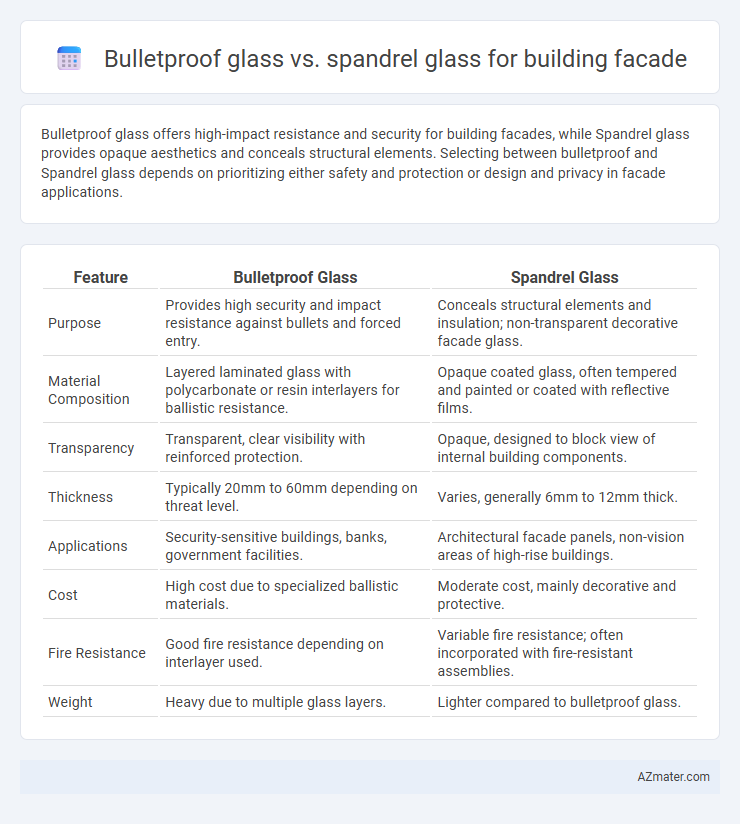
Bulletproof glass offers high-impact resistance and security for building facades, while Spandrel glass provides opaque aesthetics and conceals structural elements. Selecting between bulletproof and Spandrel glass depends on prioritizing either safety and protection or design and privacy in facade applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bulletproof Glass | Spandrel Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Provides high security and impact resistance against bullets and forced entry. | Conceals structural elements and insulation; non-transparent decorative facade glass. |
| Material Composition | Layered laminated glass with polycarbonate or resin interlayers for ballistic resistance. | Opaque coated glass, often tempered and painted or coated with reflective films. |
| Transparency | Transparent, clear visibility with reinforced protection. | Opaque, designed to block view of internal building components. |
| Thickness | Typically 20mm to 60mm depending on threat level. | Varies, generally 6mm to 12mm thick. |
| Applications | Security-sensitive buildings, banks, government facilities. | Architectural facade panels, non-vision areas of high-rise buildings. |
| Cost | High cost due to specialized ballistic materials. | Moderate cost, mainly decorative and protective. |
| Fire Resistance | Good fire resistance depending on interlayer used. | Variable fire resistance; often incorporated with fire-resistant assemblies. |
| Weight | Heavy due to multiple glass layers. | Lighter compared to bulletproof glass. |
Understanding Bulletproof Glass: Features and Functions
Bulletproof glass, also known as ballistic glass, consists of multiple layers of laminated glass and polycarbonate materials designed to absorb and disperse the energy from bullets, providing high-impact resistance and ensuring occupant safety in building facades. It offers transparency and durability without compromising structural integrity, making it suitable for security-sensitive environments such as government buildings, banks, and luxury residences. Unlike spandrel glass, which primarily serves aesthetic and insulation functions in non-vision areas, bulletproof glass prioritizes protection against ballistic threats while maintaining visibility.
What is Spandrel Glass? Purpose and Applications
Spandrel glass is an opaque or translucent glass used in building facades to conceal structural elements, insulation, and mechanical components, enhancing the aesthetic uniformity of curtain walls. Its primary purpose is to provide a seamless exterior appearance while maintaining thermal insulation and fire resistance within the facade system. Typically applied in high-rise office buildings, commercial complexes, and modern architectural designs, spandrel glass integrates with vision glass to create sleek, energy-efficient building envelopes.
