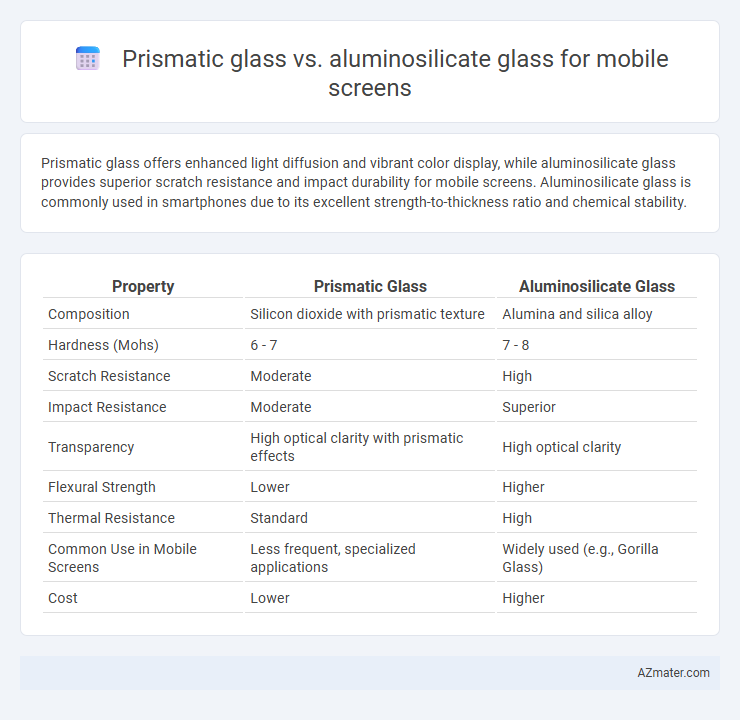
Prismatic glass offers enhanced light diffusion and vibrant color display, while aluminosilicate glass provides superior scratch resistance and impact durability for mobile screens. Aluminosilicate glass is commonly used in smartphones due to its excellent strength-to-thickness ratio and chemical stability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Prismatic Glass | Aluminosilicate Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Silicon dioxide with prismatic texture | Alumina and silica alloy |
| Hardness (Mohs) | 6 - 7 | 7 - 8 |
| Scratch Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate | Superior |
| Transparency | High optical clarity with prismatic effects | High optical clarity |
| Flexural Strength | Lower | Higher |
| Thermal Resistance | Standard | High |
| Common Use in Mobile Screens | Less frequent, specialized applications | Widely used (e.g., Gorilla Glass) |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Mobile Screen Glass Types
Prismatic glass and aluminosilicate glass are two prominent materials used in mobile screen technology, each offering distinct advantages in durability and optical clarity. Aluminosilicate glass, known for its high scratch resistance and impact strength, is commonly used in flagship smartphones due to its robust protection against daily wear. Prismatic glass, while less prevalent, provides enhanced light diffusion and color vibrancy, contributing to improved display quality in select mobile devices.
What is Prismatic Glass?
Prismatic glass for mobile screens incorporates micro-structured patterns that enhance light diffusion and reduce glare, improving display clarity and color accuracy under various lighting conditions. Compared to aluminosilicate glass, which is prized for its exceptional toughness and scratch resistance due to its alumina and silica composition, prismatic glass focuses more on optical performance rather than mechanical durability. The prismatic design optimizes user visibility, making it ideal for devices used in bright or outdoor environments where screen readability is crucial.
What is Aluminosilicate Glass?
Aluminosilicate glass is a type of specialty glass composed primarily of aluminum oxide and silicon dioxide, known for its high strength, scratch resistance, and thermal stability, making it ideal for mobile screens. This glass type offers superior toughness and durability compared to prismatic glass, which is less resistant to impacts and scratches. Mobile devices often use aluminosilicate glass, such as Corning Gorilla Glass, to provide enhanced protection against drops and daily wear.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior strength and scratch resistance compared to prismatic glass, making it ideal for mobile screens exposed to daily wear and tear. Prismatic glass, while visually striking with its light-reflecting properties, generally lacks the hardness and impact resistance required for long-term durability. The chemical composition of aluminosilicate glass, which includes aluminum oxide, enhances its ability to withstand drops and pressure without compromising clarity or touch sensitivity.
Scratch and Impact Resistance
Aluminosilicate glass, commonly used in mobile screens like Gorilla Glass, offers superior scratch resistance due to its high hardness and chemical strengthening processes, outperforming prismatic glass. Prismatic glass, although visually appealing with light-dispersing properties, tends to be more vulnerable to scratches and impact damage because it lacks the advanced ion-exchange strengthening found in aluminosilicate glass. Impact resistance in aluminosilicate glass is enhanced by its ability to flex slightly under pressure, reducing the likelihood of cracks or shattering compared to the typically more brittle prismatic glass.
Clarity and Visual Performance
Prismatic glass offers superior optical clarity with enhanced light transmission, resulting in vivid color accuracy and reduced glare for mobile screens. Aluminosilicate glass provides strong impact resistance and durability but may slightly compromise on transparency compared to prismatic variants. Choosing prismatic glass typically ensures better visual performance and sharper image quality, while aluminosilicate sacrifices minimal clarity for enhanced toughness.
Touch Sensitivity and User Experience
Prismatic glass and aluminosilicate glass differ significantly in touch sensitivity and user experience for mobile screens, with aluminosilicate glass offering superior responsiveness due to its enhanced hardness and resistance to scratches, resulting in smoother touch interactions. Prismatic glass may provide adequate sensitivity but often lacks the durability and smooth surface finish that reduces touch latency and enhances tactile feedback. Consumer satisfaction trends favor aluminosilicate glass for extended, high-precision use in smartphones, contributing to improved gesture recognition and reduced input errors.
Weight and Thickness Differences
Prismatic glass typically offers a lighter and thinner profile compared to aluminosilicate glass, making it advantageous for ultra-slim mobile screen designs. Aluminosilicate glass, known for its superior strength and scratch resistance, generally comes at the cost of increased weight and thickness. Manufacturers often balance these trade-offs by selecting prismatic glass for lighter, thinner devices, while aluminosilicate glass is preferred for enhanced durability despite added weight and bulk.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Prismatic glass typically incurs higher manufacturing costs due to complex layering processes that enhance optical clarity and scratch resistance, compared to aluminosilicate glass, which benefits from established, streamlined production methods reducing expenses. Aluminosilicate glass offers superior durability and resistance to impact, allowing manufacturers to leverage cost-effective mass production without sacrificing screen strength. Cost efficiency in mobile screens often favors aluminosilicate glass as it balances performance with scalable manufacturing, whereas prismatic glass suits premium segments demanding advanced optical properties despite higher production investments.
Which Glass Type is Better for Mobile Screens?
Aluminosilicate glass is generally better for mobile screens due to its superior hardness and scratch resistance compared to prismatic glass, enhancing durability under daily wear and tear. Its enhanced chemical composition provides higher resistance to impact, reducing the likelihood of cracks from drops or pressure. Prismatic glass, often used for decorative or specific optical purposes, lacks the robust protective properties necessary for the demanding environment of mobile device screens.
Infographic: Prismatic glass vs Aluminosilicate glass for Mobile screen
 azmater.com
azmater.com