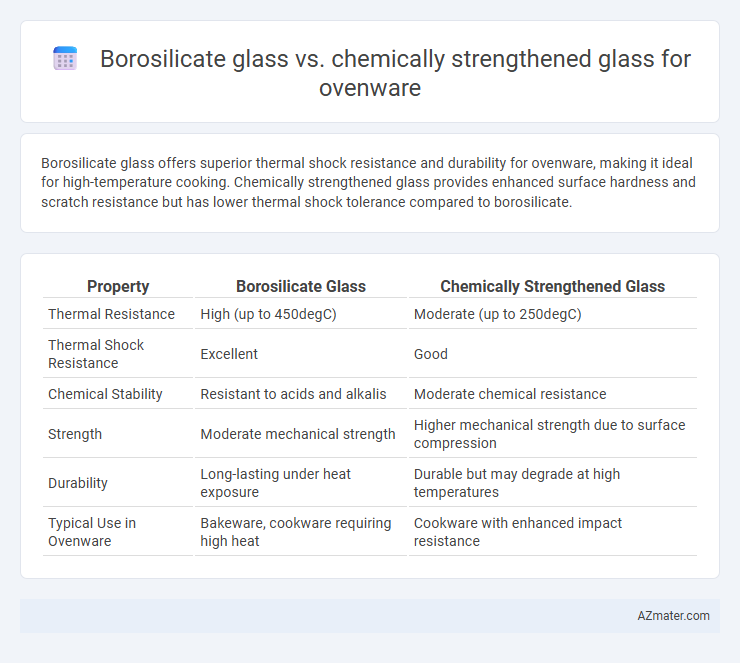
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal shock resistance and durability for ovenware, making it ideal for high-temperature cooking. Chemically strengthened glass provides enhanced surface hardness and scratch resistance but has lower thermal shock tolerance compared to borosilicate.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Borosilicate Glass | Chemically Strengthened Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Resistance | High (up to 450degC) | Moderate (up to 250degC) |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Chemical Stability | Resistant to acids and alkalis | Moderate chemical resistance |
| Strength | Moderate mechanical strength | Higher mechanical strength due to surface compression |
| Durability | Long-lasting under heat exposure | Durable but may degrade at high temperatures |
| Typical Use in Ovenware | Bakeware, cookware requiring high heat | Cookware with enhanced impact resistance |
Introduction to Ovenware Glass Types
Borosilicate glass for ovenware is renowned for its excellent thermal resistance and low expansion coefficient, making it highly durable under rapid temperature changes often encountered during cooking. Chemically strengthened glass, created through ion exchange processes, offers enhanced surface strength and scratch resistance, improving its durability but generally exhibiting less thermal shock resistance than borosilicate. Both glass types are engineered to withstand oven temperatures, but borosilicate is typically preferred for direct heat applications due to its superior thermal stability and safety.
What is Borosilicate Glass?
Borosilicate glass is a type of glass known for its exceptional thermal resistance and chemical durability, making it ideal for ovenware applications. It contains boron trioxide, which reduces thermal expansion and prevents cracking under rapid temperature changes. Compared to chemically strengthened glass, borosilicate glass offers superior performance in high-heat environments, ensuring safety and longevity in cookware.
What is Chemically Strengthened Glass?
Chemically strengthened glass is created through an ion-exchange process where smaller sodium ions in the glass surface are replaced by larger potassium ions, resulting in increased compressive stress and enhanced resistance to thermal shock and mechanical damage. In ovenware, chemically strengthened glass offers improved durability and heat resistance compared to regular glass, but borosilicate glass still outperforms it in withstanding rapid temperature changes due to its low thermal expansion. Borosilicate glass typically contains silica and boron trioxide, making it highly resistant to thermal stress, which is essential for safe and reliable ovenware performance.
Thermal Shock Resistance Comparison
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal shock resistance compared to chemically strengthened glass, withstanding rapid temperature changes up to 165degF (90degC) without cracking. Chemically strengthened glass, while harder and more scratch-resistant, typically endures lower thermal shock thresholds, making it less ideal for ovenware exposed to sudden heat fluctuations. Borosilicate's low coefficient of thermal expansion (approximately 3.3 x 10-6 /degC) ensures enhanced durability in oven applications where thermal stability is critical.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal shock resistance and mechanical strength due to its low coefficient of thermal expansion, making it highly durable for ovenware. Chemically strengthened glass achieves enhanced surface compressive stress through ion exchange, significantly improving scratch resistance and impact durability but may be less tolerant to extreme temperature fluctuations than borosilicate. Overall, borosilicate excels in thermal resilience, while chemically strengthened glass provides enhanced surface strength and scratch durability for oven applications.
Oven and Temperature Performance
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance withstanding temperatures up to 450degC, making it ideal for ovenware that requires even heat distribution and rapid temperature changes without cracking. Chemically strengthened glass provides enhanced mechanical strength and scratch resistance but typically handles lower maximum temperatures around 300degC, limiting its use in high-heat oven applications. For high-temperature baking and roasting, borosilicate glass ensures durability and safety, while chemically strengthened glass suits moderate oven use with added impact resistance.
Chemical Resistance and Food Safety
Borosilicate glass offers superior chemical resistance against acidic and alkaline substances, making it highly suitable for ovenware in contact with various food types without leaching harmful chemicals. Chemically strengthened glass, while tougher due to ion exchange processes, may be more susceptible to chemical degradation over time when exposed to harsh cleaning agents or acidic foods. Borosilicate glass remains the preferred choice for food safety and long-term durability in ovenware applications due to its stable chemical composition and resistance to thermal shock.
Cost and Availability of Each Glass
Borosilicate glass, known for its high thermal resistance and durability, is generally more affordable and widely available for ovenware compared to chemically strengthened glass. Chemically strengthened glass offers enhanced surface strength and scratch resistance but typically comes at a higher cost and limited availability due to specialized manufacturing processes. Consumers seeking cost-effective and easily accessible ovenware often prefer borosilicate glass, while chemically strengthened glass suits premium applications requiring superior mechanical strength.
Lifespan and Maintenance Requirements
Borosilicate glass, known for its thermal shock resistance, offers a longer lifespan in ovenware applications due to its ability to withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking. Chemically strengthened glass, while tougher against surface scratches and impact, may have a shorter lifespan if exposed to extreme temperature fluctuations common during baking and roasting. Maintenance for borosilicate glass is minimal, requiring gentle cleaning to preserve clarity, whereas chemically strengthened glass demands careful handling to avoid surface damage that can weaken the chemical treatment over time.
Choosing the Best Glass for Your Ovenware
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal shock resistance and durability, making it ideal for ovenware that undergoes rapid temperature changes. Chemically strengthened glass provides enhanced scratch resistance and higher surface strength but may be less resistant to sudden temperature shifts compared to borosilicate. Evaluating your ovenware needs, borosilicate glass is best for frequent high-heat use, while chemically strengthened glass suits applications requiring strong scratch protection alongside moderate heat resistance.
Infographic: Borosilicate glass vs Chemically strengthened glass for Ovenware
 azmater.com
azmater.com