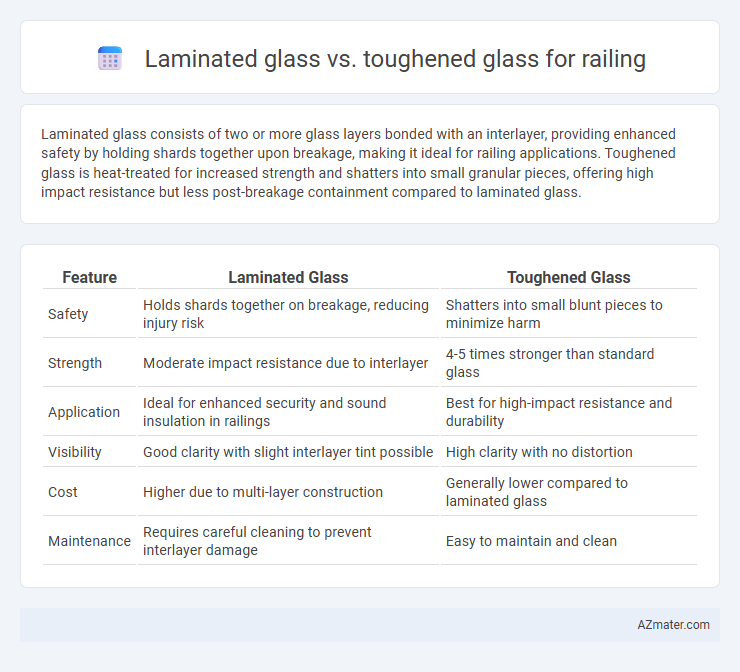
Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer, providing enhanced safety by holding shards together upon breakage, making it ideal for railing applications. Toughened glass is heat-treated for increased strength and shatters into small granular pieces, offering high impact resistance but less post-breakage containment compared to laminated glass.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Laminated Glass | Toughened Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Safety | Holds shards together on breakage, reducing injury risk | Shatters into small blunt pieces to minimize harm |
| Strength | Moderate impact resistance due to interlayer | 4-5 times stronger than standard glass |
| Application | Ideal for enhanced security and sound insulation in railings | Best for high-impact resistance and durability |
| Visibility | Good clarity with slight interlayer tint possible | High clarity with no distortion |
| Cost | Higher due to multi-layer construction | Generally lower compared to laminated glass |
| Maintenance | Requires careful cleaning to prevent interlayer damage | Easy to maintain and clean |
Introduction to Glass Options for Railings
Laminated glass and toughened glass are common choices for railing applications, each offering distinct safety and aesthetic benefits. Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer, providing enhanced impact resistance and preventing shards from scattering upon breakage. Toughened glass undergoes thermal or chemical treatment to increase strength and shatters into small, blunt pieces, making it suitable for high-stress railing environments where durability and user safety are critical.
What Is Laminated Glass?
Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded together with an interlayer, typically made of polyvinyl butyral (PVB) or ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), providing enhanced safety and sound insulation. In railing applications, laminated glass offers superior impact resistance and prevents shattering upon breakage, ensuring that shards remain adhered to the interlayer. This structural integrity makes laminated glass an ideal choice for safety-critical environments compared to toughened glass, which, while stronger than standard glass, breaks into small, blunt pieces without an interlayer to hold them together.
What Is Toughened Glass?
Toughened glass, also known as tempered glass, is a type of safety glass specially treated through controlled thermal or chemical processes to increase its strength compared to normal glass. It shatters into small, blunt pieces when broken, reducing the risk of injury, making it ideal for railing applications where safety and durability are paramount. Unlike laminated glass, which consists of layers held together by an interlayer, toughened glass offers superior impact resistance and thermal strength, ensuring enhanced performance in high-traffic or outdoor railing installations.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Laminated glass for railings consists of two or more layers bonded with an interlayer, providing enhanced impact resistance and preventing shattering upon breakage, which significantly improves safety and durability. Toughened glass undergoes thermal treatment to increase strength, offering high resistance to bending and impact but tends to break into small, blunt pieces, reducing the risk of injury. While toughened glass is stronger in terms of pure tensile strength, laminated glass excels in durability by maintaining structural integrity after damage, making it a preferred choice for safety-critical railing applications.
Safety Features: Laminated vs Toughened Glass
Laminated glass features a durable interlayer that holds shards together upon impact, significantly reducing the risk of injury and enhancing safety in railing applications. Toughened glass, while stronger and more resistant to breakage than standard glass, shatters into small blunt pieces that minimize harm but can still pose a hazard. For railing safety, laminated glass provides superior protection by maintaining structural integrity even when broken, making it the preferred choice in high-risk environments.
Aesthetic Differences Between the Two Types
Laminated glass offers a smooth, seamless appearance with clear visibility and the option to incorporate decorative interlayers for enhanced aesthetics in railing designs. Toughened glass provides a sleek, uniform look with increased strength and a slightly reflective surface that subtly enhances modern architectural styles. Both types deliver contemporary elegance, but laminated glass allows more customization in color and texture for tailor-made visual effects.
Cost Comparison: Laminated vs Toughened Glass
Laminated glass typically costs more than toughened glass due to its multi-layered structure combining glass and interlayers, enhancing safety and sound insulation for railings. Toughened glass is usually less expensive, offering high strength and impact resistance through a heat treatment process but lacks the added safety benefits of lamination. When budgeting for railing installations, laminated glass represents a higher upfront investment but provides superior durability and post-breakage integrity compared to the more economical toughened glass option.
Maintenance and Longevity
Laminated glass offers superior longevity for railings due to its multiple layers bonded with interlayers, which prevent shattering and enhance safety while requiring minimal maintenance beyond regular cleaning. Toughened glass, though highly durable and resistant to impact, can suffer from edge damage and spontaneous breakage, necessitating more frequent inspections and potential replacements over time. Both materials resist weathering, but laminated glass's enhanced structural integrity makes it a preferred choice for long-term durability and low-maintenance railing solutions.
Best Applications for Laminated Glass Railings
Laminated glass is ideal for railing applications requiring enhanced safety and sound insulation, such as balconies, staircases, and terraces in residential and commercial buildings. Its multi-layered structure holds shards in place upon impact, preventing accidents and providing superior durability against weather and vandalism. Laminated glass railings also offer better UV protection and aesthetic versatility, making them the best choice for high-traffic or coastal areas.
Best Uses for Toughened Glass Railings
Toughened glass railings are ideal for high-traffic areas due to their enhanced strength and safety features, making them perfect for balconies, staircases, and commercial buildings. Unlike laminated glass, toughened glass shatters into small, blunt pieces, reducing injury risk in case of breakage. Its superior resistance to impact and temperature changes makes toughened glass the best choice for outdoor railing applications where durability and safety are critical.
Infographic: Laminated glass vs Toughened glass for Railing
 azmater.com
azmater.com