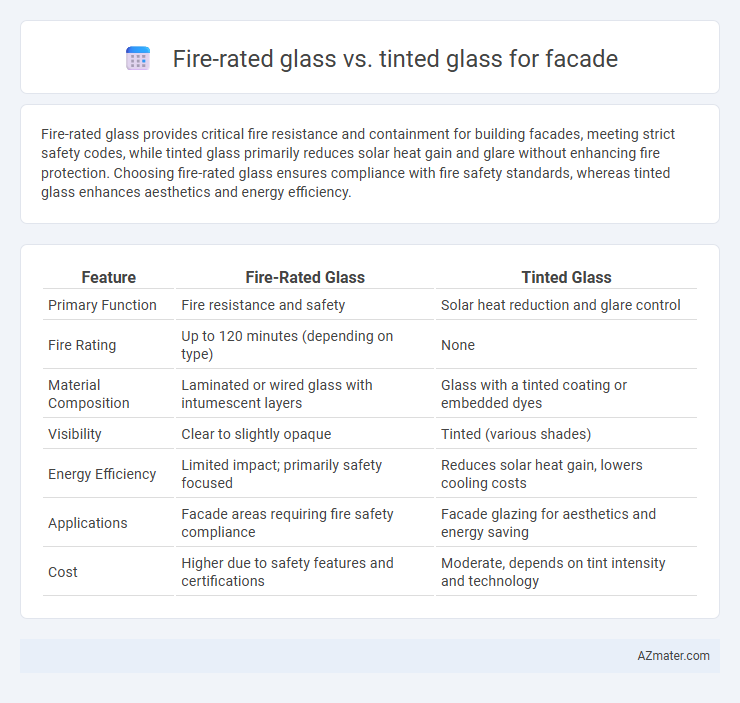
Fire-rated glass provides critical fire resistance and containment for building facades, meeting strict safety codes, while tinted glass primarily reduces solar heat gain and glare without enhancing fire protection. Choosing fire-rated glass ensures compliance with fire safety standards, whereas tinted glass enhances aesthetics and energy efficiency.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Fire-Rated Glass | Tinted Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Fire resistance and safety | Solar heat reduction and glare control |
| Fire Rating | Up to 120 minutes (depending on type) | None |
| Material Composition | Laminated or wired glass with intumescent layers | Glass with a tinted coating or embedded dyes |
| Visibility | Clear to slightly opaque | Tinted (various shades) |
| Energy Efficiency | Limited impact; primarily safety focused | Reduces solar heat gain, lowers cooling costs |
| Applications | Facade areas requiring fire safety compliance | Facade glazing for aesthetics and energy saving |
| Cost | Higher due to safety features and certifications | Moderate, depends on tint intensity and technology |
Introduction to Architectural Facade Glass
Fire-rated glass is engineered to withstand high temperatures and prevent the spread of flames and smoke, making it essential for safety in architectural facades. Tinted glass primarily serves to reduce solar heat gain and glare, enhancing energy efficiency and occupant comfort while offering aesthetic appeal. Selecting between fire-rated and tinted glass depends on building code requirements and design priorities for facade performance and safety.
What is Fire-Rated Glass?
Fire-rated glass is specially engineered to withstand high temperatures and prevent the spread of flames and smoke during a fire, ensuring safety and compliance with building regulations in facade applications. Unlike tinted glass, which primarily serves aesthetic and solar control purposes by reducing glare and heat transmission, fire-rated glass incorporates intumescent layers or ceramic materials that maintain integrity and insulation under fire exposure. This type of glass is essential in protecting occupants and property in commercial and residential buildings by providing critical fire resistance without compromising natural light.
Understanding Tinted Glass
Tinted glass for facades reduces solar heat gain and glare while enhancing privacy through its colored coatings, improving energy efficiency in buildings. Unlike fire-rated glass designed to withstand high temperatures and prevent fire spread, tinted glass primarily offers aesthetic appeal and UV protection without fire resistance capabilities. Understanding tinted glass involves evaluating its light transmission properties, color options, and impact on building comfort and facade design.
