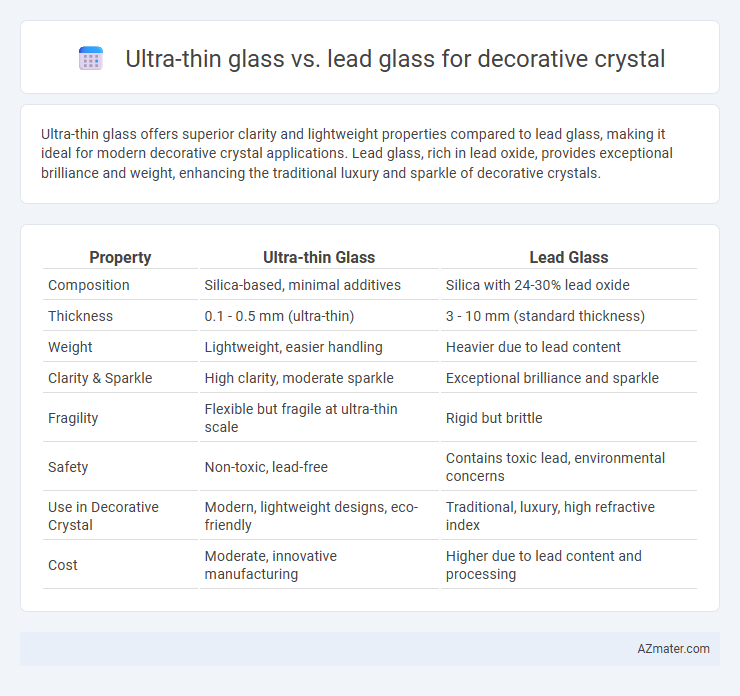
Ultra-thin glass offers superior clarity and lightweight properties compared to lead glass, making it ideal for modern decorative crystal applications. Lead glass, rich in lead oxide, provides exceptional brilliance and weight, enhancing the traditional luxury and sparkle of decorative crystals.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ultra-thin Glass | Lead Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Silica-based, minimal additives | Silica with 24-30% lead oxide |
| Thickness | 0.1 - 0.5 mm (ultra-thin) | 3 - 10 mm (standard thickness) |
| Weight | Lightweight, easier handling | Heavier due to lead content |
| Clarity & Sparkle | High clarity, moderate sparkle | Exceptional brilliance and sparkle |
| Fragility | Flexible but fragile at ultra-thin scale | Rigid but brittle |
| Safety | Non-toxic, lead-free | Contains toxic lead, environmental concerns |
| Use in Decorative Crystal | Modern, lightweight designs, eco-friendly | Traditional, luxury, high refractive index |
| Cost | Moderate, innovative manufacturing | Higher due to lead content and processing |
Introduction to Decorative Crystal Materials
Decorative crystal materials are distinguished by their clarity, brilliance, and weight, with ultra-thin glass and lead glass being prominent options. Ultra-thin glass offers exceptional transparency and lightweight properties, enhancing modern minimalist designs without compromising durability. Lead glass, known for its high refractive index and density, provides superior sparkle and a traditional luxurious feel favored in classic decorative crystal applications.
Understanding Ultra-Thin Glass
Ultra-thin glass offers a lightweight, highly transparent alternative to lead glass in decorative crystal applications, enhancing visual clarity and elegance without the added weight. Its nanoscale thickness allows for superior light transmission and modern, sleek designs that maintain durability despite being thinner than traditional lead glass. Manufacturers prioritize ultra-thin glass to achieve intricate shapes and vibrant reflections while reducing harmful lead content, meeting both aesthetic and environmental standards.
Overview of Lead Glass
Lead glass, also known as crystal glass, contains a high percentage of lead oxide (typically 24-30%), which enhances its refractive index and brilliance, making it ideal for decorative crystal applications. Its dense composition provides superior clarity and weight compared to ultra-thin glass, resulting in a luxurious appearance and enhanced light dispersion. Lead glass is favored for intricate designs and ornate detailing due to its workability and elegant sparkle.
Key Differences Between Ultra-Thin Glass and Lead Glass
Ultra-thin glass offers superior clarity and lightweight properties compared to traditional lead glass, making it ideal for delicate decorative crystal applications. Lead glass contains lead oxide, which enhances its brilliance and density but increases its weight and toxicity concerns. Ultra-thin glass provides greater flexibility and modern manufacturing options, while lead glass remains valued for its classic sparkle and heavy feel in luxury crystal products.
Aesthetic Qualities: Clarity, Color, and Sparkle
Ultra-thin glass offers exceptional clarity and a modern minimalistic appeal, with its thinner profile enhancing light transmission for a clean, crisp sparkle ideal for contemporary decorative crystal. Lead glass contains lead oxide, significantly increasing refractive index and brilliance, resulting in intense sparkle and depth of color, favored for traditional luxury crystal designs. While ultra-thin glass emphasizes sleek transparency and subtle shimmer, lead glass delivers vibrant color dispersion and pronounced sparkle that enhances ornate decorative pieces.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Ultra-thin glass demonstrates excellent durability due to its ability to resist impacts and scratches better than traditional lead glass, making it ideal for decorative crystal applications requiring both aesthetics and longevity. Lead glass, while prized for its high refractive index and brilliant clarity, tends to be softer and more prone to chipping or cracking under stress, reducing its durability in high-traffic or handled decorative pieces. The enhanced strength of ultra-thin glass allows for thinner, lighter designs without compromising structural integrity, offering a modern alternative to the heavier and more fragile lead glass.
Safety and Environmental Considerations
Ultra-thin glass offers enhanced safety in decorative crystal due to its reduced thickness and higher flexibility, minimizing the risk of breakage and injury compared to traditional lead glass, which is more brittle and prone to shattering. Environmentally, ultra-thin glass is more sustainable as it eliminates the use of toxic lead, reducing hazardous waste and potential lead contamination during manufacturing and disposal. Lead glass, while prized for clarity and weight, poses significant environmental and health risks, making ultra-thin glass a safer and eco-friendly alternative in decorative applications.
Design Flexibility and Applications
Ultra-thin glass offers superior design flexibility for decorative crystal, enabling intricate shapes and detailed patterns due to its lightweight and malleable properties compared to lead glass. Lead glass provides exceptional clarity and brilliance, ideal for traditional applications like chandeliers and fine art pieces, but is limited by its weight and rigidity. Ultra-thin glass expands applications to innovative, modern decor and wearable art where delicate, lightweight design is crucial.
Cost Implications in Decorative Crystal Products
Ultra-thin glass offers a cost-effective alternative to traditional lead glass in decorative crystal products by utilizing less raw material and reducing shipping expenses due to its lighter weight. Although lead glass provides superior brilliance and clarity, its higher production and handling costs make it less economical for large-scale or budget-conscious decorative applications. Manufacturers often balance quality and cost by choosing ultra-thin glass to achieve affordability without significantly compromising visual appeal.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Decorative Needs
Ultra-thin glass offers lightweight durability and a sleek, modern appearance ideal for minimalist decorative designs, while lead glass, known for its high refractive index and brilliance, provides exceptional sparkle and weight suitable for traditional crystal aesthetics. Choosing the right glass depends on desired visual impact, durability requirements, and budget considerations, with ultra-thin glass excelling in contemporary settings and lead glass favored for classic, high-end decorative pieces. Both materials enhance decor but cater to different style preferences and functional needs.
Infographic: Ultra-thin glass vs Lead glass for Decorative crystal
 azmater.com
azmater.com