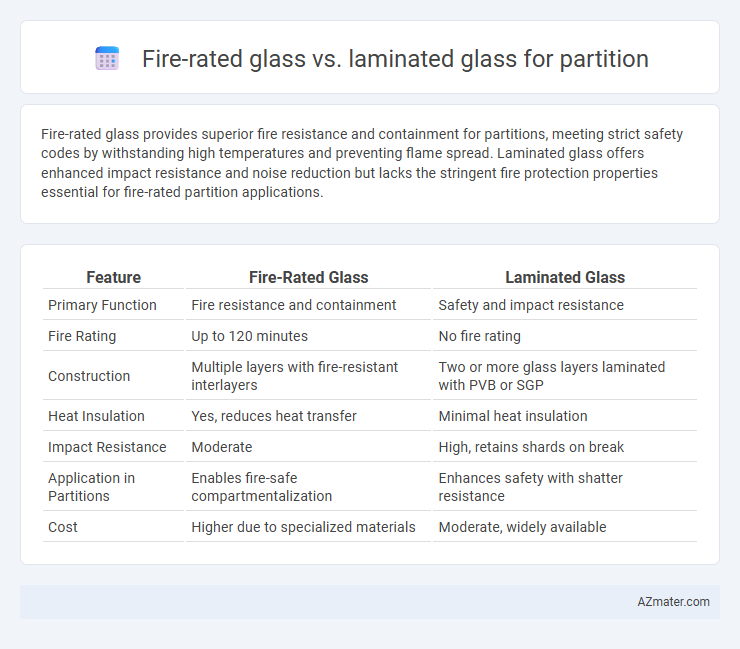
Fire-rated glass provides superior fire resistance and containment for partitions, meeting strict safety codes by withstanding high temperatures and preventing flame spread. Laminated glass offers enhanced impact resistance and noise reduction but lacks the stringent fire protection properties essential for fire-rated partition applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Fire-Rated Glass | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Fire resistance and containment | Safety and impact resistance |
| Fire Rating | Up to 120 minutes | No fire rating |
| Construction | Multiple layers with fire-resistant interlayers | Two or more glass layers laminated with PVB or SGP |
| Heat Insulation | Yes, reduces heat transfer | Minimal heat insulation |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate | High, retains shards on break |
| Application in Partitions | Enables fire-safe compartmentalization | Enhances safety with shatter resistance |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized materials | Moderate, widely available |
Introduction to Fire-Rated and Laminated Glass Partitions
Fire-rated glass partitions are engineered to withstand high temperatures and prevent the spread of fire and smoke, meeting specific safety standards such as UL 9 or BS 476. Laminated glass partitions consist of multiple layers of glass bonded with a polymer interlayer, providing enhanced security, sound insulation, and impact resistance without fire protection. Choosing between fire-rated and laminated glass depends on the building's safety requirements, regulatory compliance, and desired aesthetic or functional properties.
Understanding Fire-Rated Glass: Features and Applications
Fire-rated glass is engineered to withstand high temperatures and prevent the spread of flames and smoke, making it essential for safety in commercial and residential partitions. Its unique composition includes multiple layers bonded with intumescent interlayers that expand when exposed to heat, maintaining structural integrity during a fire. Commonly used in fire doors, walls, and partitions, fire-rated glass meets strict building codes and enhances occupant protection while allowing natural light.
Exploring Laminated Glass: Composition and Uses
Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded with one or more interlayers, typically polyvinyl butyral (PVB), providing enhanced safety and sound insulation. It is widely used in partitions for its ability to hold shards together upon impact, reducing injury risks while offering design flexibility and UV protection. Unlike fire-rated glass, laminated glass prioritizes security and aesthetics over fire resistance, making it ideal for office spaces and commercial interiors where safety and visibility are essential.
Key Differences: Fire-Rated vs Laminated Glass
Fire-rated glass is specifically engineered to withstand high temperatures and prevent the spread of fire for a designated period, typically ranging from 20 to 120 minutes, making it essential for safety in commercial buildings. Laminated glass consists of two or more layers of glass bonded together with a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer, offering enhanced impact resistance and sound insulation but lacking significant fire resistance. The key difference lies in fire-rated glass's ability to contain flames and heat, whereas laminated glass provides durability and security without fire protection certification.
Safety and Compliance Standards
Fire-rated glass for partitions offers superior protection by withstanding high temperatures and preventing the spread of flames and smoke, meeting stringent UL 9 and BS 476 safety standards. Laminated glass, while providing enhanced impact resistance and noise reduction, primarily focuses on shatter resistance rather than fire containment, complying with safety standards like EN 356 for security glazing. Selecting fire-rated glass ensures compliance with building codes for fire safety, whereas laminated glass supports overall occupant protection through durability and structural integrity.
Performance in Fire and Impact Resistance
Fire-rated glass offers superior fire performance by withstanding high temperatures and preventing the spread of flames and smoke for up to 120 minutes, meeting stringent building safety codes. Laminated glass provides excellent impact resistance due to its interlayer that holds glass fragments together upon breakage, enhancing security and occupant protection. For partitions requiring both fire safety and impact durability, fire-rated laminated glass combines these benefits, ensuring structural integrity and safety during fire incidents and physical impacts.
Aesthetics and Acoustic Properties
Fire-rated glass offers superior heat resistance and safety compliance while maintaining clear visibility, ideal for partitions in commercial spaces requiring stringent fire codes; its aesthetic appeal is modern but often slightly tinted or textured to enhance fire performance. Laminated glass excels in acoustic insulation due to its inner PVB interlayer that dampens sound transmission, providing a quieter environment with sleek, transparent aesthetics suited for office partitions and conference rooms. Both glass types enhance design flexibility, but laminated glass typically prioritizes sound control and visual clarity, whereas fire-rated glass balances safety with aesthetic transparency.
Installation Requirements and Considerations
Fire-rated glass requires precise installation within fire-resistant frames to maintain its integrity under high temperatures, complying with strict building codes and standards such as UL 10B and NFPA 80. Laminated glass installation demands careful sealing and structural support to ensure safety and sound insulation but lacks the specialized fireproof framing necessary for fire-rated applications. Proper selection depends on assessing fire safety regulations, installation complexity, and the intended use of partitions in commercial or residential spaces.
Cost Comparison and Maintenance Needs
Fire-rated glass typically costs 50-70% more than laminated glass due to its specialized materials and certification standards designed to withstand high temperatures and prevent fire spread. Maintenance for fire-rated glass involves regular inspections to ensure integrity and compliance with safety regulations, whereas laminated glass requires less frequent checks focused mainly on surface damage and delamination risks. Choosing fire-rated glass increases upfront investment and ongoing compliance costs, while laminated glass offers lower initial expenses and simpler maintenance for standard partition needs.
Choosing the Right Glass Partition for Your Project
Fire-rated glass offers superior heat resistance and smoke containment, making it ideal for partitions in high-risk areas where fire safety codes are strict. Laminated glass provides enhanced strength and sound insulation but lacks the same fire resistance level, best suited for office or commercial spaces prioritizing security and noise control. Selecting the right glass partition depends on project requirements such as fire safety standards, acoustic performance, and structural durability.
Infographic: Fire-rated glass vs Laminated glass for Partition
 azmater.com
azmater.com