Key Performance Differences
Fire-rated glass provides critical resistance to heat and flames, maintaining structural integrity and slowing fire spread for a specified duration, typically 20 to 120 minutes, while tinted glass primarily reduces solar heat gain and glare without offering fire protection. Fire-rated glass often incorporates multiple layers or intumescent materials to withstand high temperatures, whereas tinted glass utilizes coatings or films that absorb or reflect sunlight to improve energy efficiency and occupant comfort. The key performance difference lies in fire-rated glass's compliance with stringent fire safety standards (e.g., NFPA 257, EN 13501-2) versus tinted glass's focus on solar control and aesthetics for facade applications.
Fire Safety and Building Codes
Fire-rated glass is specifically engineered to provide a barrier against flames, heat, and smoke, meeting stringent fire safety standards such as ASTM E119 or UL 972, essential for compliance with building codes in high-risk areas of a facade. Tinted glass, while offering solar control and glare reduction, does not offer fire resistance or meet fire safety regulations, making it unsuitable for areas requiring fire-rated glazing. Choosing fire-rated glass ensures adherence to fire safety codes and protects occupants and property by maintaining compartmentalization during a fire event.
Aesthetic and Design Considerations
Fire-rated glass enhances facade safety while maintaining a clear, unobstructed view, ideal for modern, minimalistic designs emphasizing transparency and light transmission. Tinted glass offers a customizable aesthetic by reducing glare and controlling solar heat gain, available in various shades that complement architectural styles and color schemes. Designers balance fire protection requirements with energy efficiency and visual appeal by integrating fire-rated glass with selective tinting or combining tinted sections for dynamic facade compositions.
Energy Efficiency and UV Protection
Fire-rated glass for facades offers superior energy efficiency through its ability to contain heat and prevent fire spread, while also providing effective UV protection to maintain interior comfort and reduce fading of furnishings. Tinted glass enhances energy efficiency by minimizing solar heat gain and glare, significantly lowering cooling costs, and it blocks a substantial portion of harmful UV rays. Selecting the appropriate glass type depends on balancing fire safety standards with desired levels of solar control and UV protection for optimal facade performance.
Cost Comparison: Fire-Rated vs Tinted Glass
Fire-rated glass generally costs significantly more than tinted glass due to its specialized manufacturing process, incorporating multiple layers and intumescent materials to withstand high temperatures and prevent fire spread. Tinted glass, designed primarily for solar control and aesthetic purposes, involves simpler production methods and is therefore more affordable, typically costing 20-50% less than fire-rated alternatives. When budgeting for facade projects, the added expense of fire-rated glass is justified by its critical safety benefits and code compliance, whereas tinted glass offers cost-effective energy savings and glare reduction without fire protection.
Installation and Maintenance Factors
Fire-rated glass requires specialized installation techniques, including precise framing and sealing to ensure compliance with fire safety standards, whereas tinted glass installation is generally more straightforward, focusing on aesthetics and UV protection. Maintenance of fire-rated glass involves regular inspections for integrity and adherence to fire codes, with any damage necessitating immediate repair or replacement to maintain safety performance. Tinted glass maintenance primarily addresses cleaning and potential film degradation over time without stringent regulatory requirements.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Facade
Fire-rated glass offers enhanced safety by withstanding high temperatures and preventing fire spread, making it essential for facades requiring strict fire codes compliance. Tinted glass primarily reduces solar heat gain and glare, improving energy efficiency and occupant comfort without fire protection capabilities. Selecting the right glass depends on balancing safety requirements and energy performance goals, with fire-rated glass prioritized in high-risk zones and tinted glass favored for its shading benefits.
Infographic: Fire-rated glass vs Tinted glass for Facade
 azmater.com
azmater.com