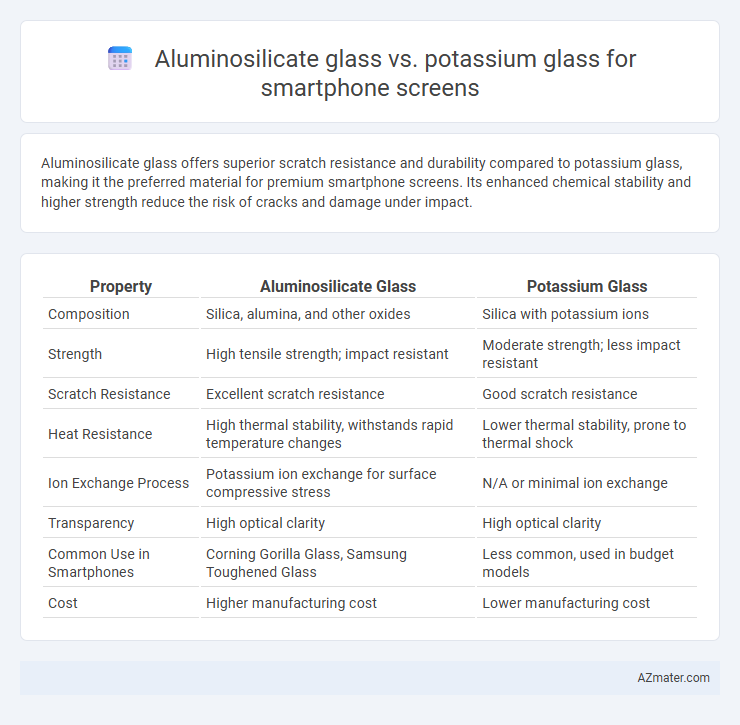
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior scratch resistance and durability compared to potassium glass, making it the preferred material for premium smartphone screens. Its enhanced chemical stability and higher strength reduce the risk of cracks and damage under impact.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Aluminosilicate Glass | Potassium Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Silica, alumina, and other oxides | Silica with potassium ions |
| Strength | High tensile strength; impact resistant | Moderate strength; less impact resistant |
| Scratch Resistance | Excellent scratch resistance | Good scratch resistance |
| Heat Resistance | High thermal stability, withstands rapid temperature changes | Lower thermal stability, prone to thermal shock |
| Ion Exchange Process | Potassium ion exchange for surface compressive stress | N/A or minimal ion exchange |
| Transparency | High optical clarity | High optical clarity |
| Common Use in Smartphones | Corning Gorilla Glass, Samsung Toughened Glass | Less common, used in budget models |
| Cost | Higher manufacturing cost | Lower manufacturing cost |
Introduction to Smartphone Screen Materials
Aluminosilicate glass, composed primarily of aluminum, silicon, and oxygen, offers exceptional hardness and scratch resistance, making it a popular choice for smartphone screens. Potassium glass, infused with potassium ions through an ion-exchange process, enhances surface strength by creating compressive stress, improving durability against drops and impacts. The selection between aluminosilicate and potassium glass depends on balancing scratch resistance and shatterproof performance in smartphone screen design.
What is Aluminosilicate Glass?
Aluminosilicate glass is a type of highly durable glass composed primarily of aluminum oxide and silicon dioxide, widely used in smartphone screens for its superior resistance to scratches, impact, and thermal stress. This glass offers enhanced strength compared to potassium glass, also known as soda-lime glass, due to its chemically strengthened structure through ion exchange processes that replace smaller ions with larger potassium ions in the glass matrix. The aluminosilicate composition ensures improved durability and longevity, making it a preferred choice for high-end mobile devices requiring robust and clear display surfaces.
What is Potassium Glass?
Potassium glass is a type of aluminosilicate glass that undergoes an ion-exchange process where smaller sodium ions are replaced by larger potassium ions, enhancing its strength and scratch resistance. This glass is favored for smartphone screens due to its superior durability and ability to withstand impact better than traditional soda-lime glass. The chemical composition and dense molecular structure contribute to improved hardness and resistance to damage, making potassium glass a popular choice for premium display protection in mobile devices.
Composition Differences: Aluminosilicate vs Potassium Glass
Aluminosilicate glass for smartphone screens contains aluminum oxide (Al2O3) and silicon dioxide (SiO2) in a robust matrix, offering enhanced scratch resistance and mechanical strength. Potassium glass, characterized by a high concentration of potassium ions (K+), undergoes an ion-exchange process that replaces smaller sodium ions with larger potassium ions, increasing surface compression and improving damage resistance. The distinct ionic composition in aluminosilicate versus potassium glass directly impacts their durability and performance in touchscreen applications.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Aluminosilicate glass, commonly used in smartphone screens, offers superior strength and scratch resistance due to its chemically strengthened structure and higher aluminum oxide content, enhancing drop protection and longevity. Potassium glass, while providing some durability benefits through ion exchange strengthening, generally demonstrates lower impact resistance and is more prone to surface scratches compared to aluminosilicate glass. The enhanced toughness of aluminosilicate glass makes it the preferred choice for premium smartphones requiring robust durability against everyday wear and accidental drops.
Scratch and Impact Resistance
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior scratch resistance due to its dense, chemically strengthened surface, making it highly effective against everyday abrasions. Its enhanced impact resistance stems from the aluminum oxide content, which increases toughness compared to potassium glass that primarily relies on potassium ions for ion exchange strengthening. While potassium glass provides good surface hardness, aluminosilicate glass balances both scratch and impact resistance, making it the preferred material in modern smartphone screens.
Clarity and Display Quality
Aluminosilicate glass, commonly used in smartphone screens, offers superior clarity due to its high resistance to scratches and impact, maintaining display quality over time. Potassium glass, enriched with potassium ions through an ion-exchange process, enhances strength but can slightly affect optical transparency compared to aluminosilicate variants. The higher purity and durability of aluminosilicate glass result in sharper color reproduction and less distortion, optimizing the visual experience on smartphones.
Manufacturing Process and Cost
Aluminosilicate glass, used in smartphone screens due to its high strength and scratch resistance, involves a complex manufacturing process including ion exchange and thermal tempering, increasing production costs. Potassium glass, characterized by a similar ion-exchange process but with a higher potassium ion concentration, offers comparable durability with potentially lower production expenses. The manufacturing cost difference arises from raw material pricing and process control, making aluminosilicate glass preferred in premium devices despite its higher cost.
Market Adoption in Smartphones
Aluminosilicate glass dominates the smartphone screen market due to its superior scratch resistance, impact durability, and affordability, making it the preferred choice for leading brands like Apple and Samsung. Potassium glass, while offering enhanced ion-exchange strengthening through potassium ions, has seen limited adoption primarily due to higher production costs and challenges in large-scale manufacturing. Market trends show aluminosilicate glass maintaining a strong presence, supported by extensive supply chains and proven performance in flagship devices.
Which Glass is Better for Smartphone Screens?
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior scratch resistance and higher durability compared to potassium glass, making it more suitable for smartphone screens subjected to daily wear and tear. Potassium glass, commonly known as Gorilla Glass, undergoes an ion-exchange process that enhances its strength by replacing smaller sodium ions with larger potassium ions, but aluminosilicate glass's composite structure provides better impact resistance. For enhanced screen protection and longevity, aluminosilicate glass is generally considered the better choice in modern smartphone manufacturing.
Infographic: Aluminosilicate glass vs Potassium glass for Smartphone screen
 azmater.com
azmater.com