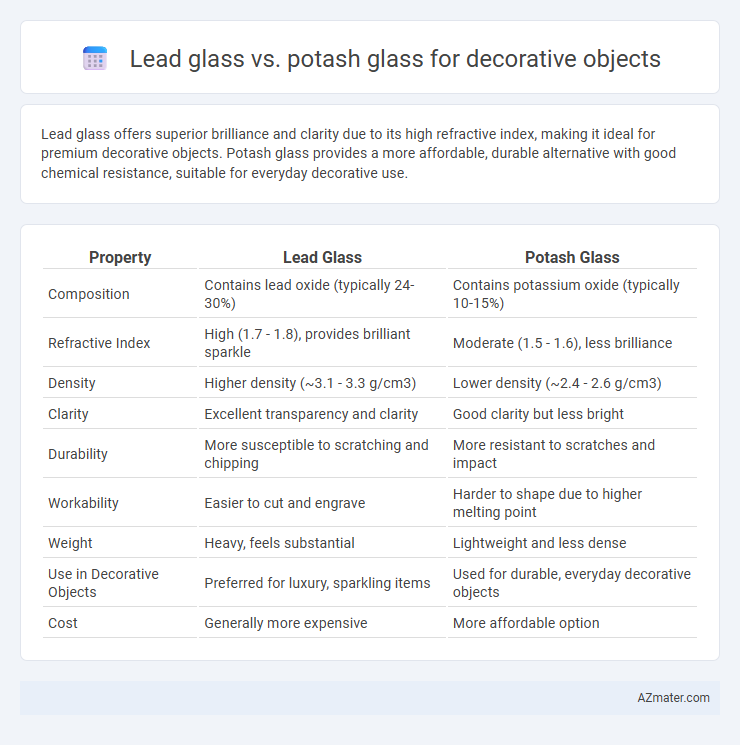
Lead glass offers superior brilliance and clarity due to its high refractive index, making it ideal for premium decorative objects. Potash glass provides a more affordable, durable alternative with good chemical resistance, suitable for everyday decorative use.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Lead Glass | Potash Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Contains lead oxide (typically 24-30%) | Contains potassium oxide (typically 10-15%) |
| Refractive Index | High (1.7 - 1.8), provides brilliant sparkle | Moderate (1.5 - 1.6), less brilliance |
| Density | Higher density (~3.1 - 3.3 g/cm3) | Lower density (~2.4 - 2.6 g/cm3) |
| Clarity | Excellent transparency and clarity | Good clarity but less bright |
| Durability | More susceptible to scratching and chipping | More resistant to scratches and impact |
| Workability | Easier to cut and engrave | Harder to shape due to higher melting point |
| Weight | Heavy, feels substantial | Lightweight and less dense |
| Use in Decorative Objects | Preferred for luxury, sparkling items | Used for durable, everyday decorative objects |
| Cost | Generally more expensive | More affordable option |
Introduction to Decorative Glass: Lead vs Potash
Lead glass offers superior brilliance and clarity due to its high refractive index, making it ideal for luxury decorative objects. Potash glass, rich in potassium oxide, provides enhanced durability and is often preferred for vibrant colors and intricate designs in artistic glassware. Both types serve distinct aesthetic and functional purposes, with lead glass favored for sparkling elegance and potash glass for robust, colorful decor.
Chemical Composition: Lead Glass and Potash Glass Compared
Lead glass contains approximately 18-40% lead oxide (PbO), which enhances its refractive index and brilliance, making it ideal for decorative objects requiring high clarity and sparkle. Potash glass primarily consists of potassium oxide (K2O) combined with silica, providing improved chemical durability and heat resistance but lower optical brilliance compared to lead glass. The distinct chemical compositions influence their physical properties, with lead glass offering superior weight and luster, while potash glass excels in environmental stability and resistance to weathering.
Visual Appeal: Clarity and Brilliance Differences
Lead glass exhibits superior clarity and brilliance due to its high refractive index, which enhances light dispersion and creates sparkling visual effects in decorative objects. Potash glass, while offering good transparency, lacks the same level of brightness and depth, resulting in a subtler, less vibrant appearance. The crystalline shine and prismatic colors of lead glass make it a preferred choice for luxury decorative pieces seeking maximum visual impact.
Working Properties: Crafting Potash Glass and Lead Glass
Potash glass offers excellent thermal shock resistance and a lower melting point, making it easier to shape and mold for intricate decorative objects. Lead glass, containing up to 30% lead oxide, provides superior brilliance and clarity with a higher density, but requires careful temperature control during annealing to prevent stress and cracking. Both types demand specific reheating schedules to maintain workability, with potash glass favored for durability and lead glass prized for its aesthetic sparkle in fine craftsmanship.
Strength and Durability: Which Glass Lasts Longer?
Lead glass exhibits higher density and increased refractive index, contributing to superior strength compared to potash glass, which contains potassium oxide but lacks lead's reinforcing properties. The lead content in lead glass enhances its durability and resistance to chipping, making it a preferred choice for long-lasting decorative objects subjected to frequent handling. Potash glass offers moderate strength but is more prone to scratching and breakage over time, resulting in shorter lifespan for high-use decorative items.
Weight and Handling: Practical Considerations
Lead glass is denser and heavier than potash glass, providing a substantial feel that enhances the perceived value of decorative objects. Potash glass is lighter and easier to handle, making it suitable for larger pieces or items that require frequent movement. Choosing between the two depends on balancing the tactile weight against ease of handling for display or use.
Safety Concerns: Toxicity and Environmental Impact
Lead glass contains lead oxide, which poses significant toxicity risks through prolonged exposure or breakage, requiring careful handling and disposal to prevent environmental contamination. Potash glass, made from potassium carbonate, offers a safer alternative with minimal toxic effects, reducing health hazards for both users and manufacturers. The environmental impact of potash glass is lower due to non-toxic components, making it a more sustainable choice for decorative objects.
Suitability for Artistic Techniques: Cutting, Engraving, and Staining
Lead glass offers higher density and brilliance, making it exceptionally suitable for intricate cutting and engraving techniques, enhancing the clarity and depth of decorative objects. Potash glass, with its increased durability and lower cost, supports detailed staining processes but is less ideal for precision cutting due to its comparatively lower refractive index. Artistic applications requiring sharp, reflective surfaces benefit from lead glass, while those prioritizing vibrant coloration and affordability often favor potash glass.
Cost and Availability of Lead and Potash Glass
Lead glass typically costs more due to the higher price of lead oxide and its complex manufacturing process, making it less readily available compared to potash glass. Potash glass is generally more affordable and widely accessible, as it uses potassium carbonate, a more common and less expensive raw material. Cost efficiency and supply stability often make potash glass the preferred choice for decorative objects in budget-conscious markets.
Choosing the Ideal Glass for Your Decorative Objects
Lead glass offers superior clarity and brilliance, making it ideal for decorative objects that require a sparkling, luxurious appearance due to its high refractive index. Potash glass, containing potassium oxide, provides better chemical durability and is more resistant to environmental degradation, ensuring long-lasting decorative pieces. When choosing the ideal glass for your decorative objects, consider lead glass for enhanced visual impact and potash glass for greater strength and durability.
Infographic: Lead glass vs Potash glass for Decorative object
 azmater.com
azmater.com