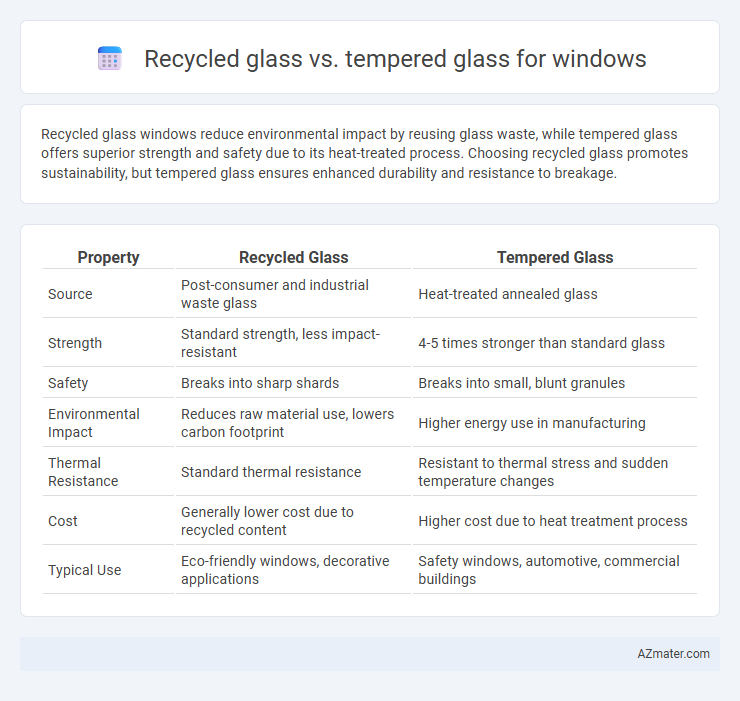
Recycled glass windows reduce environmental impact by reusing glass waste, while tempered glass offers superior strength and safety due to its heat-treated process. Choosing recycled glass promotes sustainability, but tempered glass ensures enhanced durability and resistance to breakage.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Recycled Glass | Tempered Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Post-consumer and industrial waste glass | Heat-treated annealed glass |
| Strength | Standard strength, less impact-resistant | 4-5 times stronger than standard glass |
| Safety | Breaks into sharp shards | Breaks into small, blunt granules |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces raw material use, lowers carbon footprint | Higher energy use in manufacturing |
| Thermal Resistance | Standard thermal resistance | Resistant to thermal stress and sudden temperature changes |
| Cost | Generally lower cost due to recycled content | Higher cost due to heat treatment process |
| Typical Use | Eco-friendly windows, decorative applications | Safety windows, automotive, commercial buildings |
Introduction to Recycled Glass and Tempered Glass
Recycled glass is made from post-consumer glass waste that is melted and reformed into new glass products, offering environmental sustainability and energy efficiency. Tempered glass undergoes a controlled thermal or chemical treatment to enhance strength and safety, making it resistant to impact and thermal stress. Both materials serve distinct purposes in window applications, balancing ecological benefits with structural performance.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Recycled glass for windows is primarily made from post-consumer or industrial glass waste, melted and reformed to reduce environmental impact while maintaining the silica, soda ash, and limestone base. Tempered glass undergoes a rigorous manufacturing process involving heating to approximately 620degC followed by rapid cooling, which induces compressive stresses on the surface to enhance strength and safety. The key compositional difference lies in recycled glass's eco-conscious raw material source, whereas tempered glass focuses on thermal treatment to improve durability and thermal resistance in window applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Recycled glass significantly reduces energy consumption by requiring up to 40% less energy during production compared to tempered glass, which typically involves higher temperatures and more intensive processing. Utilizing recycled glass in windows decreases landfill waste and conserves natural resources by reusing cullet, while tempered glass, despite its strength and safety benefits, relies heavily on primary raw materials and emits more CO2. Sustainable building projects increasingly prefer recycled glass for its lower carbon footprint and contribution to circular economy principles, promoting eco-friendly glazing solutions in window manufacturing.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Tempered glass offers superior strength due to its thermal treatment process, making it up to five times stronger than standard glass, including recycled variants. Recycled glass, while environmentally beneficial, often has inconsistencies in composition that can reduce its overall structural integrity compared to tempered glass. For windows requiring high impact resistance and durability, tempered glass remains the preferred choice, especially in safety-critical applications.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation Properties
Recycled glass windows offer superior thermal insulation due to their lower thermal conductivity, effectively reducing energy loss and improving indoor temperature regulation. Tempered glass provides enhanced acoustic insulation by its increased strength and uniform structure, which helps dampen sound transmission and reduce noise pollution. Combining recycled glass with tempering techniques can optimize both thermal and acoustic performance for energy-efficient and quiet window solutions.
Safety Features and Breakage Behavior
Recycled glass for windows offers environmental benefits but generally lacks the enhanced safety features of tempered glass, which is heat-treated to increase strength and resistance to impact. Tempered glass breaks into small, blunt granules instead of sharp shards, significantly reducing injury risk during breakage. Recycled glass often fractures unpredictably, posing higher safety hazards compared to the controlled breakage behavior of tempered glass in window applications.
Cost Analysis and Economical Aspects
Recycled glass windows generally offer lower production costs due to reduced raw material expenses and lower energy consumption during manufacturing, leading to economically attractive options for budget-conscious projects. Tempered glass, while more expensive due to its heat treatment process and enhanced strength, provides longer-term durability and safety benefits that can reduce replacement and maintenance costs over time. Cost analysis must balance initial investment in tempered glass with potential savings from fewer repairs, while recycled glass supports sustainability initiatives and may qualify for green building incentives, further influencing economic decisions.
Aesthetic and Design Flexibility
Recycled glass offers unique aesthetic qualities with its varying textures and colors, adding an eco-friendly, artisanal charm to window designs. Tempered glass provides sleek, clear surfaces with high strength, enabling large, uninterrupted panes for modern and minimalist design flexibility. Both materials enhance window aesthetics but differ in visual texture and customization options, catering to different architectural styles.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Recycled glass windows typically require similar installation methods as standard glass but may involve additional handling precautions due to potential variations in thickness and composition, impacting labor time and cost. Tempered glass offers straightforward installation with enhanced safety features, as it is pre-treated for strength and shatters into small granules rather than sharp shards, reducing maintenance risks. Maintenance for recycled glass windows may necessitate more frequent inspections for chips or inclusions, whereas tempered glass requires minimal upkeep due to its durability and resistance to impact and thermal stress.
Best Applications: Choosing the Right Glass for Your Windows
Recycled glass for windows offers eco-friendly benefits and excellent thermal insulation, making it ideal for residential buildings focused on sustainability and energy efficiency. Tempered glass, known for its high strength and safety features, suits commercial and high-traffic areas where impact resistance and durability are critical. Selecting between recycled and tempered glass depends on specific application needs such as environmental impact, safety standards, and performance requirements.
Infographic: Recycled glass vs Tempered glass for Window
 azmater.com
azmater.com