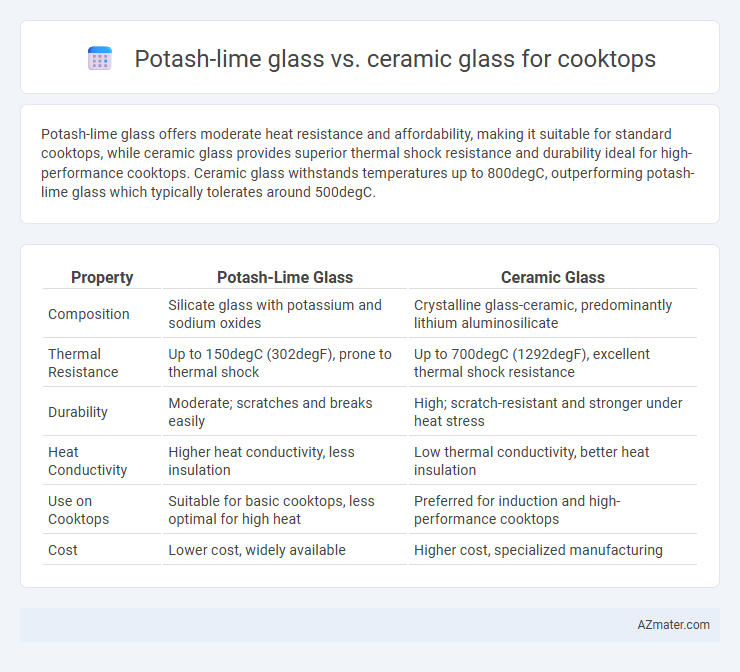
Potash-lime glass offers moderate heat resistance and affordability, making it suitable for standard cooktops, while ceramic glass provides superior thermal shock resistance and durability ideal for high-performance cooktops. Ceramic glass withstands temperatures up to 800degC, outperforming potash-lime glass which typically tolerates around 500degC.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Potash-Lime Glass | Ceramic Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Silicate glass with potassium and sodium oxides | Crystalline glass-ceramic, predominantly lithium aluminosilicate |
| Thermal Resistance | Up to 150degC (302degF), prone to thermal shock | Up to 700degC (1292degF), excellent thermal shock resistance |
| Durability | Moderate; scratches and breaks easily | High; scratch-resistant and stronger under heat stress |
| Heat Conductivity | Higher heat conductivity, less insulation | Low thermal conductivity, better heat insulation |
| Use on Cooktops | Suitable for basic cooktops, less optimal for high heat | Preferred for induction and high-performance cooktops |
| Cost | Lower cost, widely available | Higher cost, specialized manufacturing |
Introduction to Cooktop Glass Materials
Potash-lime glass and ceramic glass are two common materials used in cooktop surfaces, each offering distinct thermal and mechanical properties. Potash-lime glass provides cost-effective transparency and moderate heat resistance, making it suitable for basic cooktops. Ceramic glass, composed of special glass-ceramic composites, delivers superior heat resistance, thermal shock durability, and scratch resistance, making it ideal for high-performance, induction, and radiant cooktops.
What is Potash-Lime Glass?
Potash-lime glass is a type of glass commonly used in cooktops due to its excellent thermal resistance and durability, composed primarily of silica, potash (potassium oxide), calcium oxide, and other minor ingredients. This glass type offers good heat distribution and shock resistance, making it suitable for stovetop surfaces that experience rapid temperature changes. Compared to ceramic glass, potash-lime glass generally has lower thermal conductivity and is less resistant to higher temperatures, which can influence its performance and longevity in heat-intensive cooking environments.
What is Ceramic Glass?
Ceramic glass is a high-strength, heat-resistant material made from a combination of glass and ceramic fibers, designed specifically for cooktop surfaces. Unlike potash-lime glass, ceramic glass withstands rapid temperature changes and extreme heat without cracking or warping, ensuring durability and safety during cooking. This material offers excellent thermal shock resistance and superior mechanical strength, making it ideal for electric and induction cooktops.
Thermal Resistance Comparison
Potash-lime glass cooktops offer moderate thermal resistance with a maximum operating temperature around 300degC, making them suitable for everyday cooking but less ideal for high-heat applications. Ceramic glass, often made from alumino-silicate materials, withstands temperatures up to 700degC, providing superior thermal shock resistance and durability under rapid temperature changes. This enhanced thermal tolerance makes ceramic glass the preferred choice for modern cooktops requiring both safety and performance at elevated heat levels.
Durability and Scratch Resistance
Potash-lime glass cooktops offer good thermal resistance but tend to be less durable and more prone to scratches compared to ceramic glass surfaces. Ceramic glass cooktops, made from a special glass-ceramic composite, provide superior durability with enhanced scratch resistance and better ability to withstand sudden temperature changes. For long-term use, ceramic glass is preferred due to its robust structure and higher resistance to thermal shock and physical abrasions.
Heat Distribution and Cooking Performance
Potash-lime glass offers moderate heat distribution but tends to heat unevenly, which can cause hot spots affecting cooking performance on cooktops. Ceramic glass provides superior heat resistance and more uniform heat distribution, enhancing cooking precision and energy efficiency. Its ability to maintain consistent surface temperatures minimizes the risk of burns and improves overall cooking results.
Safety Features of Both Glass Types
Potash-lime glass cooktops offer moderate heat resistance and are less prone to shattering but may crack under extreme temperature changes, posing a safety risk. Ceramic glass cooktops provide superior thermal shock resistance and can withstand higher temperatures, reducing the chances of breakage and enhancing user safety during cooking. Both materials feature smooth surfaces for easy cleaning, but ceramic glass's higher durability makes it a safer choice for frequent and high-heat cooking applications.
Cost and Availability
Potash-lime glass cooktops are generally more affordable due to lower manufacturing costs and widespread availability in most markets. Ceramic glass cooktops, often made from specialized glass-ceramic materials like Schott Ceran, tend to be pricier but offer superior heat resistance and durability. Availability of ceramic glass is somewhat limited to premium appliance brands, while potash-lime glass is more common in budget-friendly cooktops.
Aesthetic Differences in Kitchen Design
Potash-lime glass cooktops offer a sleek, glossy finish that enhances modern kitchen aesthetics with their reflective surface and vibrant colors. Ceramic glass cooktops provide a smooth, matte appearance that complements minimalist or contemporary kitchen designs by reducing glare and blending seamlessly with countertops. Both materials improve visual appeal, but potash-lime glass emphasizes brightness and color saturation, while ceramic glass focuses on subtle elegance and durability.
Which Cooktop Glass is Best for You?
Potash-lime glass offers affordability and adequate heat resistance, making it suitable for budget-conscious users, while ceramic glass provides superior thermal shock resistance and durability, ideal for high-performance cooktops. Ceramic glass maintains a sleek appearance longer due to its scratch resistance and easier cleaning properties, enhancing long-term aesthetics. Choose potash-lime glass for basic cooking needs or ceramic glass for professional-grade use and enhanced longevity in your cooktop.
Infographic: Potash-lime glass vs Ceramic glass for Cooktop
 azmater.com
azmater.com