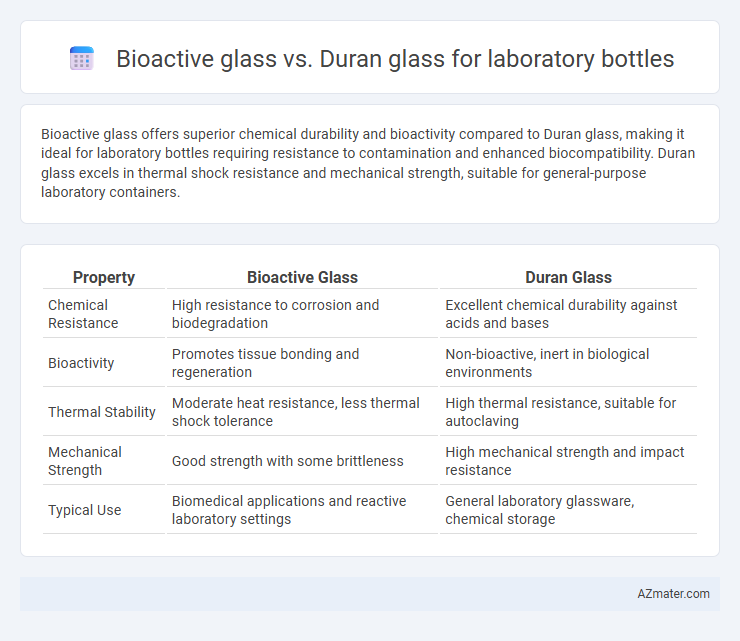
Bioactive glass offers superior chemical durability and bioactivity compared to Duran glass, making it ideal for laboratory bottles requiring resistance to contamination and enhanced biocompatibility. Duran glass excels in thermal shock resistance and mechanical strength, suitable for general-purpose laboratory containers.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bioactive Glass | Duran Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | High resistance to corrosion and biodegradation | Excellent chemical durability against acids and bases |
| Bioactivity | Promotes tissue bonding and regeneration | Non-bioactive, inert in biological environments |
| Thermal Stability | Moderate heat resistance, less thermal shock tolerance | High thermal resistance, suitable for autoclaving |
| Mechanical Strength | Good strength with some brittleness | High mechanical strength and impact resistance |
| Typical Use | Biomedical applications and reactive laboratory settings | General laboratory glassware, chemical storage |
Introduction to Laboratory Glassware: Bioactive Glass vs Duran Glass
Bioactive glass offers enhanced chemical durability and biocompatibility, making it ideal for specialized laboratory applications involving bioactive substances and cell cultures. Duran glass, a borosilicate glass, is widely used for laboratory bottles due to its excellent thermal resistance, mechanical strength, and chemical inertness under common laboratory conditions. Both materials provide reliable containment, but bioactive glass is preferred when bioactivity and interaction with biological systems are critical, while Duran glass excels in general-purpose laboratory use with strong resistance to thermal shock.
Composition and Manufacturing Differences
Bioactive glass typically contains silica, calcium oxide, phosphorus pentoxide, and sodium oxide, designed for bioactivity and tissue compatibility, whereas Duran glass is borosilicate glass with high silica and boron trioxide content, offering excellent chemical resistance and thermal stability. Bioactive glass is manufactured through controlled melting processes that promote network connectivity for ion exchange beneficial in biomedical applications, while Duran glass undergoes precise melting and refining to achieve a durable, low thermal expansion structure ideal for laboratory glassware. The compositional focus on bioactive elements in bioactive glass contrasts with Duran's emphasis on chemical inertness and mechanical strength, influencing their respective manufacturing techniques and end-use performance.
Physical and Chemical Properties
Bioactive glass exhibits superior chemical durability and biocompatibility compared to Duran glass, making it ideal for applications requiring bioactivity and resistance to bodily fluids. Physically, bioactive glass has a higher surface reactivity that promotes bond formation with biological tissues, whereas Duran glass is known for its excellent thermal resistance and mechanical strength in laboratory environments. The chemical composition of bioactive glass typically includes calcium, sodium, and phosphate oxides that enable bioactivity, while Duran glass primarily consists of borosilicate, contributing to its low thermal expansion and high chemical stability.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Bioactive glass offers enhanced chemical durability and resistance to corrosive agents, making it ideal for long-term storage in laboratory bottles. Duran glass, composed of borosilicate, exhibits superior mechanical strength and thermal shock resistance, sustaining integrity under rapid temperature changes. When comparing durability, bioactive glass excels in bioactivity and corrosion resistance, while Duran glass provides greater structural robustness and fracture toughness for rigorous laboratory use.
Thermal and Chemical Resistance
Bioactive glass demonstrates superior chemical resistance compared to Duran glass, resisting corrosion and chemical degradation from acidic and alkaline substances commonly used in laboratory settings. Thermal resistance in bioactive glass is enhanced by its unique composition, allowing it to withstand higher temperature fluctuations without cracking or deforming. Duran glass, while highly resistant to thermal shock and suitable for autoclaving, generally offers lower chemical durability against aggressive reagents than bioactive glass, making bioactive glass preferable for experiments involving reactive chemicals.
Applications in Laboratory Settings
Bioactive glass and Duran glass serve distinct roles in laboratory settings, with bioactive glass being favored for applications involving cell culture and tissue engineering due to its biocompatibility and ability to support cell growth. Duran glass, known for its thermal resistance and chemical durability, is predominantly used for general-purpose laboratory bottles requiring stability under high temperatures and exposure to aggressive chemicals. Laboratories handling biological experiments benefit from bioactive glass, while those involved in chemical synthesis and storage typically prefer Duran glass due to its robustness and inertness.
Bio-compatibility and Reactivity
Bioactive glass exhibits superior biocompatibility compared to Duran glass, making it ideal for laboratory bottles used in biomedical applications where minimal cellular toxicity is critical. Its reactive surface facilitates controlled ion exchange, promoting bioactivity without compromising chemical stability, unlike inert Duran glass which shows minimal surface interaction. This enhanced reactivity supports biological integration while maintaining resistance to chemical degradation, positioning bioactive glass as the preferred material for lab bottles in biosensitive environments.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Bioactive glass laboratory bottles typically exhibit higher costs due to their advanced material properties and specialized manufacturing processes compared to Duran glass, which is more widely produced and hence more affordable. Duran glass offers greater availability in various sizes and forms, making it a cost-effective choice for laboratories requiring standard chemical resistance without the premium price. Cost efficiency and accessibility make Duran glass preferable for routine lab applications, whereas bioactive glass is selected for niche uses demanding enhanced bioactivity despite its elevated price and limited supply.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bioactive glass demonstrates superior environmental benefits over Duran glass due to its biodegradability and ability to promote natural material regeneration, reducing long-term waste accumulation. Duran glass, while durable and reusable, relies on energy-intensive manufacturing processes and lacks bioactivity, contributing to higher carbon emissions and limited ecological integration. Sustainable lab practices favor bioactive glass for minimizing environmental impact through enhanced recyclability and reduced ecological footprint.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Laboratory Needs
Bioactive glass offers superior biocompatibility and chemical durability, making it ideal for laboratory applications requiring corrosion resistance and bioactivity. Duran glass, known for its exceptional thermal resistance and mechanical strength, is preferred in high-temperature and pressure-intensive experiments. Selecting between bioactive glass and Duran glass depends largely on the specific laboratory processes, with bioactive glass suited for biologically sensitive tasks and Duran glass optimized for robust chemical and thermal performance.
Infographic: Bioactive glass vs Duran glass for Laboratory bottle
 azmater.com
azmater.com