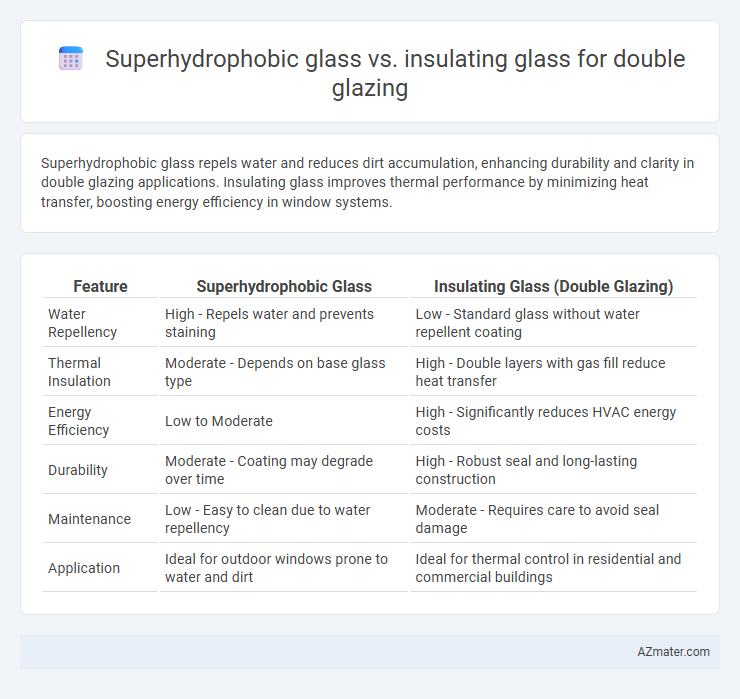
Superhydrophobic glass repels water and reduces dirt accumulation, enhancing durability and clarity in double glazing applications. Insulating glass improves thermal performance by minimizing heat transfer, boosting energy efficiency in window systems.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Superhydrophobic Glass | Insulating Glass (Double Glazing) |
|---|---|---|
| Water Repellency | High - Repels water and prevents staining | Low - Standard glass without water repellent coating |
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate - Depends on base glass type | High - Double layers with gas fill reduce heat transfer |
| Energy Efficiency | Low to Moderate | High - Significantly reduces HVAC energy costs |
| Durability | Moderate - Coating may degrade over time | High - Robust seal and long-lasting construction |
| Maintenance | Low - Easy to clean due to water repellency | Moderate - Requires care to avoid seal damage |
| Application | Ideal for outdoor windows prone to water and dirt | Ideal for thermal control in residential and commercial buildings |
Introduction to Double Glazing Technologies
Double glazing technologies enhance energy efficiency and comfort by using two glass panes separated by a spacer filled with air or inert gas. Superhydrophobic glass features a water-repellent coating that prevents condensation and dirt buildup, maintaining clearer windows and reducing maintenance. Insulating glass units (IGUs) incorporate low-emissivity coatings and gas fills like argon or krypton to minimize heat transfer and improve thermal insulation.
What is Superhydrophobic Glass?
Superhydrophobic glass features an ultra-water-repellent coating that causes water droplets to bead and roll off the surface, reducing dirt and moisture buildup on double glazing windows. This property enhances visibility and reduces maintenance, making it ideal for exterior glass in various climates. In contrast, insulating glass prioritizes thermal efficiency by incorporating multiple glass panes with gas-filled spaces, focusing on energy conservation rather than water repellency.
Understanding Insulating Glass: Key Features
Insulating glass typically consists of two or more glass panes separated by a spacer filled with inert gas, designed to reduce heat transfer and enhance energy efficiency. Its key features include superior thermal insulation, noise reduction, and improved condensation resistance, which contribute to maintaining indoor comfort and lowering energy costs. Unlike superhydrophobic glass, which primarily repels water and reduces surface contamination, insulating glass focuses on creating an effective barrier against temperature fluctuations and sound penetration.
Comparative Thermal Performance
Superhydrophobic glass features a nanoscale textured coating that repels water and dirt, enhancing durability without significantly impacting thermal insulation. Insulating glass, typically composed of two or more panes separated by a gas-filled space, offers superior thermal performance by minimizing heat transfer through conduction and convection. When comparing thermal efficiency, insulating glass provides better U-values and reduces energy loss more effectively than superhydrophobic glass, making it the preferred choice for energy-saving double glazing applications.
Energy Efficiency: Which Glass Performs Better?
Superhydrophobic glass offers superior water repellency and self-cleaning properties but has minimal impact on thermal insulation in double glazing systems. Insulating glass features multiple panes with inert gas fills and low-emissivity coatings, significantly reducing heat transfer and improving overall energy efficiency by maintaining indoor temperatures. For maximizing energy savings and thermal performance in double glazing, insulating glass outperforms superhydrophobic glass.
Maintenance and Durability Considerations
Superhydrophobic glass exhibits superior self-cleaning properties due to its water-repellent surface, significantly reducing maintenance needs compared to conventional insulating glass in double glazing. Its enhanced durability resists dirt, stains, and weathering, extending the lifespan of the glazing unit by minimizing surface degradation. While insulating glass primarily focuses on thermal performance, superhydrophobic coatings offer a dual benefit of energy efficiency and reduced upkeep, promoting long-term cost savings.
Visual Clarity and Aesthetic Differences
Superhydrophobic glass maintains superior visual clarity by repelling water and dirt, reducing the need for frequent cleaning and preventing stains that can obscure the view, which is ideal for double glazing in aesthetically focused applications. Insulating glass, often composed of multiple panes with gas-filled spaces, enhances energy efficiency but may introduce slight visual distortions or reflections due to its layered structure. While superhydrophobic glass prioritizes a cleaner, clearer appearance over time, insulating glass focuses on thermal performance at the potential cost of some optical clarity and aesthetic uniformity.
Cost Implications: Superhydrophobic vs Insulating Glass
Superhydrophobic glass typically incurs higher initial costs than insulating glass due to advanced nanocoating technologies that repel water and contaminants, reducing cleaning and maintenance expenses over time. Insulating glass, designed with multiple panes and gas fills, offers energy efficiency benefits that lower heating and cooling costs but generally has a lower upfront price compared to superhydrophobic variants. Long-term cost implications depend on climate conditions and maintenance priorities, with superhydrophobic glass favoring durability and cleanliness, while insulating glass emphasizes thermal performance and energy savings.
Applications in Residential and Commercial Settings
Superhydrophobic glass offers superior water repellency and self-cleaning properties, making it ideal for high-rise residential and commercial buildings where maintenance is challenging. Insulating glass excels at thermal performance and energy efficiency, reducing heating and cooling costs in both homes and office complexes. Combining double glazing with these specialized glasses enhances comfort, durability, and sustainability across various architectural applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Double Glazing Needs
Superhydrophobic glass offers superior water repellency and self-cleaning properties, reducing maintenance in double glazing applications. Insulating glass excels in thermal performance, minimizing heat transfer to enhance energy efficiency in buildings. Choosing between these depends on priorities such as climate, maintenance preferences, and energy conservation goals for optimal double glazing results.
Infographic: Superhydrophobic glass vs Insulating glass for Double glazing
 azmater.com
azmater.com