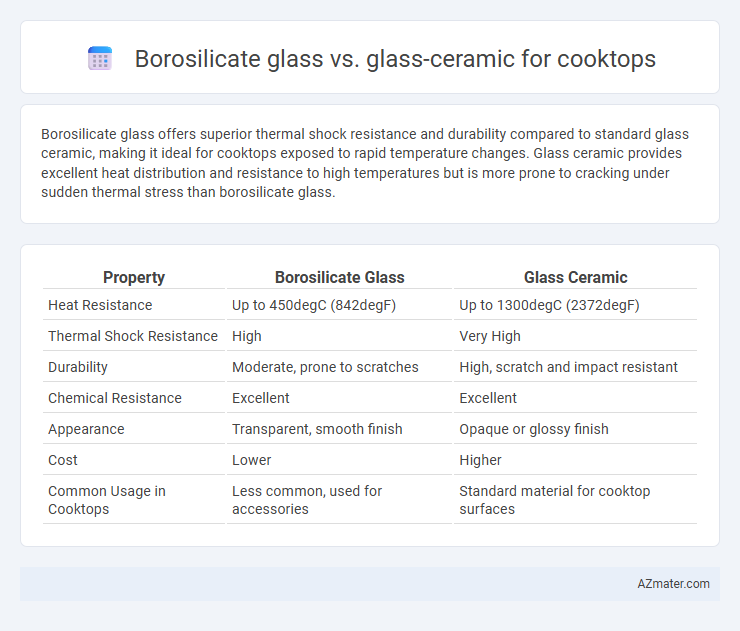
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal shock resistance and durability compared to standard glass ceramic, making it ideal for cooktops exposed to rapid temperature changes. Glass ceramic provides excellent heat distribution and resistance to high temperatures but is more prone to cracking under sudden thermal stress than borosilicate glass.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Borosilicate Glass | Glass Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Resistance | Up to 450degC (842degF) | Up to 1300degC (2372degF) |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | High | Very High |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to scratches | High, scratch and impact resistant |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Excellent |
| Appearance | Transparent, smooth finish | Opaque or glossy finish |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Common Usage in Cooktops | Less common, used for accessories | Standard material for cooktop surfaces |
Introduction to Cooktop Materials
Borosilicate glass offers high thermal shock resistance and durability, making it ideal for cooktops exposed to sudden temperature changes. Glass ceramic combines strength and heat resistance with the ability to withstand extreme temperatures without cracking or breaking. Both materials enhance cooktop performance, but glass ceramic typically provides superior thermal stability and scratch resistance for long-term use.
What is Borosilicate Glass?
Borosilicate glass, composed primarily of silica and boron trioxide, is renowned for its exceptional thermal resistance and low thermal expansion, making it highly resistant to cracking under rapid temperature changes. This type of glass is often used in cooktops due to its durability, chemical stability, and ability to withstand high temperatures without warping. In contrast, glass ceramic cooktops utilize a crystalline structure that combines glass and ceramic properties, offering enhanced heat resistance and mechanical strength but differing in composition and performance characteristics compared to borosilicate glass.
What is Glass Ceramic?
Glass ceramic is a specialized material engineered through controlled crystallization, offering superior heat resistance and thermal shock stability compared to borosilicate glass. Unlike borosilicate glass, which is prized for its chemical durability and moderate heat resistance, glass ceramic cooktops can withstand rapid temperature changes and maintain structural integrity under intense heat. This makes glass ceramic the preferred choice for cooktops where durability, heat tolerance, and safety are critical performance factors.
Key Differences Between Borosilicate Glass and Glass Ceramic
Borosilicate glass is known for its high thermal resistance and excellent chemical durability, making it ideal for laboratory glassware and some cooktops that require rapid thermal changes. Glass ceramic offers superior heat resistance and mechanical strength, with the ability to withstand direct and prolonged heat exposure commonly found in induction and radiant cooktops. Key differences include borosilicate's moderate thermal expansion versus glass ceramic's near-zero thermal expansion, enhancing glass ceramic's resistance to thermal shock during intense cooking conditions.
Heat Resistance Comparison
Borosilicate glass offers excellent heat resistance with a thermal expansion coefficient of about 3.3 x 10^-6 /degC, making it highly durable under rapid temperature changes up to around 450degC. Glass ceramic, commonly used in cooktops, boasts superior heat resistance due to its low thermal expansion rate of nearly zero, allowing it to withstand temperatures exceeding 700degC without cracking. This exceptional thermal stability in glass ceramic reduces the risk of thermal shock, making it more suitable for high-temperature cooktop applications compared to borosilicate glass.
Durability and Strength Factors
Borosilicate glass offers high thermal resistance and durability due to its low coefficient of thermal expansion, reducing the risk of cracking under rapid temperature changes. Glass ceramic cooktops exhibit superior strength and impact resistance, with enhanced ability to withstand mechanical stress and thermal shock, making them ideal for heavy cookware usage. The choice between borosilicate glass and glass ceramic depends largely on the desired balance between thermal shock resistance and mechanical toughness for cooktop applications.
Thermal Shock Performance
Borosilicate glass exhibits superior thermal shock resistance with a low coefficient of thermal expansion (~3.3 x 10^-6 /degC), making it highly durable against rapid temperature changes in cooktops. Glass ceramic also offers exceptional thermal shock performance due to its crystalline structure, providing near-zero thermal expansion and enhanced resistance to cracking under sudden heat exposure. Both materials excel in thermal shock endurance, but glass ceramic typically surpasses borosilicate glass in sustained high-heat applications and extreme temperature fluctuations.
Aesthetic and Design Variations
Borosilicate glass cooktops offer a sleek, transparent surface that emphasizes minimalism and modernity, available in various tinted shades for customizable aesthetics. Glass ceramic cooktops provide a smooth, opaque finish with embedded heating elements, allowing for seamless integration of design features like color accents and pattern variations. Both materials support flush installation, but borosilicate glass excels in clarity while glass ceramic offers more versatility in decorative design options.
Cost and Availability
Borosilicate glass cooktops are generally more affordable, widely available, and popular in both residential and commercial kitchen appliances due to their excellent thermal resistance and durability. Glass ceramic cooktops, although more expensive, offer superior heat distribution and resistance to thermal shock, making them a preferred choice for high-end and specialty cooking surfaces. Availability of glass ceramic cooktops is more limited and tends to be found primarily in premium or specialized kitchen product lines.
Which Material is Better for Your Cooktop?
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal shock resistance and durability, making it ideal for cooktops exposed to rapid temperature changes, while glass ceramic provides excellent heat retention and evenly distributes heat for consistent cooking performance. Glass ceramic cooktops often feature smooth surfaces that resist scratches and stains, enhancing both functionality and aesthetics. Choosing between borosilicate glass and glass ceramic depends on whether you prioritize thermal resistance or heat distribution for your cooking needs.
Infographic: Borosilicate glass vs Glass ceramic for Cooktop
 azmater.com
azmater.com