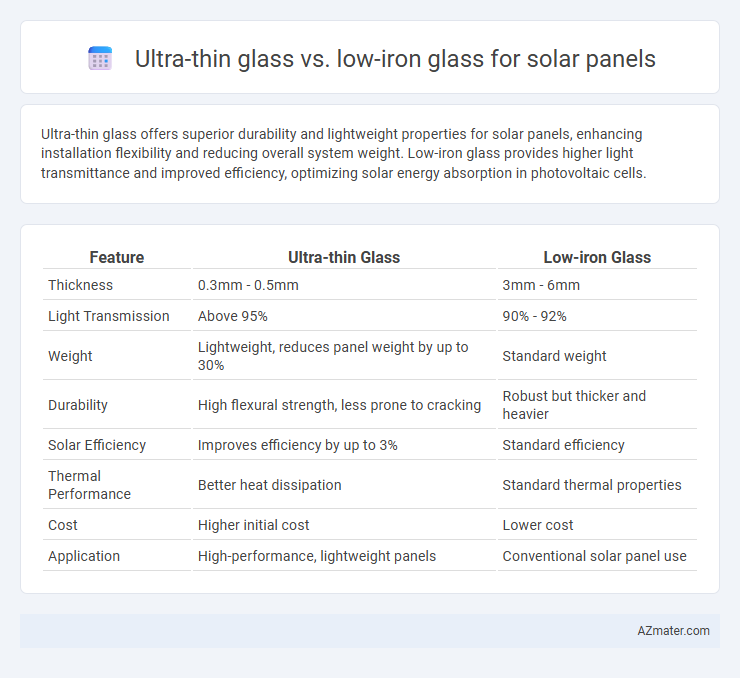
Ultra-thin glass offers superior durability and lightweight properties for solar panels, enhancing installation flexibility and reducing overall system weight. Low-iron glass provides higher light transmittance and improved efficiency, optimizing solar energy absorption in photovoltaic cells.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ultra-thin Glass | Low-iron Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | 0.3mm - 0.5mm | 3mm - 6mm |
| Light Transmission | Above 95% | 90% - 92% |
| Weight | Lightweight, reduces panel weight by up to 30% | Standard weight |
| Durability | High flexural strength, less prone to cracking | Robust but thicker and heavier |
| Solar Efficiency | Improves efficiency by up to 3% | Standard efficiency |
| Thermal Performance | Better heat dissipation | Standard thermal properties |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower cost |
| Application | High-performance, lightweight panels | Conventional solar panel use |
Introduction to Solar Panel Glass Types
Solar panel glass types primarily include ultra-thin glass and low-iron glass, both designed to maximize solar energy transmission and durability. Ultra-thin glass offers a lightweight, flexible solution with high transmissivity, enhancing solar panel efficiency while reducing overall weight. Low-iron glass features a higher light transmittance rate due to reduced iron content, improving energy output and preventing the greenish tint seen in standard glass.
What is Ultra-thin Glass?
Ultra-thin glass, typically ranging from 0.3 to 0.5 millimeters in thickness, is engineered to enhance solar panel efficiency by reducing weight and increasing light transmittance. Compared to conventional low-iron glass, ultra-thin glass offers superior flexibility and improved durability against thermal stress and mechanical impacts. This innovative material optimizes photovoltaic performance by allowing more sunlight to reach solar cells, thereby boosting overall energy output.
What is Low-iron Glass?
Low-iron glass is a high-transparency material used in solar panels that contains significantly reduced iron content compared to standard glass, resulting in enhanced light transmission and improved energy efficiency. Its low iron concentration minimizes the greenish tint typically found in regular glass, allowing more sunlight to reach the photovoltaic cells, boosting solar panel output. When compared to ultra-thin glass, low-iron glass combines durability with superior optical clarity, making it a preferred choice for maximizing sunlight absorption in solar energy systems.
Key Material Properties Comparison
Ultra-thin glass for solar panels offers exceptional flexibility and reduced weight, enhancing module durability and allowing for lightweight, curved installations. Low-iron glass delivers superior optical clarity and higher light transmittance, typically exceeding 92%, which maximizes solar energy absorption and efficiency. Comparing key material properties, ultra-thin glass typically ranges from 0.3 to 0.5 mm in thickness with increased mechanical flexibility, while low-iron glass usually measures 2 to 4 mm thick, providing higher stiffness and excellent UV resistance for long-term performance.
Light Transmission Efficiency
Ultra-thin glass offers higher light transmission efficiency than low-iron glass due to its reduced thickness, minimizing reflective losses and allowing more sunlight to reach the solar cells. Low-iron glass enhances clarity by reducing iron content, improving light transmittance compared to standard glass but still having higher reflection than ultra-thin variants. For maximizing solar panel performance, the superior light transmission of ultra-thin glass results in better energy yield, especially in applications where weight and efficiency are critical.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Ultra-thin glass offers enhanced durability and superior resistance to harsh weather conditions due to its high strength-to-weight ratio and flexibility, making it less prone to cracking under thermal stress. Low-iron glass provides excellent clarity but exhibits slightly lower durability and weather resistance, being more susceptible to surface scratches and impact damage. Both materials improve solar panel longevity, yet ultra-thin glass is preferred for maximizing durability in extreme climates.
Impact on Solar Panel Efficiency
Ultra-thin glass enhances solar panel efficiency by reducing weight and improving light transmission through its minimal thickness, allowing more sunlight to reach photovoltaic cells. Low-iron glass increases solar panel efficiency by minimizing iron content, which reduces yellow-green tinting and maximizes visible light transmittance. Combining both ultra-thin and low-iron glass can significantly improve solar panel performance by optimizing durability, weight, and light absorption.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Ultra-thin glass typically offers weight reduction and improved flexibility for solar panels but involves higher manufacturing costs due to specialized processing techniques. Low-iron glass provides enhanced light transmission with more established, cost-effective production methods, making it a more economical choice for large-scale solar module manufacturing. Cost efficiency depends on the balance between material savings from ultra-thin glass and the lower fabrication expenses associated with low-iron glass.
Suitability for Different Solar Applications
Ultra-thin glass offers superior flexibility and lightweight properties, making it ideal for curved and flexible solar panel applications such as building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV) and portable solar devices. Low-iron glass provides higher light transmittance and durability, making it more suitable for traditional fixed solar panel installations requiring maximum efficiency and long-term performance. The choice between ultra-thin and low-iron glass depends on the specific application's design constraints, efficiency requirements, and mechanical flexibility.
Choosing the Right Glass for Optimal Solar Performance
Ultra-thin glass and low-iron glass both enhance solar panel efficiency but differ in application-specific benefits. Ultra-thin glass offers superior light transmission and flexibility, reducing weight and improving durability for advanced solar designs, while low-iron glass maximizes clarity and solar energy absorption due to its minimal iron content, making it ideal for traditional, high-performance installations. Selecting the right glass depends on balancing factors such as environmental exposure, panel design constraints, and desired energy output to optimize long-term solar performance.
Infographic: Ultra-thin glass vs Low-iron glass for Solar panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com