistant glass fiber |
| Transparency | High optical transparency (up to 85%) | Opaque to translucent |
| Density | Approximately 1.2 g/cm3 | Approximately 2.54 g/cm3 |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength (~150 MPa) | Very high tensile strength (~3450 MPa) |
| Thermal Stability | Moderate, stable up to ~200degC | High, stable up to ~800degC |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, renewable, biodegradable | Non-biodegradable, synthetic |
| Cost | Moderate, depends on wood processing | Low to moderate, mass-produced |
| Applications | Optical devices, sustainable construction | Reinforced plastics, composites, aerospace |
Overview of Fiber Reinforced Composites
Fiber reinforced composites combine fibers and a matrix to enhance mechanical properties such as strength and durability. Transparent wood glass offers improved optical clarity and sustainability compared to traditional E-glass fibers, which are widely used for their high tensile strength and electrical insulation in composites. The choice between transparent wood glass and E-glass depends on specific application requirements like transparency, environmental impact, and mechanical performance.
Introduction to Transparent Wood Glass
Transparent wood glass is an innovative fiber reinforcement material derived from chemically treated wood combined with polymer infiltration, offering high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent optical transparency. Unlike conventional E-glass fibers made from silica-based glass, transparent wood glass exhibits superior sustainability, biodegradability, and enhanced mechanical properties such as improved impact resistance and flexibility. Its unique microstructure enables efficient light transmission with minimal scattering, positioning it as a promising alternative in eco-friendly composite applications.
What is E-Glass?
E-Glass, or electrical-grade glass, is a type of fiberglass known for its excellent electrical insulation properties and high tensile strength, making it a popular choice in fiber reinforcement composites. Compared to transparent wood glass, E-Glass offers superior durability and moisture resistance, though it lacks the natural aesthetics and sustainability benefits of wood-based materials. The use of E-Glass in composite structures enhances mechanical performance, especially in applications requiring lightweight yet strong reinforcement.
Manufacturing Processes: Transparent Wood vs. E-Glass
Transparent wood manufacturing involves delignification of natural wood followed by impregnation with a polymer resin, creating a composite with enhanced optical transparency and mechanical strength. E-glass production requires melting raw materials like silica sand, limestone, and soda ash at high temperatures, followed by forming continuous glass fibers through fiberizing processes. While transparent wood emphasizes eco-friendly, bio-based materials and complex chemical treatments, E-glass relies on high-temperature thermal processes and inorganic raw materials for scalable fiber reinforcement production.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Transparent wood glass composites exhibit superior mechanical strength due to their unique cellulose nanofiber network, providing enhanced tensile and flexural properties compared to traditional E-glass fibers. E-glass fibers, while cost-effective and widely used, typically offer lower impact resistance and stiffness in fiber reinforcement applications. Studies demonstrate that transparent wood glass composites achieve up to 20-30% higher tensile strength, making them a promising alternative for lightweight and high-performance structural materials.
Optical Properties and Transparency
Transparent wood glass exhibits superior optical clarity with light transmittance rates exceeding 85%, leveraging its natural cellulose structure for enhanced transparency and reduced haze compared to conventional E-glass fibers. E-glass, while strong and cost-effective, typically presents lower transparency and higher light scattering due to its amorphous silica composition, limiting its application in optical-sensitive composites. Innovations in transparent wood composites enable tailored refractive indices and improved mechanical strength without sacrificing visual transparency, making it a compelling alternative for fiber reinforcement in applications demanding both durability and optical performance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Transparent wood glass offers superior sustainability compared to E-glass, as it is derived from renewable cellulose fibers and uses less energy-intensive production processes, reducing carbon footprints significantly. E-glass, though recyclable, relies on non-renewable raw materials and high-temperature manufacturing, resulting in greater environmental impact and resource depletion. The biodegradability of transparent wood glass further enhances its ecological advantages, making it a more environmentally friendly choice for fiber reinforcement applications.
Cost Analysis: Transparent Wood Glass vs. E-Glass
Transparent wood glass typically incurs higher manufacturing costs due to complex processing techniques and limited large-scale production compared to E-glass, which benefits from established mass production and lower raw material expenses. E-glass offers cost advantages with its widespread availability and lower energy consumption during fabrication, making it more economically favorable for large-scale fiber reinforcement applications. While transparent wood glass provides unique optical properties and sustainability benefits, its current cost premium limits widespread adoption against the more affordable and industry-standard E-glass fibers.
Key Applications and Use Cases
Transparent wood glass offers superior sustainability and biodegradability, making it ideal for eco-friendly construction, lightweight windows, and energy-efficient building panels. E-glass fibers provide high tensile strength, corrosion resistance, and electrical insulation properties, making them widely used in aerospace components, marine vessels, and automotive parts. While transparent wood glass is favored for renewable material applications and thermal insulation, E-glass dominates in performance-critical environments requiring durability and structural reinforcement.
Future Prospects and Industry Trends
Transparent wood glass offers revolutionary potential for sustainable fiber reinforcement due to its enhanced biodegradability and superior optical properties compared to traditional E-glass fibers, which dominate current composite industries. Future prospects indicate increasing adoption of transparent wood glass in lightweight structural applications and energy-efficient building materials, driven by advancements in material processing and eco-friendly manufacturing techniques. Industry trends reveal a growing emphasis on hybrid composite systems integrating transparent wood glass with E-glass to optimize mechanical strength, environmental impact, and cost-efficiency.
Infographic: Transparent wood glass vs E-glass for Fiber reinforcement
 azmater.com
azmater.com