Transparent wood glass offers enhanced light transmission and reduced weight compared to traditional crown glass, improving telescope lens performance. Its superior strength and lower thermal expansion minimize image distortion, making it a promising alternative for advanced optical applications.
Table of Comparison
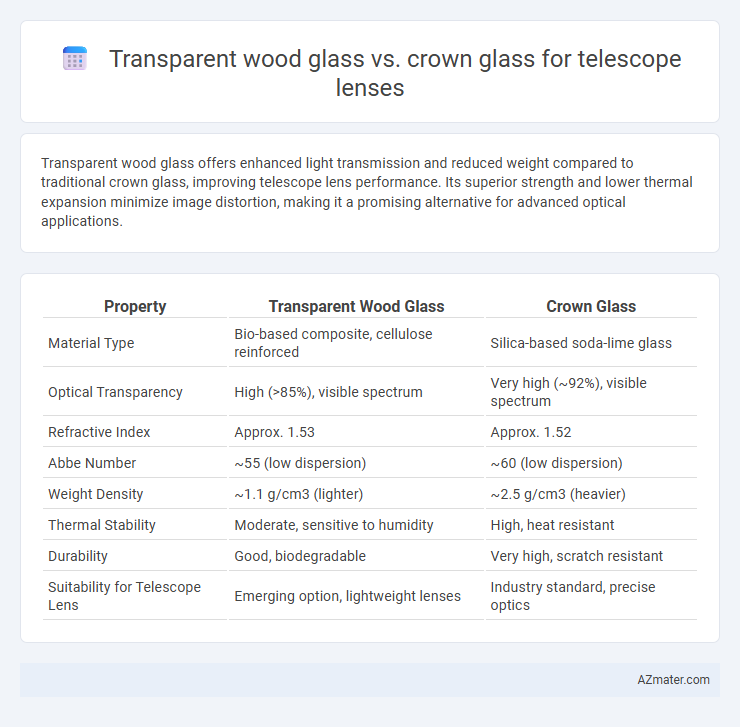
| Property | Transparent Wood Glass | Crown Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Bio-based composite, cellulose reinforced | Silica-based soda-lime glass |
| Optical Transparency | High (>85%), visible spectrum | Very high (~92%), visible spectrum |
| Refractive Index | Approx. 1.53 | Approx. 1.52 |
| Abbe Number | ~55 (low dispersion) | ~60 (low dispersion) |
| Weight Density | ~1.1 g/cm3 (lighter) | ~2.5 g/cm3 (heavier) |
| Thermal Stability | Moderate, sensitive to humidity | High, heat resistant |
| Durability | Good, biodegradable | Very high, scratch resistant |
| Suitability for Telescope Lens | Emerging option, lightweight lenses | Industry standard, precise optics |
Introduction to Telescope Lens Materials
Transparent wood glass, an innovative composite material, offers enhanced mechanical strength and lightweight properties compared to traditional crown glass used in telescope lenses. Crown glass, a common optical material with moderate dispersion and high transparency, provides well-understood refractive indexes essential for precise image formation. The choice between transparent wood glass and crown glass impacts the telescope's durability, weight, and optical clarity, influencing overall performance in astronomical observations.
Overview of Transparent Wood Glass
Transparent wood glass is an innovative composite material combining the natural strength and lightweight properties of wood with high optical clarity, making it a promising alternative to traditional crown glass for telescope lenses. Its superior impact resistance, reduced weight, and enhanced thermal stability offer potential improvements in durability and performance for astronomical instruments. Unlike crown glass, which is primarily silica-based with high refractive index uniformity, transparent wood glass integrates cellulose fibers and polymer matrices to achieve comparable transparency while reducing environmental impact.
Properties of Crown Glass
Crown glass, commonly used in telescope lenses, offers high optical clarity and low dispersion, which minimizes chromatic aberration and enhances image sharpness. Its refractive index typically ranges from 1.52 to 1.54, providing reliable light transmission with minimal distortion. Compared to transparent wood glass, crown glass exhibits superior durability and stability under varying temperatures, making it a preferred material for precision astronomical optics.
Optical Clarity and Light Transmission
Transparent wood glass offers enhanced optical clarity with reduced glare and improved contrast compared to traditional crown glass, making it ideal for high-precision telescope lenses. Its unique microstructure allows superior light transmission, resulting in clearer and brighter celestial images. Crown glass, while durable and cost-effective, typically exhibits lower light transmission and more chromatic aberration, affecting overall image sharpness.
Durability and Environmental Resistance
Transparent wood glass offers superior durability compared to crown glass, with enhanced resistance to impacts and fractures due to its fibrous, laminated structure. Its environmental resistance is notable, providing better performance in varying humidity and temperature conditions, resisting moisture absorption and thermal expansion more effectively than crown glass. Crown glass, while optically clear, tends to be more prone to cracking and weathering over time, making transparent wood glass a more robust choice for telescope lenses in harsh outdoor environments.
Weight Comparison and Structural Strength
Transparent wood glass exhibits significantly lower weight compared to traditional crown glass, making it advantageous for lightweight telescope lenses without compromising optical clarity. Its unique composite structure enhances structural strength, providing better impact resistance and durability than conventional crown glass lenses. This combination of reduced mass and increased toughness improves portability and longevity in telescope lens applications.
Manufacturing Complexity and Cost
Transparent wood glass involves advanced manufacturing processes such as chemical treatment and polymer impregnation to achieve optical clarity, resulting in higher production complexity and costs compared to traditional crown glass. Crown glass, produced by melting and cooling silica with soda lime, offers simpler manufacturing with well-established, cost-effective techniques widely used in telescope lenses. The higher durability and unique thermal properties of transparent wood glass may justify its cost in specialized applications, but crown glass remains the economical standard for most telescopes.
Lens Shape Precision and Aberration Control
Transparent wood glass offers superior lens shape precision due to its uniform microstructure, resulting in enhanced control over spherical aberrations compared to crown glass. Crown glass, while traditionally used in telescope lenses, often exhibits higher chromatic aberration due to its less consistent refractive index distribution. The precise machining capabilities of transparent wood glass enable more accurate curvature and smoother surfaces, directly improving image clarity and reducing optical distortions.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Transparent wood glass offers a sustainable alternative to traditional crown glass in telescope lenses, utilizing renewable wood fibers that reduce reliance on non-renewable silica resources. The production process of transparent wood glass generates lower carbon emissions and consumes less energy compared to the high-temperature manufacturing of crown glass. Furthermore, transparent wood glass is biodegradable and easier to recycle, significantly minimizing environmental impact throughout its lifecycle.
Future Prospects: Transparent Wood Glass vs Crown Glass
Transparent wood glass shows promising future prospects in telescope lens manufacturing due to its superior strength-to-weight ratio and enhanced light diffusion properties, which can improve image clarity and reduce optical aberrations. Crown glass, with its well-established refractive index range and minimal chromatic dispersion, remains a reliable material but faces limitations in weight and durability for advanced telescope designs. Innovations in transparent wood composites may lead to lighter, more sustainable lenses that outperform traditional crown glass, especially in large-aperture telescopes and space applications.
Infographic: Transparent wood glass vs Crown glass for Telescope lens
 azmater.com
azmater.com