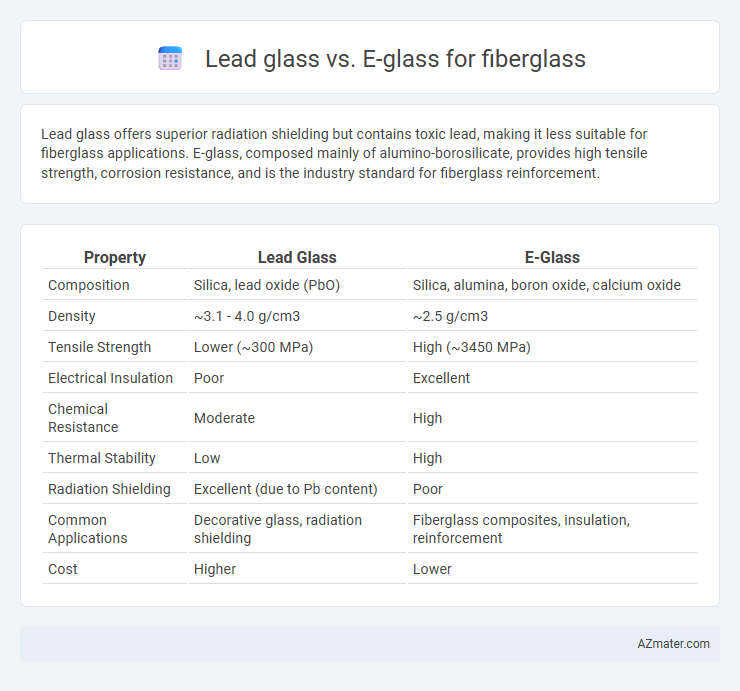
Lead glass offers superior radiation shielding but contains toxic lead, making it less suitable for fiberglass applications. E-glass, composed mainly of alumino-borosilicate, provides high tensile strength, corrosion resistance, and is the industry standard for fiberglass reinforcement.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Lead Glass | E-Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Silica, lead oxide (PbO) | Silica, alumina, boron oxide, calcium oxide |
| Density | ~3.1 - 4.0 g/cm3 | ~2.5 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | Lower (~300 MPa) | High (~3450 MPa) |
| Electrical Insulation | Poor | Excellent |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Thermal Stability | Low | High |
| Radiation Shielding | Excellent (due to Pb content) | Poor |
| Common Applications | Decorative glass, radiation shielding | Fiberglass composites, insulation, reinforcement |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to Lead Glass and E-Glass
Lead glass and E-glass are two distinct types of glass used in fiberglass applications, each offering unique properties tailored to specific industry needs. Lead glass is characterized by its high density and excellent radiation shielding capabilities due to its lead oxide content, making it ideal for medical and nuclear settings. E-glass, or electrical glass, is the most common fiberglass variant known for its high strength, chemical resistance, and electrical insulating properties, widely used in construction, automotive, and electronics industries.
Composition and Material Properties
Lead glass used in fiberglass contains significant amounts of lead oxide, providing high density and excellent radiation shielding but lower mechanical strength and higher brittleness compared to E-glass. E-glass, composed primarily of silica, alumina, and boron oxide, offers superior tensile strength, chemical resistance, and electrical insulation, making it the most common choice for fiberglass reinforcement. The difference in composition directly impacts their material properties, with lead glass favored for radiation protection and E-glass preferred for structural applications requiring durability and toughness.
Manufacturing Processes
Lead glass fibers require specialized manufacturing processes involving high-temperature melting and precise lead oxide incorporation to enhance density and radiation shielding properties. E-glass production utilizes a controlled melting process with aluminum, calcium, and boron oxides, optimized for electrical insulation and mechanical strength in fiberglass applications. The distinct chemical compositions dictate variations in melting temperatures, fiber formation techniques, and post-processing treatments critical to achieving desired performance characteristics.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Lead glass and E-glass exhibit distinct differences in strength and durability for fiberglass applications; E-glass offers higher tensile strength typically around 3.5 GPa compared to lead glass, which has lower mechanical strength due to its composition. E-glass fibers provide superior resistance to chemical degradation and environmental factors, enhancing longevity in structural composites. Lead glass, while beneficial for radiation shielding, lacks the robustness of E-glass in mechanical performance and long-term durability under stress.
Weight Differences and Implications
Lead glass composites exhibit a higher density compared to E-glass fibers, resulting in increased weight for structures using lead glass reinforcement. E-glass fibers offer a lightweight alternative with densities around 2.54 g/cm3, whereas lead glass composites can exceed 3 g/cm3, impacting overall load and handling characteristics. This weight difference influences applications where weight savings are critical, such as in aerospace and automotive components, favoring E-glass for its strength-to-weight advantages and lead glass where radiation shielding is required.
Optical and Electrical Characteristics
Lead glass offers superior optical clarity with high refractive indices and excellent light transmission, making it ideal for applications requiring precise optical performance. E-glass, known for its electrical insulation properties, provides high dielectric strength and low electrical conductivity, ensuring effective electrical isolation in fiberglass composites. While lead glass excels in optical applications, E-glass is predominantly used for its electrical insulation and mechanical strength in industrial fiberglass products.
Applications in Industry
Lead glass, known for its high density and excellent radiation shielding properties, is primarily used in specialized industrial applications such as nuclear facilities and medical imaging equipment to protect against gamma and X-rays. E-glass, characterized by its high tensile strength, chemical resistance, and low dielectric constant, is the predominant choice for general fiberglass manufacturing, including automotive components, aerospace structures, and construction materials. The industrial preference shifts between lead glass for radiation safety and E-glass for mechanical reinforcement and insulation.
Cost Analysis and Availability
Lead glass fibers are significantly more expensive than E-glass due to their specialized lead oxide content, which increases raw material and manufacturing costs. E-glass fibers dominate the fiberglass market owing to their cost-effectiveness and widespread availability from multiple global suppliers. The lower production costs and abundant sourcing options make E-glass the preferred choice for most commercial fiberglass applications.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Lead glass in fiberglass manufacturing poses significant environmental and health risks due to the toxic nature of lead, which can leach into ecosystems and cause hazardous exposure for workers during production and disposal. E-glass, composed primarily of alumino-borosilicate, offers a safer alternative with lower environmental impact and non-toxic properties, making it more suitable for sustainable fiberglass applications. Regulatory standards increasingly favor E-glass because it reduces occupational health hazards and limits harmful emissions throughout the fiberglass lifecycle.
Choosing the Right Fiberglass: Lead Glass vs. E-Glass
Choosing the right fiberglass between lead glass and E-glass depends on the application requirements, as lead glass offers superior radiation shielding properties due to its high lead content, making it ideal for medical and nuclear environments. E-glass, composed primarily of silica and alumina oxides, provides excellent electrical insulation, high tensile strength, and cost-effectiveness, widely used in aerospace, construction, and marine industries. Evaluating factors like mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and radiation protection ensures optimal performance tailored to specific industry needs.
Infographic: Lead glass vs E-glass for Fiberglass
 azmater.com
azmater.com