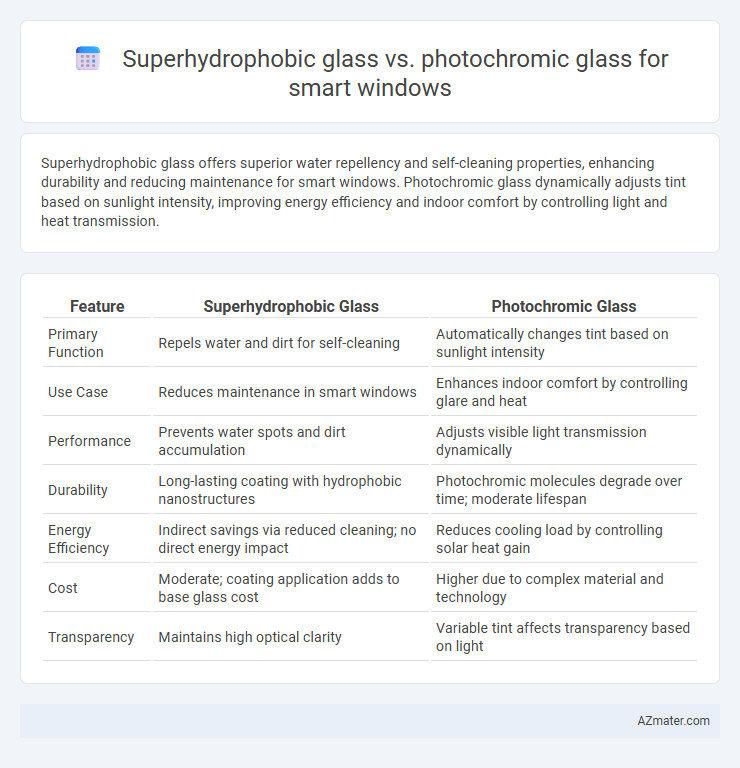
Superhydrophobic glass offers superior water repellency and self-cleaning properties, enhancing durability and reducing maintenance for smart windows. Photochromic glass dynamically adjusts tint based on sunlight intensity, improving energy efficiency and indoor comfort by controlling light and heat transmission.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Superhydrophobic Glass | Photochromic Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Repels water and dirt for self-cleaning | Automatically changes tint based on sunlight intensity |
| Use Case | Reduces maintenance in smart windows | Enhances indoor comfort by controlling glare and heat |
| Performance | Prevents water spots and dirt accumulation | Adjusts visible light transmission dynamically |
| Durability | Long-lasting coating with hydrophobic nanostructures | Photochromic molecules degrade over time; moderate lifespan |
| Energy Efficiency | Indirect savings via reduced cleaning; no direct energy impact | Reduces cooling load by controlling solar heat gain |
| Cost | Moderate; coating application adds to base glass cost | Higher due to complex material and technology |
| Transparency | Maintains high optical clarity | Variable tint affects transparency based on light |
Introduction to Smart Window Technologies
Superhydrophobic glass and photochromic glass represent advanced smart window technologies that enhance energy efficiency and user comfort. Superhydrophobic glass features a water-repellent coating that maintains clarity and reduces cleaning frequency by preventing water and dirt accumulation. Photochromic glass dynamically adjusts its tint in response to sunlight, optimizing indoor lighting and thermal regulation through adaptive light modulation.
What is Superhydrophobic Glass?
Superhydrophobic glass features an ultra-water-repellent surface created by nanostructures that cause water droplets to bead and roll off, enhancing self-cleaning and anti-fogging properties. This technology improves the durability and visibility of smart windows by reducing water-related stains and condensation. Unlike photochromic glass, which adapts to light conditions by changing tint, superhydrophobic glass focuses on maintaining cleanliness and clarity through water resistance.
What is Photochromic Glass?
Photochromic glass is a smart glass technology that automatically adjusts its tint based on the intensity of sunlight, providing dynamic shading and UV protection. Unlike superhydrophobic glass, which primarily repels water and improves surface cleanliness, photochromic glass enhances energy efficiency by reducing glare and heat gain indoors. This adaptive property makes photochromic glass ideal for smart windows in residential and commercial buildings seeking comfort and reduced energy costs.
Key Functional Differences
Superhydrophobic glass repels water and prevents dirt accumulation, enhancing self-cleaning and durability for smart windows, while photochromic glass dynamically adjusts its tint based on light intensity to control solar heat and glare. Superhydrophobic coatings primarily improve surface maintenance and visibility, whereas photochromic technology optimizes energy efficiency and indoor comfort by modulating light transmission. The key functional difference lies in superhydrophobic glass's protective, anti-fouling properties versus photochromic glass's adaptive light regulation capabilities.
Performance Under Different Weather Conditions
Superhydrophobic glass excels in repelling water and maintaining clarity during rain or high humidity, preventing water spots and enhancing visibility. Photochromic glass adapts to varying light intensities by darkening in bright sunlight, reducing glare and heat gain but may underperform in low UV conditions such as cloudy or rainy weather. Combining these technologies can optimize smart window performance, ensuring clear visibility and dynamic light control across diverse weather environments.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Superhydrophobic glass enhances energy efficiency by maintaining transparency and self-cleaning properties that reduce cooling loads through minimized dirt accumulation, thereby optimizing natural light transmission. Photochromic glass dynamically adjusts its tint in response to sunlight intensity, significantly reducing heat gain and glare, which lowers air conditioning energy consumption. Comparing both, photochromic glass offers superior active regulation of solar heat, while superhydrophobic glass contributes to passive energy savings through sustained optical clarity and reduced maintenance needs.
Maintenance and Durability
Superhydrophobic glass offers superior resistance to water, dirt, and stains, significantly reducing cleaning frequency and maintenance costs, while its durable nanocoating withstands environmental wear and UV exposure. Photochromic glass requires minimal maintenance as it self-adjusts to light conditions, but frequent exposure to intense UV rays can degrade its performance over time, necessitating occasional replacement or recalibration. Both glasses enhance smart window functionality, but superhydrophobic glass generally provides longer-lasting durability and lower upkeep in harsh climates.
Cost Analysis
Superhydrophobic glass typically incurs higher initial costs due to advanced nanocoating technology designed for water and dirt repellency, increasing fabrication expenses for smart windows. Photochromic glass demands moderate investment as it involves integrating light-sensitive molecules, balancing material costs with functionality for controlling light transmission and energy savings. Long-term cost analysis favors photochromic glass for reduced maintenance and energy bills, while superhydrophobic glass reduces cleaning frequency but may require specialized coatings replacement, impacting total cost of ownership.
Applications and Best Use Cases
Superhydrophobic glass excels in smart window applications requiring self-cleaning and water-repellent properties, making it ideal for high-rise buildings, automotive windshields, and outdoor solar panels where maintenance reduction and clear visibility are crucial. Photochromic glass is best suited for environments demanding dynamic light control and UV protection, such as residential and commercial windows that adapt to changing sunlight conditions to enhance energy efficiency and occupant comfort. Combining these technologies can optimize smart windows for both environmental resilience and adaptive daylight management in diverse architectural applications.
Future Trends in Smart Window Glass Technologies
Superhydrophobic glass enhances smart windows by offering self-cleaning and anti-fogging properties, improving durability and reducing maintenance costs. Photochromic glass dynamically adjusts transparency based on light intensity, optimizing energy efficiency and occupant comfort in buildings. Future trends in smart window technologies integrate these features with advanced materials and IoT connectivity to create adaptive, energy-saving facades for sustainable architecture.
Infographic: Superhydrophobic glass vs Photochromic glass for Smart window
 azmater.com
azmater.com