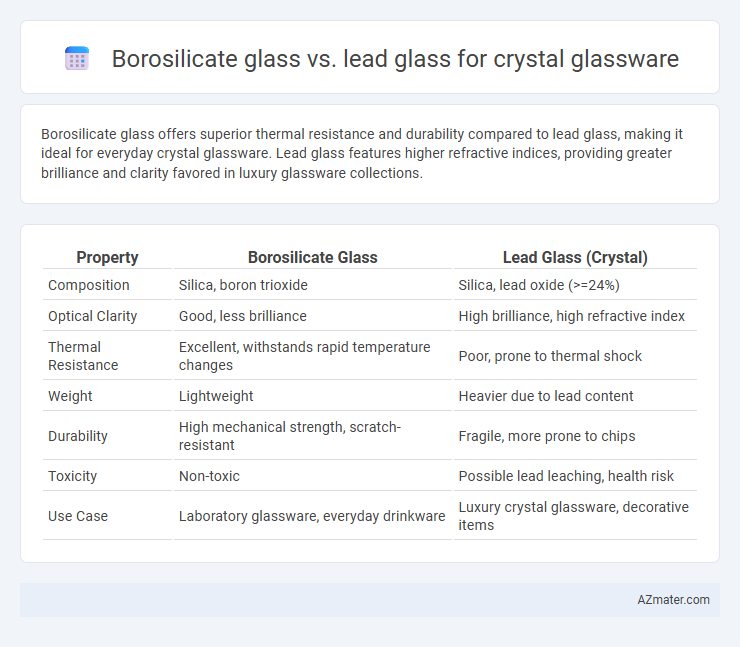
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and durability compared to lead glass, making it ideal for everyday crystal glassware. Lead glass features higher refractive indices, providing greater brilliance and clarity favored in luxury glassware collections.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Borosilicate Glass | Lead Glass (Crystal) |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Silica, boron trioxide | Silica, lead oxide (>=24%) |
| Optical Clarity | Good, less brilliance | High brilliance, high refractive index |
| Thermal Resistance | Excellent, withstands rapid temperature changes | Poor, prone to thermal shock |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier due to lead content |
| Durability | High mechanical strength, scratch-resistant | Fragile, more prone to chips |
| Toxicity | Non-toxic | Possible lead leaching, health risk |
| Use Case | Laboratory glassware, everyday drinkware | Luxury crystal glassware, decorative items |
Introduction to Crystal Glassware
Crystal glassware, often valued for its clarity and brilliance, is primarily crafted from lead glass or borosilicate glass. Lead glass, containing up to 30% lead oxide, enhances refractive index and weight, producing exceptional sparkle and resonance in crystal pieces. Borosilicate glass, known for its durability and thermal resistance, offers a lighter, more chip-resistant alternative while maintaining a clear appearance for everyday glassware use.
What is Borosilicate Glass?
Borosilicate glass is a type of glass composed primarily of silica and boron trioxide, known for its high thermal resistance and durability, making it ideal for crystal glassware that requires strength and clarity. Unlike lead glass, which contains lead oxide to enhance refractive properties and brilliance, borosilicate glass offers superior resistance to temperature changes and chemical corrosion without the health risks associated with lead. Its excellent mechanical stability and low thermal expansion coefficient ensure that borosilicate glassware maintains clarity and structural integrity over time in both everyday use and laboratory environments.
What is Lead Glass?
Lead glass, also known as lead crystal, contains lead oxide typically ranging from 18% to 30%, enhancing its refractive index and providing exceptional brilliance and clarity compared to borosilicate glass. This increased lead content makes lead glass softer and more malleable, allowing intricate cuts and designs that enhance its visual appeal in crystal glassware. Though borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and durability, lead glass remains preferred in luxury tableware for its sparkling finish and weight.
Key Differences Between Borosilicate and Lead Glass
Borosilicate glass is known for its exceptional thermal resistance and durability, making it ideal for everyday crystal glassware that requires heat and chemical resistance. Lead glass, containing lead oxide, offers superior brilliance and clarity, enhancing the crystal's light refraction and aesthetic appeal but is less resistant to thermal shock compared to borosilicate. The main differences lie in durability, optical properties, and chemical composition, with borosilicate glass favoring functionality and lead glass prioritizing decorative elegance.
Durability: Borosilicate Glass vs Lead Glass
Borosilicate glass offers superior durability due to its high resistance to thermal shock and mechanical stress, making it less prone to cracking or shattering under temperature changes. Lead glass, while prized for its brilliance and clarity, is softer and more susceptible to scratches and damage from impacts. The composition of borosilicate glass, rich in silica and boron oxide, enhances its strength and longevity compared to the lead oxide content in lead glass which reduces durability.
Health and Safety Considerations
Borosilicate glass offers superior health and safety benefits compared to lead glass, as it contains no harmful lead content and is resistant to thermal shock and chemical corrosion, reducing contamination risks. Lead glass, while prized for its brilliance and weight, can leach toxic lead ions into beverages, posing significant health hazards, especially with prolonged use. For crystal glassware, choosing borosilicate glass ensures safer drinking practices without compromising durability or clarity.
Aesthetic Qualities: Clarity and Shine
Borosilicate glass offers exceptional clarity with a subtle, cool brilliance due to its high thermal resistance and low dispersion, making it ideal for modern, minimalist crystal glassware. Lead glass, enriched with lead oxide, delivers superior refractive index and increased dispersion, resulting in a pronounced sparkle and vibrant shine favored in traditional, luxurious crystal craftsmanship. The choice between borosilicate and lead glass hinges on desired aesthetic effects: borosilicate emphasizes clarity and durability, while lead glass maximizes brilliance and scintillation.
Price Comparison
Borosilicate glass is generally more affordable than lead glass due to its simpler manufacturing process and widespread availability, making it a cost-effective choice for crystal glassware. Lead glass, often prized for its brilliance and weight, commands a higher price because of the lead oxide content and more intricate production methods. Consumers seeking premium crystal glassware are often willing to pay a premium for lead glass's enhanced clarity despite borosilicate glass's lower cost.
Environmental Impact
Borosilicate glass has a lower environmental impact compared to lead glass due to its non-toxic composition and higher durability, which reduces waste and extends product lifespan. Lead glass, while valued for its brilliance and weighted feel, poses environmental and health risks because lead is a hazardous material that can leach into ecosystems during manufacturing and disposal. Recycling borosilicate glass is more feasible and eco-friendly, whereas lead glass requires specialized disposal methods to prevent soil and water contamination.
Which Glass is Best for Crystal Glassware?
Borosilicate glass offers exceptional thermal and chemical resistance, making it ideal for durable crystal glassware used in everyday settings, while lead glass is prized for its higher refractive index and brilliance, giving luxury crystal glassware a sparkling, elegant appearance. The best glass for crystal glassware depends on the intended use: borosilicate glass suits practical, heat-resistant applications, whereas lead glass excels in ornamental and high-end pieces requiring exceptional clarity and weight. Manufacturers often choose lead glass for fine crystal due to its superior aesthetic qualities, despite borosilicate's durability advantages.
Infographic: Borosilicate glass vs Lead glass for Crystal glassware
 azmater.com
azmater.com