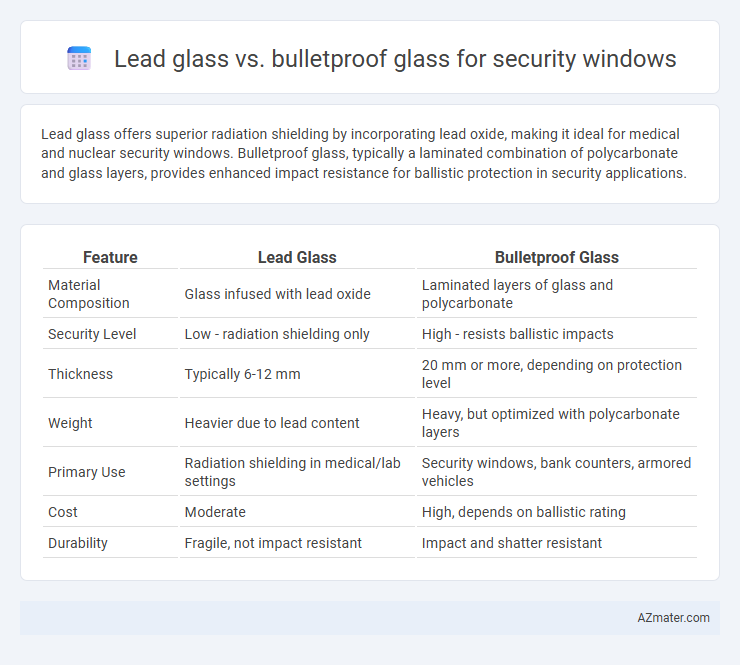
Lead glass offers superior radiation shielding by incorporating lead oxide, making it ideal for medical and nuclear security windows. Bulletproof glass, typically a laminated combination of polycarbonate and glass layers, provides enhanced impact resistance for ballistic protection in security applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Lead Glass | Bulletproof Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Glass infused with lead oxide | Laminated layers of glass and polycarbonate |
| Security Level | Low - radiation shielding only | High - resists ballistic impacts |
| Thickness | Typically 6-12 mm | 20 mm or more, depending on protection level |
| Weight | Heavier due to lead content | Heavy, but optimized with polycarbonate layers |
| Primary Use | Radiation shielding in medical/lab settings | Security windows, bank counters, armored vehicles |
| Cost | Moderate | High, depends on ballistic rating |
| Durability | Fragile, not impact resistant | Impact and shatter resistant |
Introduction to Security Window Materials
Lead glass offers excellent radiation shielding properties, commonly used in medical and nuclear environments, but lacks the impact resistance required for security windows. Bulletproof glass, composed of laminated layers of glass and polycarbonate, provides high impact resistance designed to withstand ballistic threats and forced entry. Choosing between lead glass and bulletproof glass depends on the primary security need, whether radiation protection or ballistic resistance.
Composition of Lead Glass
Lead glass, also known as lead crystal, contains a high percentage of lead oxide typically ranging from 24% to 30%, which enhances its density and refractive index, providing better clarity and brilliance compared to standard glass. Bulletproof glass, on the other hand, is composed of multiple layers of laminated polycarbonate and glass, designed to absorb and disperse the energy from ballistic impacts rather than relying on lead content. The significant lead oxide content in lead glass contributes to its weight and radiation shielding properties, making it suitable for specific security applications but less effective against high-velocity projectiles than bulletproof glass.
Composition of Bulletproof Glass
Bulletproof glass for security windows is typically composed of multiple layers of laminated glass and polycarbonate or other plastics, engineered to absorb and disperse the kinetic energy of bullets. Unlike lead glass, which contains lead oxide to enhance density and radiation shielding, bulletproof glass emphasizes layered construction with polymer interlayers to prevent penetration and fragmentation. The combination of glass and plastic layers creates a durable, transparent barrier capable of withstanding high-velocity impacts, making it essential for secure environments.
Key Security Features of Lead Glass
Lead glass offers exceptional radiation shielding and enhanced threat detection capabilities due to its high density and atomic number, making it ideal for security windows in sensitive environments. Unlike bulletproof glass, lead glass can block X-rays and gamma rays, providing a unique layer of protection against radiation-based threats. Its ability to maintain optical clarity while offering radiation attenuation ensures security without compromising visibility or aesthetics.
Key Security Features of Bulletproof Glass
Bulletproof glass offers enhanced security features compared to lead glass, primarily due to its multi-layered construction of polycarbonate and laminated glass that provides high resistance to ballistic impacts and forced entry. Unlike lead glass, which primarily serves radiation shielding purposes, bulletproof glass is designed to absorb and dissipate the energy from projectiles, preventing penetration and reducing risk of injury. Key security features include its ability to withstand various calibers of gunfire, resistance to shattering, and durability that meets ASTM standards for ballistic protection in security windows.
Protection Levels: Lead Glass vs Bulletproof Glass
Lead glass provides excellent protection against radiation, making it ideal for environments requiring nuclear or X-ray shielding, but offers limited resistance to physical impact. Bulletproof glass is engineered with multiple layers of laminated glass and polycarbonate materials, delivering superior ballistic protection capable of stopping bullets from handguns and rifles. For security windows, bulletproof glass ensures higher levels of defense against forced entry and projectile threats, whereas lead glass focuses primarily on radiation shielding rather than physical security.
Applications in Security Infrastructure
Lead glass provides radiation shielding in security infrastructure, commonly used in medical and nuclear facilities to protect personnel from harmful radiation. Bulletproof glass, made from laminated polycarbonate and glass layers, is essential in security windows for banks, government buildings, and armored vehicles to resist ballistic impacts. Both materials enhance safety, but bulletproof glass prioritizes impact resistance, while lead glass focuses on radiation protection.
Cost Comparison: Lead Glass vs Bulletproof Glass
Lead glass for security windows generally costs less than bulletproof glass, making it a more budget-friendly option for moderate protection needs. Bulletproof glass, composed of multiple layers of laminated polycarbonate and glass, demands higher manufacturing and installation expenses due to its superior impact resistance and durability. While lead glass offers radiation shielding benefits at a lower price point, bulletproof glass justifies its higher cost with enhanced ballistic protection and longevity.
Durability and Maintenance Considerations
Lead glass offers moderate durability with enhanced radiation shielding but is prone to surface scratches and requires careful handling to avoid damage. Bulletproof glass, composed of multiple layers of laminated polycarbonate and glass, provides superior impact resistance and longevity under high-stress conditions. Maintenance for bulletproof glass focuses on regular inspections for delamination and stress fractures, while lead glass demands more delicate cleaning procedures to preserve its structural integrity.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Security Needs
Selecting between lead glass and bulletproof glass for security windows depends on the specific protection required; lead glass excels in radiation shielding due to its high-density lead content, making it ideal for medical or nuclear applications. Bulletproof glass, composed of multiple laminated layers of polycarbonate and glass, offers ballistic resistance to withstand firearm impacts, suitable for military, law enforcement, and secure commercial settings. Evaluate threat levels, transparency needs, and regulatory compliance to determine the optimal glass type for effective security and visibility.
Infographic: Lead glass vs Bulletproof glass for Security window
 azmater.com
azmater.com