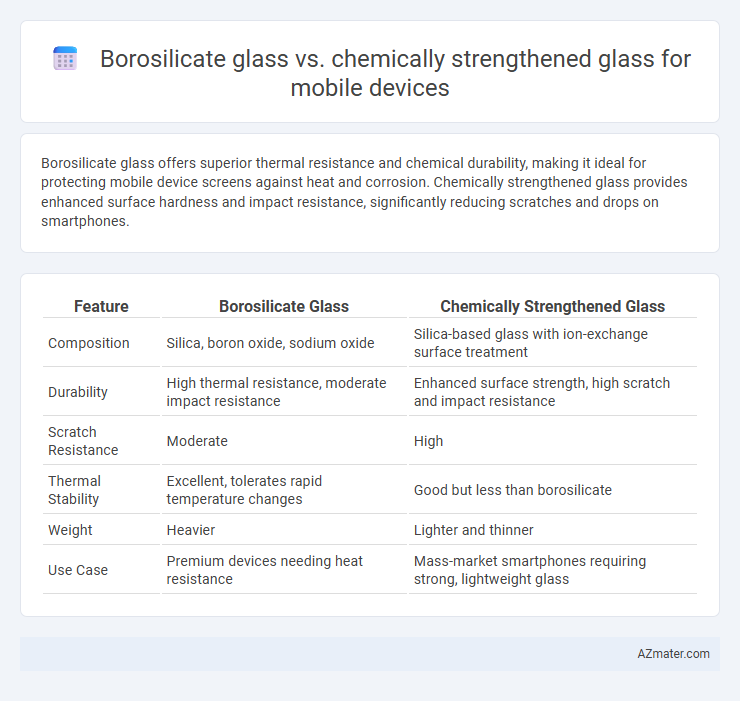
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and chemical durability, making it ideal for protecting mobile device screens against heat and corrosion. Chemically strengthened glass provides enhanced surface hardness and impact resistance, significantly reducing scratches and drops on smartphones.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Borosilicate Glass | Chemically Strengthened Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Silica, boron oxide, sodium oxide | Silica-based glass with ion-exchange surface treatment |
| Durability | High thermal resistance, moderate impact resistance | Enhanced surface strength, high scratch and impact resistance |
| Scratch Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Thermal Stability | Excellent, tolerates rapid temperature changes | Good but less than borosilicate |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter and thinner |
| Use Case | Premium devices needing heat resistance | Mass-market smartphones requiring strong, lightweight glass |
Introduction to Glass Types in Mobile Devices
Borosilicate glass is known for its high thermal resistance and durability, making it ideal for mobile devices that require protection from temperature fluctuations and impact. Chemically strengthened glass undergoes an ion-exchange process that enhances surface compressive stress, significantly improving scratch resistance and overall toughness in smartphones and tablets. Both glass types offer distinct advantages, with borosilicate excelling in heat resistance and chemically strengthened glass providing superior surface strength and durability.
What is Borosilicate Glass?
Borosilicate glass is a type of glass known for its high thermal resistance and durability, commonly used in mobile devices for enhanced protection against temperature variations and mechanical stress. It is composed mainly of silica and boron trioxide, which provide excellent chemical stability and low thermal expansion. Compared to chemically strengthened glass, borosilicate offers superior resistance to heat and chemical corrosion but typically has lower surface hardness and scratch resistance.
What is Chemically Strengthened Glass?
Chemically strengthened glass for mobile devices undergoes an ion-exchange process, replacing smaller sodium ions with larger potassium ions on the glass surface to create compressive stress, making it more resistant to scratches and impacts compared to standard glass types. Borosilicate glass, known for its thermal resistance and durability, lacks this ion-exchange treatment, resulting in lower surface strength but higher resistance to thermal shock. Chemically strengthened glass is preferred in mobile screens for its enhanced mechanical toughness and improved resistance to everyday wear and tear.
Chemical Composition and Structure Comparison
Borosilicate glass features a silica (SiO2) base combined with boron oxide (B2O3), imparting excellent thermal resistance and chemical stability, while chemically strengthened glass primarily consists of alkali aluminosilicate glass enhanced through an ion-exchange process that replaces smaller sodium ions with larger potassium ions in the surface layer. This ion-exchange creates significant compressive stress on chemically strengthened glass surfaces, increasing scratch resistance and mechanical strength compared to the inherently rigid, network-structured borosilicate glass. The borosilicate's open network structure resists thermal shock, whereas the chemically strengthened glass's dense ion-exchanged surface layer offers superior durability against impact and abrasion in mobile devices.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and chemical durability but generally has lower mechanical strength compared to chemically strengthened glass, which undergoes ion exchange to significantly enhance toughness and scratch resistance. Chemically strengthened glass, such as Gorilla Glass, provides higher impact resistance and better protection against drops, making it ideal for mobile device screens that require both durability and lightweight properties. The enhanced mechanical properties of chemically strengthened glass result from its compressive surface layer, which improves fracture toughness beyond that of borosilicate glass.
Scratch and Impact Resistance
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and excellent scratch resistance due to its dense silica content, making it highly durable for mobile devices. Chemically strengthened glass, such as aluminosilicate glass, undergoes an ion-exchange process that enhances its surface compressive stress, significantly boosting impact resistance and preventing cracks from drops. While borosilicate glass resists scratches better, chemically strengthened glass provides enhanced protection against shattering, balancing durability aspects critical for mobile device screens.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance
Borosilicate glass exhibits superior thermal stability and heat resistance compared to chemically strengthened glass, with a low coefficient of thermal expansion around 3.3 x 10^-6 /degC, enabling it to withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking. Chemically strengthened glass, typically aluminosilicate, offers enhanced mechanical strength but has a higher thermal expansion coefficient, making it less resistant to thermal shock. For mobile devices exposed to variable temperatures, borosilicate glass provides better durability against heat-related damage, ensuring longer-lasting screen performance.
Thickness, Weight, and Design Flexibility
Borosilicate glass typically offers greater chemical and thermal resistance but is thicker and heavier, impacting mobile device design constraints compared to chemically strengthened glass. Chemically strengthened glass, such as Gorilla Glass, provides thinner, lighter protection with enhanced surface hardness, allowing for slimmer, more flexible device designs. The reduced thickness and weight of chemically strengthened glass enable manufacturers to optimize both durability and aesthetics without compromising the structural integrity of mobile devices.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal and chemical resistance at a lower manufacturing cost due to its simpler production process compared to chemically strengthened glass, which requires expensive ion-exchange treatments to enhance surface toughness. Chemically strengthened glass, such as Gorilla Glass variants, demands precise temperature control and high-purity raw materials, increasing manufacturing complexity and cost. The trade-off between cost efficiency and enhanced durability impacts material selection for mobile device screens based on target market and performance requirements.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Glass for Mobile Devices
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and chemical durability, making it ideal for devices exposed to harsh environments, while chemically strengthened glass provides enhanced surface hardness and scratch resistance suited for everyday mobile use. The optimal choice depends on usage scenarios, with borosilicate glass preferred for durability in extreme conditions and chemically strengthened glass favored for impact protection and frequent handling. Manufacturers must balance factors like cost, weight, and performance requirements to select the best glass technology for mobile devices.
Infographic: Borosilicate glass vs Chemically strengthened glass for Mobile device
 azmater.com
azmater.com