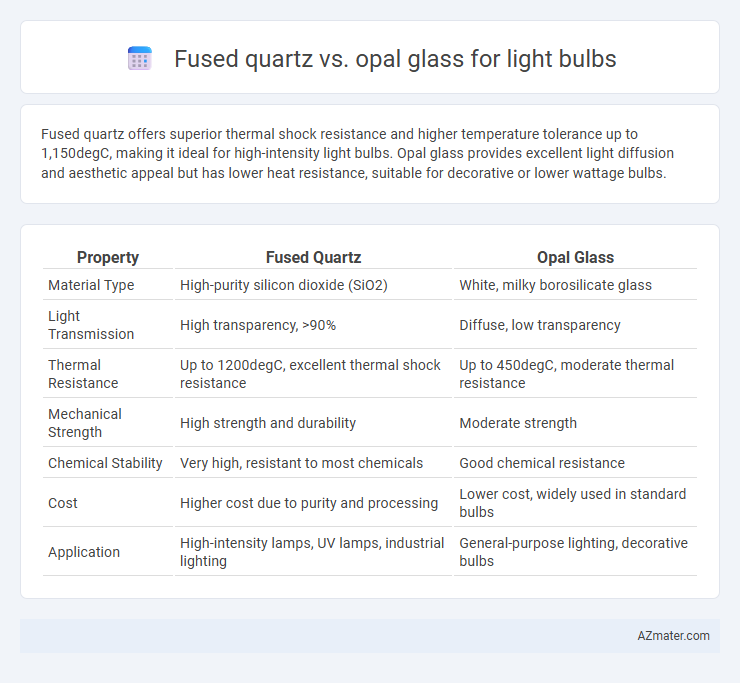
Fused quartz offers superior thermal shock resistance and higher temperature tolerance up to 1,150degC, making it ideal for high-intensity light bulbs. Opal glass provides excellent light diffusion and aesthetic appeal but has lower heat resistance, suitable for decorative or lower wattage bulbs.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fused Quartz | Opal Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | High-purity silicon dioxide (SiO2) | White, milky borosilicate glass |
| Light Transmission | High transparency, >90% | Diffuse, low transparency |
| Thermal Resistance | Up to 1200degC, excellent thermal shock resistance | Up to 450degC, moderate thermal resistance |
| Mechanical Strength | High strength and durability | Moderate strength |
| Chemical Stability | Very high, resistant to most chemicals | Good chemical resistance |
| Cost | Higher cost due to purity and processing | Lower cost, widely used in standard bulbs |
| Application | High-intensity lamps, UV lamps, industrial lighting | General-purpose lighting, decorative bulbs |
Introduction to Fused Quartz and Opal Glass
Fused quartz is a high-purity silica glass known for its exceptional thermal stability, high melting point, and excellent resistance to thermal shock, making it ideal for light bulbs operating under extreme temperature conditions. Opal glass, composed primarily of borosilicate with added opacifying agents, provides a diffused light output and superior aesthetic qualities due to its milky, translucent appearance. Both materials offer distinct advantages in light bulb manufacturing, with fused quartz excelling in durability and heat resistance while opal glass enhances light diffusion and visual comfort.
Material Composition: Fused Quartz vs Opal Glass
Fused quartz consists primarily of pure silicon dioxide (SiO2) with a high purity level exceeding 99.9%, offering exceptional thermal and optical properties ideal for high-temperature light bulb applications. Opal glass is a type of soda-lime glass mixed with opacifying agents such as titanium dioxide or tin oxide to create its characteristic milky white appearance but has lower thermal resistance compared to fused quartz. The superior chemical purity and thermal stability of fused quartz enable better performance in intense lighting environments, while opal glass provides diffused light with aesthetic appeal but limited durability under extreme heat.
Light Transmission and Diffusion Properties
Fused quartz offers superior light transmission with over 90% clarity, making it ideal for applications requiring maximum brightness and minimal distortion in light bulbs. Opal glass provides enhanced diffusion properties, scattering light evenly to reduce glare and create a softer, more uniform illumination. Selecting fused quartz prioritizes intensity and clarity, while opal glass optimizes light distribution and visual comfort in lighting design.
Thermal Resistance and Heat Management
Fused quartz exhibits superior thermal resistance compared to opal glass, with a melting point above 1600degC and excellent thermal shock resistance, making it ideal for high-heat light bulb applications. Opal glass, while offering diffused light and aesthetic appeal, has a lower thermal tolerance around 600-700degC, limiting its effectiveness in heat management. The enhanced heat resistance of fused quartz ensures longer lifespan and stability under intense operational temperatures, crucial for energy-efficient and durable light bulbs.
Durability and Mechanical Strength
Fused quartz offers superior durability and mechanical strength compared to opal glass, with a higher resistance to thermal shock and mechanical stress, making it ideal for high-intensity light bulb applications. Opal glass, while providing better diffusion and aesthetic qualities, is more prone to cracking and breaking under rapid temperature changes or physical impact. The inherent structural integrity of fused quartz ensures longer lifespan and reliability in demanding lighting environments.
Aesthetic Differences in Lighting
Fused quartz offers superior light transmission with minimal color distortion, resulting in a cooler, cleaner illumination that enhances the crispness of light bulbs. Opal glass diffuses light more evenly, producing a softer, warmer glow that reduces glare and creates a more inviting atmosphere. The choice between fused quartz and opal glass significantly impacts the mood and visual appeal of lighting fixtures in interior design.
Cost Comparison and Availability
Fused quartz offers superior thermal stability and durability but comes at a higher cost compared to opal glass, making it less economical for large-scale light bulb production. Opal glass is widely available, more affordable, and provides good diffusion for light bulbs, which benefits mass-market applications. Cost and availability factors often drive manufacturers to choose opal glass for budget-friendly lighting, while fused quartz is reserved for high-performance or specialized uses.
Applications in Modern Light Bulb Design
Fused quartz and opal glass serve distinct roles in modern light bulb design due to their unique material properties. Fused quartz offers exceptional thermal resistance and UV transparency, making it ideal for high-intensity and UV light bulbs used in industrial and medical applications. Opal glass provides diffuse light distribution with a soft glow, enhancing aesthetic appeal and reducing glare in residential and commercial lighting fixtures.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Fused quartz exhibits superior environmental sustainability due to its high thermal resistance, durability, and recyclability, resulting in longer-lasting light bulbs with reduced waste compared to opal glass. Opal glass, while offering effective light diffusion, generally has a lower heat tolerance and shorter lifespan, leading to more frequent replacements and increased resource consumption. Manufacturing fused quartz involves higher energy input but yields products with enhanced durability, reducing overall environmental impact through extended use cycles.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Lighting Needs
Fused quartz offers exceptional thermal shock resistance and high UV transmission, making it ideal for high-intensity and industrial light bulbs requiring durability and efficiency. Opal glass provides a diffused light output with a softer glow, suitable for decorative and ambient lighting applications where aesthetics and glare reduction are important. Selecting the right glass depends on balancing the need for heat resistance, light diffusion, and the specific lighting environment.
Infographic: Fused quartz vs Opal glass for Light bulb
 azmater.com
azmater.com