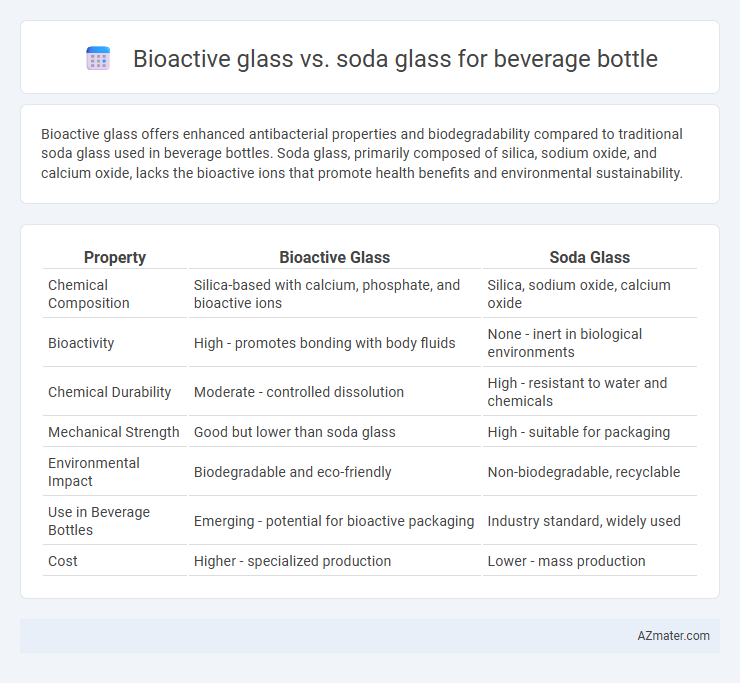
Bioactive glass offers enhanced antibacterial properties and biodegradability compared to traditional soda glass used in beverage bottles. Soda glass, primarily composed of silica, sodium oxide, and calcium oxide, lacks the bioactive ions that promote health benefits and environmental sustainability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bioactive Glass | Soda Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Silica-based with calcium, phosphate, and bioactive ions | Silica, sodium oxide, calcium oxide |
| Bioactivity | High - promotes bonding with body fluids | None - inert in biological environments |
| Chemical Durability | Moderate - controlled dissolution | High - resistant to water and chemicals |
| Mechanical Strength | Good but lower than soda glass | High - suitable for packaging |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable and eco-friendly | Non-biodegradable, recyclable |
| Use in Beverage Bottles | Emerging - potential for bioactive packaging | Industry standard, widely used |
| Cost | Higher - specialized production | Lower - mass production |
Introduction to Beverage Bottle Materials
Bioactive glass offers enhanced chemical durability and antimicrobial properties compared to traditional soda-lime glass, making it a promising material for beverage bottles. Soda-lime glass, composed mainly of silica, sodium oxide, and calcium oxide, is widely used due to its cost-effectiveness and ease of manufacturing. The superior bioactivity of bioactive glass allows it to interact beneficially with contained liquids, potentially improving beverage preservation and safety.
Overview of Bioactive Glass
Bioactive glass is a highly innovative material designed to interact beneficially with its environment, unlike soda glass, which is primarily inert and used widely in beverage bottles for durability and cost-efficiency. This glass type releases ions such as calcium, phosphate, and silicon, promoting surface bioactivity and potential health benefits when used in applications like medical implants, though its use in beverage bottles remains experimental due to cost and production complexity. Bioactive glass offers enhanced chemical resistance and biointeraction, making it a cutting-edge alternative to traditional soda glass for specialized packaging solutions.
Understanding Soda Glass
Soda glass, primarily composed of silica, sodium oxide, and calcium oxide, is widely used for beverage bottles due to its cost-effectiveness and ease of manufacturing. It offers sufficient chemical stability and durability but lacks the enhanced bioactivity and antimicrobial properties found in bioactive glass. Understanding soda glass's lower bio-interaction helps in evaluating its suitability for traditional beverage packaging compared to innovative bioactive glass solutions.
Chemical Composition Comparison
Bioactive glass for beverage bottles typically contains high levels of silicon dioxide (SiO2), calcium oxide (CaO), and phosphorus pentoxide (P2O5), promoting bioactivity and ion exchange beneficial for health. Soda-lime glass, the most common material for beverage containers, primarily consists of SiO2, sodium oxide (Na2O), and calcium oxide (CaO), providing chemical durability and cost-efficiency but lacking bioactive properties. The key chemical distinction lies in phosphate content and sodium levels, where bioactive glass balances ions to encourage surface reactions, unlike soda glass which prioritizes structural stability.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Bioactive glass exhibits superior mechanical strength and durability compared to soda-lime glass due to its unique composition, which enhances resistance to cracking and chemical degradation. Its bioactive properties promote surface healing and improved fracture toughness, making it an ideal material for long-lasting beverage bottles. Conversely, soda glass, while cost-effective, is more prone to brittleness and chemical wear, limiting its lifespan under mechanical stress.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bioactive glass offers superior environmental benefits compared to soda glass, as it is composed of non-toxic, naturally derived materials that biodegrade more efficiently, reducing landfill waste. While soda glass is energy-intensive to produce and recycle, bioactive glass requires lower energy input in manufacturing and can contribute to soil health when bioactive residues degrade. The sustainability profile of bioactive glass aligns well with circular economy principles, promoting reduced carbon emissions and enhancing eco-friendly packaging solutions for the beverage industry.
Safety and Health Considerations
Bioactive glass exhibits superior biocompatibility and antimicrobial properties compared to soda glass, reducing the risk of contamination in beverage bottles. Soda glass, composed mainly of silica, sodium oxide, and calcium oxide, may leach trace amounts of alkali metals under acidic conditions, potentially affecting beverage safety. The ion release from bioactive glass not only enhances safety by minimizing harmful leachates but also promotes a healthier environment by inhibiting microbial growth in bottled beverages.
Cost and Manufacturing Differences
Bioactive glass offers enhanced durability and antibacterial properties but incurs higher raw material and production costs compared to soda-lime glass, which remains the industry standard for beverage bottles due to its cost-effectiveness and ease of mass production. Manufacturing bioactive glass involves specialized melting processes at higher temperatures and longer cooling times, increasing energy consumption and cycle times, whereas soda glass benefits from established, energy-efficient techniques optimized for rapid shaping and annealing. The cost differential impacts scalability, with soda glass preferable for large-volume runs, while bioactive glass suits premium or functional beverage packaging where added material performance justifies the expense.
Market Availability and Applications
Bioactive glass is emerging in niche beverage bottle markets due to its antimicrobial properties and potential to enhance beverage shelf-life, though it remains limited in widespread commercial availability compared to soda-lime glass. Soda-lime glass dominates the beverage industry, prized for its low production cost, recyclability, and availability in large quantities for bottles and jars. Applications of bioactive glass are primarily experimental or specialized, while soda glass is extensively utilized in soft drinks, water, and alcoholic beverage packaging worldwide.
Bioactive Glass vs Soda Glass: Which is Better for Beverage Bottles?
Bioactive glass offers enhanced chemical durability and antimicrobial properties compared to soda glass, making it a superior choice for beverage bottles that require extended shelf life and safety. While soda glass is cost-effective and widely used, it lacks the bioactive properties that can inhibit bacterial growth and improve beverage preservation. The integration of bioactive glass in beverage packaging can result in improved product quality, consumer health benefits, and reduced risk of contamination.
Infographic: Bioactive glass vs Soda glass for Beverage bottle
 azmater.com
azmater.com