Comparing Safety Standards: Bulletproof vs Spandrel Glass
Bulletproof glass adheres to rigorous safety standards such as UL 752 and EN 1063, designed to resist ballistic impacts and provide high-level protection against forced entry and explosions. Spandrel glass meets structural safety standards like ASTM E1300 for load-bearing and thermal performance but lacks specific ballistic resistance properties. In building facades, bulletproof glass ensures enhanced occupant safety through impact resistance, while spandrel glass primarily contributes to aesthetic and insulation functions without specialized security certifications.
Aesthetic Impact on Building Façades
Bulletproof glass enhances building facades by providing a sleek, transparent appearance that maintains visibility while ensuring security, making it ideal for modern, high-profile structures. Spandrel glass offers a uniform, opaque surface that conceals structural elements and mechanical systems, creating a smooth, seamless facade with customizable colors and textures for aesthetic versatility. Combining both materials allows architects to balance transparency and concealment, achieving a visually striking and functional building exterior.
Durability and Maintenance Considerations
Bulletproof glass offers superior durability with high resistance to impacts and forced entry, making it ideal for security-focused building facades, though it requires specialized cleaning to avoid surface damage. Spandrel glass, while less impact-resistant, provides effective protection against weather and UV exposure, with low maintenance due to its coated or painted back surface that conceals structural elements. Maintenance considerations for bulletproof glass include periodic inspection for seal integrity to prevent delamination, whereas spandrel glass demands minimal upkeep, focusing primarily on exterior cleaning and occasional resealing.
Cost Analysis: Investment and Long-Term Value
Bulletproof glass demands a higher initial investment due to its multi-layered construction involving polycarbonate and tempered glass, significantly enhancing security but increasing upfront costs. Spandrel glass, often used for aesthetic masking of structural elements, offers a more cost-effective option with lower material and installation expenses, though it lacks the protective benefits of bulletproof glass. Over the long term, bulletproof glass adds value through enhanced safety and potential insurance discounts, while spandrel glass reduces maintenance costs and improves energy efficiency by integrating with insulated glass units.
Energy Efficiency and Insulation Properties
Bulletproof glass offers high impact resistance but typically has lower energy efficiency and insulation properties compared to spandrel glass, which is engineered to improve thermal performance and reduce solar heat gain in building facades. Spandrel glass incorporates insulating materials and coatings that enhance energy conservation by minimizing heat transfer, making it a superior choice for maintaining indoor climate control. While bulletproof glass prioritizes security, spandrel glass optimizes facade insulation, contributing significantly to reduced HVAC energy consumption and overall sustainability.
Installation Processes and Structural Requirements
Bulletproof glass installation demands robust framing systems capable of supporting its considerable weight and thickness, often requiring steel or aluminum structural reinforcements to ensure safety and impact resistance. Spandrel glass installations focus on concealing building elements, necessitating precise alignment with curtain wall systems and lighter support structures since it is typically opaque and less load-bearing. Both materials require specialized sealants and anchoring methods, but bulletproof glass mandates stricter tolerances and higher load-bearing capacity due to its security functions in building facades.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bulletproof glass, typically made with multiple laminated layers of polycarbonate and glass, offers high durability but involves energy-intensive manufacturing processes and limited recyclability, impacting its environmental footprint. Spandrel glass, often composed of coated or treated glass panels, provides enhanced sustainability by allowing for better insulation and daylight control, reducing building energy consumption. Choosing spandrel glass over bulletproof glass in facades can significantly lower carbon emissions through improved thermal performance and more eco-friendly production methods.
Choosing the Best Glass Type for Your Building Façade
Bulletproof glass offers high-security benefits ideal for buildings requiring enhanced protection against forced entry and ballistic threats, making it suitable for government or financial institutions. Spandrel glass provides a decorative, opaque finish that conceals structural elements and mechanical systems, enhancing aesthetic appeal without compromising insulation performance. When choosing the best glass type for your building facade, consider the balance between security needs, visual design goals, and thermal efficiency to ensure optimal functionality and style.
Infographic: Bulletproof glass vs Spandrel glass for Building façade
 azmater.com
azmater.com