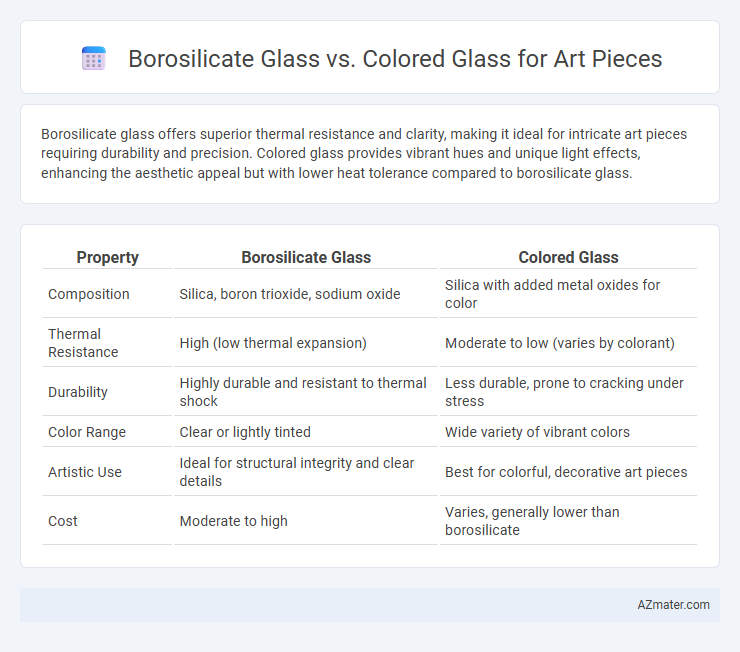
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and clarity, making it ideal for intricate art pieces requiring durability and precision. Colored glass provides vibrant hues and unique light effects, enhancing the aesthetic appeal but with lower heat tolerance compared to borosilicate glass.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Borosilicate Glass | Colored Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Silica, boron trioxide, sodium oxide | Silica with added metal oxides for color |
| Thermal Resistance | High (low thermal expansion) | Moderate to low (varies by colorant) |
| Durability | Highly durable and resistant to thermal shock | Less durable, prone to cracking under stress |
| Color Range | Clear or lightly tinted | Wide variety of vibrant colors |
| Artistic Use | Ideal for structural integrity and clear details | Best for colorful, decorative art pieces |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Varies, generally lower than borosilicate |
Introduction to Borosilicate and Colored Glass
Borosilicate glass, known for its high thermal resistance and durability, is favored for intricate art pieces requiring precision and stability under heat. Colored glass, enriched with metal oxides, offers vibrant hues and translucency, enabling artists to create visually striking and luminous artworks. The choice between borosilicate and colored glass depends on the desired combination of functional strength and aesthetic vibrancy in the final art piece.
Chemical Composition Differences
Borosilicate glass contains boron trioxide, which reduces thermal expansion and enhances chemical durability, making it resistant to temperature changes and chemicals. Colored glass incorporates metal oxides or other additives such as cobalt, chromium, or iron to achieve its hues, which can alter its thermal and chemical properties compared to borosilicate glass. The differences in chemical composition impact the strength, clarity, and resistance of each glass type, influencing their suitability for various art piece applications.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Borosilicate glass offers superior durability and thermal resistance compared to colored glass, making it less prone to cracking under temperature changes. Its high chemical stability ensures long-lasting strength, ideal for art pieces exposed to varying environments. Colored glass, while visually appealing, often contains additives that may compromise its structural integrity and make it more susceptible to breakage over time.
Heat Resistance in Art Applications
Borosilicate glass offers superior heat resistance compared to colored glass, making it ideal for art pieces exposed to high temperatures during processes like lampworking or kiln forming. Its low thermal expansion reduces the risk of cracking or thermal shock, ensuring durability and stability in heat-intensive artistic applications. Colored glass often contains additives that can lower its heat tolerance, limiting its use in environments requiring consistent thermal performance.
Color Options and Visual Effects
Borosilicate glass offers a wide range of vibrant color options with excellent clarity and durability, making it ideal for intricate art pieces that require precision and longevity. Colored glass, while available in diverse hues, often provides richer, more saturated tones and dynamic visual effects such as light diffusion and translucency, enhancing the aesthetic impact of stained glass or fused glass artworks. The choice between borosilicate and colored glass depends on whether the artist prioritizes structural strength and sharp color contrasts or prefers bold, luminous color depth and texture in the art piece.
Workability for Artists
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal shock resistance and durability, making it ideal for intricate and detailed art pieces that require multiple reheating cycles. Colored glass, while visually striking, often has varied melting points and lower resistance to thermal stress, which can complicate the workability for artists during processes like lampworking or kiln-forming. Artists prioritize borosilicate glass for its consistent malleability and stability, enabling precise shaping and layering without crack risks.
Cost and Availability
Borosilicate glass typically costs more than colored glass due to its superior durability and heat resistance, making it ideal for intricate art pieces that require longevity. Colored glass is generally more affordable and available in a wider range of hues, making it a popular choice for vibrant and cost-effective artworks. Availability of borosilicate glass can be limited compared to the more common and easily sourced colored glass, impacting project timelines and budgets.
Suitability for Various Art Techniques
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and durability, making it ideal for lampworking, flameworking, and sculpting techniques that require precise heat control and repeated reheating. Colored glass, often softer and less heat-resistant, is better suited for techniques emphasizing vibrant hues, such as stained glass and fused glass art, where color depth and opacity are prioritized over structural strength. Artists select borosilicate for functional and detailed glasswork, while colored glass is favored for decorative, colorful applications in mixed-media and surface treatments.
Longevity and Preservation of Art Pieces
Borosilicate glass offers superior longevity and preservation for art pieces due to its high resistance to thermal shock, chemical corrosion, and mechanical stress, ensuring artworks remain stable over time. Colored glass, while visually striking, can deteriorate faster under UV exposure and environmental factors, potentially compromising the integrity and original hues of the artwork. Preservation experts often recommend borosilicate glass for archival-quality art displays to maintain durability and color fidelity across decades.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Borosilicate glass, known for its durability and thermal resistance, offers enhanced sustainability by lasting longer and reducing the need for frequent replacements, thus minimizing waste. Colored glass often involves additional chemical treatments and heavy metals, which can increase environmental toxicity during production and disposal. Choosing borosilicate glass for art pieces promotes eco-friendly practices by supporting recyclability and lowering the overall carbon footprint in comparison to colored glass alternatives.
Infographic: Borosilicate glass vs Colored glass for Art piece
 azmater.com
azmater.com