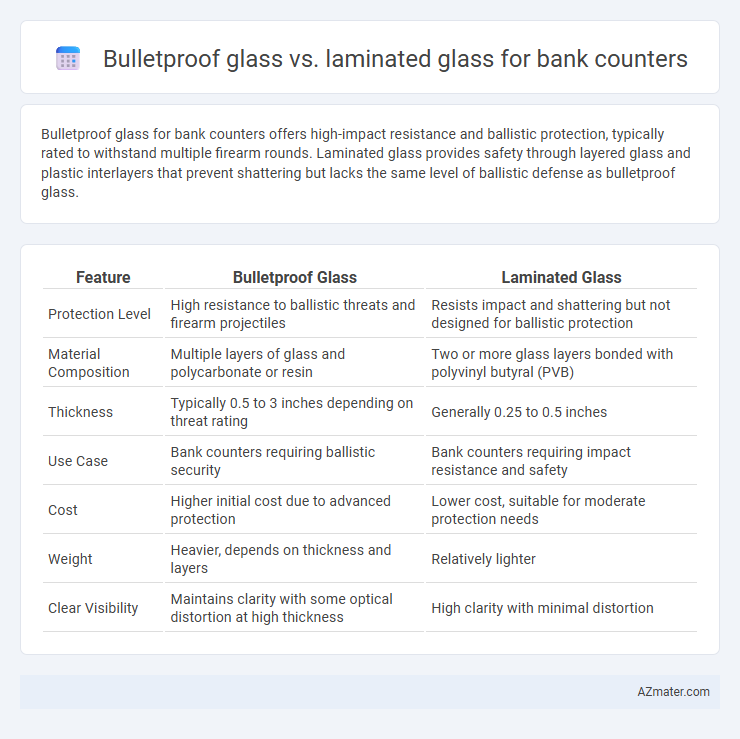
Bulletproof glass for bank counters offers high-impact resistance and ballistic protection, typically rated to withstand multiple firearm rounds. Laminated glass provides safety through layered glass and plastic interlayers that prevent shattering but lacks the same level of ballistic defense as bulletproof glass.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bulletproof Glass | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Protection Level | High resistance to ballistic threats and firearm projectiles | Resists impact and shattering but not designed for ballistic protection |
| Material Composition | Multiple layers of glass and polycarbonate or resin | Two or more glass layers bonded with polyvinyl butyral (PVB) |
| Thickness | Typically 0.5 to 3 inches depending on threat rating | Generally 0.25 to 0.5 inches |
| Use Case | Bank counters requiring ballistic security | Bank counters requiring impact resistance and safety |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to advanced protection | Lower cost, suitable for moderate protection needs |
| Weight | Heavier, depends on thickness and layers | Relatively lighter |
| Clear Visibility | Maintains clarity with some optical distortion at high thickness | High clarity with minimal distortion |
Introduction to Bank Counter Security Glass
Bank counter security glass, essential for safeguarding employees and assets, primarily uses bulletproof glass or laminated glass. Bulletproof glass offers multiple layers of polycarbonate and glass designed to withstand firearm impacts, ensuring high-level ballistic protection. Laminated glass, composed of bonded glass layers with interlayers like PVB, provides strong resistance against forced entry and shattering while maintaining clear visibility and sound insulation.
What is Bulletproof Glass?
Bulletproof glass, also known as ballistic glass, is a multi-layered material designed to resist high-velocity projectiles, providing maximum security for bank counters against armed attacks. It combines layers of polycarbonate and tempered glass bonded under heat and pressure to absorb and disperse the impact energy of bullets. This technology offers superior protection compared to laminated glass, which primarily guards against forced entry and impact rather than ballistic threats.
What is Laminated Glass?
Laminated glass is a safety glass composed of two or more glass layers bonded together with an interlayer, typically polyvinyl butyral (PVB), which holds the layers in place even when shattered. This feature makes laminated glass highly effective for bank counters by preventing glass shards from causing injury and providing a clear barrier against theft or attack. Unlike bulletproof glass, laminated glass offers impact resistance and security at a lower cost but may not withstand high-velocity ballistic threats.
Key Differences Between Bulletproof and Laminated Glass
Bulletproof glass for bank counters is engineered with multiple layers of polycarbonate and laminated glass, designed to withstand high-velocity firearm impacts and prevent penetration. Laminated glass primarily consists of two or more layers of glass bonded with a plastic interlayer, which offers basic shatter resistance and protection against forced entry but is not rated for ballistic resistance. The key differences lie in bulletproof glass's certified ballistic protection standards versus laminated glass's emphasis on durability and safety against breakage without ballistic capabilities.
Security Performance Comparison
Bulletproof glass offers superior resistance to high-velocity projectiles and explosive impacts compared to laminated glass, making it ideal for bank counters where maximum security is crucial. Laminated glass provides effective protection against forced entry through impact and prevents glass shards from causing injuries, but it generally cannot withstand sustained ballistic attacks as bulletproof glass can. For bank counters requiring advanced security, bulletproof glass is the preferred choice due to its multi-layered composition of polycarbonate and glass, delivering enhanced ballistic performance and preventing penetration.
Cost Analysis: Bulletproof vs Laminated Glass
Bulletproof glass typically costs significantly more than laminated glass due to its multi-layered construction and higher impact resistance, making it a more expensive option for bank counters. Laminated glass offers a budget-friendly alternative with adequate security against lower-impact threats but may require thicker layers or additional treatments to match bullet resistance. Banks must weigh the higher upfront expense of bulletproof glass against potential long-term savings in safety and liability reduction.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Bulletproof glass for bank counters requires professional installation to ensure maximum protection against ballistic threats, often involving heavier and thicker panels that demand reinforced framing. Laminated glass is easier to install due to its lighter weight and typically uses standard frames, offering sufficient resistance to physical attacks but less ballistic protection. Maintenance for bulletproof glass involves regular inspections for cracks or impact damage to maintain security integrity, whereas laminated glass requires less frequent checks and simple cleaning to preserve transparency and durability.
Durability and Lifespan Factors
Bulletproof glass for bank counters offers superior durability with multi-layered construction of polycarbonate and glass, providing high resistance to ballistic impacts and forced entry attempts. Laminated glass, composed of bonded glass layers with a plastic interlayer, delivers strong resistance to shattering and improves safety, but typically has lower impact resistance than bulletproof glass. Lifespan for bulletproof glass often exceeds 15 years under normal conditions due to its robust materials, while laminated glass may require replacement sooner when exposed to frequent impacts or harsh environmental factors.
Regulatory Standards and Compliance
Bulletproof glass for bank counters must comply with UL 752 standards, ensuring resistance to specific ballistic threats, while laminated glass adheres to ANSI Z97.1 and CPSC 16 CFR 1201 standards focused on impact resistance and shatter prevention. Regulatory compliance for bank counters requires bulletproof glass to meet strict ballistic resistance certifications that surpass the safety thresholds of laminated glass, which primarily provides protection against forced entry and fragmentation. Selection depends on security protocols specified by regulatory bodies like the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and local banking security regulations.
Choosing the Best Glass for Bank Counters
Bulletproof glass provides superior ballistic resistance, making it ideal for bank counters requiring high security against armed threats, while laminated glass offers enhanced impact resistance and shatter control at a lower cost. Selecting the best glass involves assessing threat levels, budget constraints, and desired clarity, with bulletproof glass often preferred for maximum protection and laminated glass suited for general safety and vandal resistance. Both types can be customized in thickness and layering to meet specific security standards and regulatory requirements for bank environments.
Infographic: Bulletproof glass vs Laminated glass for Bank counter
 azmater.com
azmater.com