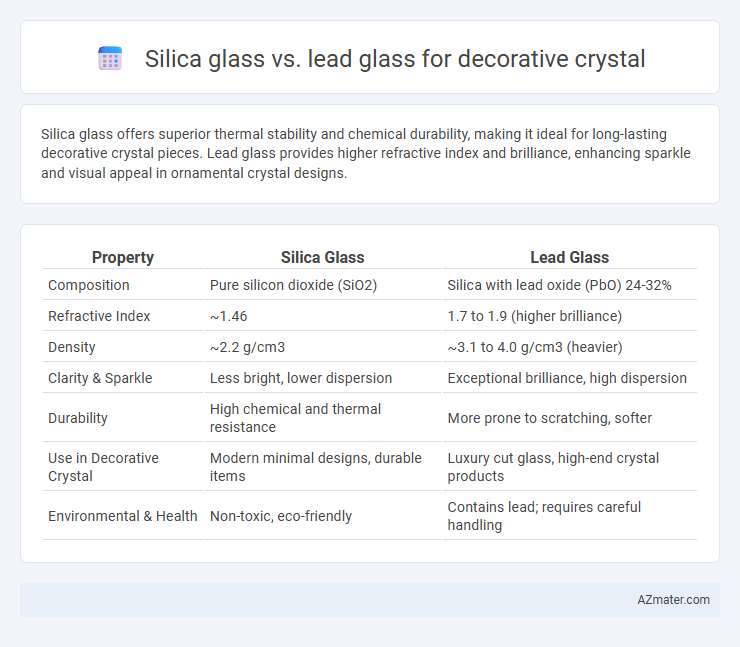
Silica glass offers superior thermal stability and chemical durability, making it ideal for long-lasting decorative crystal pieces. Lead glass provides higher refractive index and brilliance, enhancing sparkle and visual appeal in ornamental crystal designs.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Silica Glass | Lead Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Pure silicon dioxide (SiO2) | Silica with lead oxide (PbO) 24-32% |
| Refractive Index | ~1.46 | 1.7 to 1.9 (higher brilliance) |
| Density | ~2.2 g/cm3 | ~3.1 to 4.0 g/cm3 (heavier) |
| Clarity & Sparkle | Less bright, lower dispersion | Exceptional brilliance, high dispersion |
| Durability | High chemical and thermal resistance | More prone to scratching, softer |
| Use in Decorative Crystal | Modern minimal designs, durable items | Luxury cut glass, high-end crystal products |
| Environmental & Health | Non-toxic, eco-friendly | Contains lead; requires careful handling |
Introduction to Decorative Crystal Glasses
Decorative crystal glasses are primarily classified into silica glass and lead glass, each with distinct properties that influence their appearance and usage. Silica glass, composed mainly of silicon dioxide, offers high durability and clarity but lacks the brilliance and weight characteristic of lead glass. Lead glass contains lead oxide, which increases its refractive index and density, creating a sparkling effect ideal for luxury crystal decorations used in chandeliers and fine glassware.
Composition of Silica Glass vs Lead Glass
Silica glass primarily consists of silicon dioxide (SiO2), offering high chemical purity and thermal stability, while lead glass contains significant lead oxide (PbO) typically between 18% to 40%, enhancing its refractive index and weight. The addition of lead oxide in lead glass increases its density and brilliance, making it popular for decorative crystal applications, whereas pure silica glass is valued for its clarity and resistance to chemical corrosion. Differences in composition directly affect optical properties, with lead glass providing superior sparkle and silica glass excelling in durability.
Physical Properties Comparison
Silica glass offers superior thermal stability and hardness with a Mohs hardness of about 6.5-7, whereas lead glass is softer at around 5-6 due to its lead oxide content. Lead glass features a higher density (around 3.1-3.5 g/cm3) compared to silica glass (about 2.2 g/cm3), resulting in a heavier and more refractive decorative crystal. The refractive index of lead glass (1.7-1.9) surpasses that of silica glass (1.46), enhancing brilliance and sparkle in ornamental applications.
Visual Clarity and Brilliance
Silica glass offers high visual clarity with excellent transmission of light, making it ideal for simple decorative crystal items where purity and subtle elegance are desired. Lead glass, containing lead oxide typically between 24% and 30%, exhibits superior brilliance and sparkle due to its higher refractive index and density, enhancing the light dispersion and creating a dazzling effect. While lead glass is favored for premium decorative crystals for its vibrant sparkle, silica glass remains a durable alternative with clearer transparency and less weight.
Durability and Hardness
Silica glass exhibits superior durability and higher hardness compared to lead glass, making it more resistant to scratches and daily wear in decorative crystal applications. Lead glass, while prized for its brilliance and clarity due to high refractive index, is softer and more prone to damage from impacts and abrasions. The enhanced chemical stability of silica glass also ensures longer-lasting luster and structural integrity in ornamental crystal pieces.
Safety and Toxicity Concerns
Silica glass, primarily composed of silicon dioxide, is non-toxic and safe for decorative crystal applications, presenting minimal health risks during manufacturing and use. Lead glass contains significant amounts of lead oxide, which enhances its refractive properties but raises concerns due to lead's toxicity and potential leaching, especially in items used for food or drink. Safety protocols are critical when handling lead glass to minimize lead exposure, whereas silica glass offers a safer alternative with lower environmental and health impacts.
Artistic Flexibility and Workability
Silica glass offers superior artistic flexibility due to its high melting point and chemical stability, allowing intricate designs and detailed engraving without deformation. Lead glass, with its lower melting point and higher refractive index, provides easier workability for cutting and polishing, resulting in brilliant, sparkling finishes ideal for decorative crystals. Artists often select silica glass for complex sculptural forms and lead glass for brilliance and clarity in faceted designs.
Cost and Availability
Silica glass is generally more affordable and readily available for decorative crystal applications due to its abundant raw materials and widespread manufacturing processes. Lead glass, while prized for its brilliance and weight, tends to be more expensive and less accessible because of lead content regulations and higher production costs. Cost-efficiency and broad availability make silica glass a preferred choice for mass-produced decorative crystal products.
Applications in Decorative Arts
Silica glass and lead glass differ significantly in their applications within decorative arts, with lead glass prized for its high refractive index and brilliance that enhances the sparkle and clarity of decorative crystal pieces such as chandeliers, vases, and intricate glass sculptures. Silica glass, known for its durability and chemical resistance, is preferred for modern minimalist designs and outdoor decorative items where structural integrity and weather resistance are essential. The choice between silica and lead glass depends on the desired optical properties and functional requirements, with lead glass favored for luxury and ornate decoration and silica glass for practical and contemporary decorative uses.
Choosing the Right Glass for Decorative Crystals
Silica glass offers high thermal stability and clarity, making it ideal for decorative crystals requiring durability and a pure, clear appearance, while lead glass provides exceptional brilliance and weight due to its higher refractive index and density. Choosing the right glass depends on factors such as desired sparkle, weight, and safety, with lead glass favored for luxurious, sparkling finishes and silica glass preferred for non-toxic, heat-resistant designs. Consider the specific aesthetic and functional needs of the decorative crystal to balance brilliance, clarity, and material properties effectively.
Infographic: Silica glass vs Lead glass for Decorative crystal
 azmater.com
azmater.com