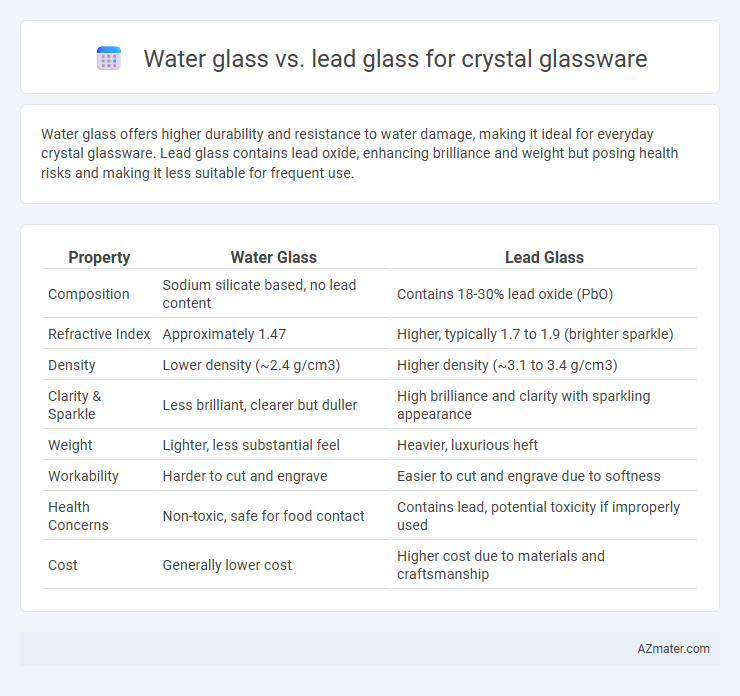
Water glass offers higher durability and resistance to water damage, making it ideal for everyday crystal glassware. Lead glass contains lead oxide, enhancing brilliance and weight but posing health risks and making it less suitable for frequent use.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Water Glass | Lead Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Sodium silicate based, no lead content | Contains 18-30% lead oxide (PbO) |
| Refractive Index | Approximately 1.47 | Higher, typically 1.7 to 1.9 (brighter sparkle) |
| Density | Lower density (~2.4 g/cm3) | Higher density (~3.1 to 3.4 g/cm3) |
| Clarity & Sparkle | Less brilliant, clearer but duller | High brilliance and clarity with sparkling appearance |
| Weight | Lighter, less substantial feel | Heavier, luxurious heft |
| Workability | Harder to cut and engrave | Easier to cut and engrave due to softness |
| Health Concerns | Non-toxic, safe for food contact | Contains lead, potential toxicity if improperly used |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to materials and craftsmanship |
Introduction to Crystal Glassware
Crystal glassware is distinguished by its high refractive index, clarity, and brilliance, achieved through the inclusion of specific additives like lead oxide or potassium oxide (in water glass). Lead glass, containing 24-30% lead oxide, offers superior weight, enhanced sparkle, and greater malleability for intricate designs. Water glass, often referred to as potassium glass, provides a lead-free alternative with excellent clarity and durability while maintaining brilliance suitable for fine crystal glassware.
What Is Water Glass?
Water glass, also known as sodium silicate, is a transparent, colorless compound used in the production of crystal glassware to enhance durability and resistance to thermal shock. Unlike lead glass, which contains lead oxide for increased brilliance and weight, water glass offers an eco-friendly alternative without compromising clarity or strength. This makes water glass a preferred choice for manufacturers seeking non-toxic and sustainable crystal glass options.
Understanding Lead Glass
Lead glass, also known as lead crystal, contains a high percentage of lead oxide (typically 24-30%), which increases its refractive index and density, creating exceptional brilliance and clarity compared to water glass. Its softness allows intricate cuts and engravings, making it the preferred choice for fine crystal glassware that showcases sparkling patterns and light dispersion. However, lead's toxicity requires careful handling, especially for items in contact with food or drink, prompting some manufacturers to opt for lead-free or water glass alternatives.
Composition Differences: Water Glass vs Lead Glass
Water glass, also known as soda-lime glass, primarily consists of silica (SiO2), sodium oxide (Na2O), and calcium oxide (CaO), making it less dense and more durable compared to lead glass. Lead glass, or crystal glass, contains a significant percentage of lead oxide (typically 24-35%), which increases its density, refractive index, and brilliance, giving it the distinctive sparkle and weight. The presence of lead oxide in lead glass lowers the melting point and enhances workability, whereas water glass has a higher melting point and is more resistant to chemical corrosion.
Visual and Aesthetic Qualities
Water glass exhibits higher clarity and a more neutral refractive index, resulting in a crisp, clean appearance ideal for minimalist or modern crystal glassware designs. Lead glass is renowned for its exceptional brilliance and sparkle due to its high lead oxide content, which enhances light refraction and produces vibrant rainbow colors. The rich luster and weight of lead glass contribute to a luxurious, elegant visual appeal, making it favored for ornate and high-end crystal pieces.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Water glass, typically made from soda-lime silica, offers moderate durability but is less resistant to impact and scratching compared to lead glass. Lead glass, containing 24-30% lead oxide, provides superior strength and enhanced brilliance due to its higher density and refractive index, making it more durable for fine crystal glassware. The lead content also imparts greater resistance to mechanical stress, ensuring better longevity in luxury and decorative applications.
Health and Safety Considerations
Water glass, often made with sodium silicate, is typically safer for everyday use as it contains no toxic elements, reducing health risks during extended contact with beverages. Lead glass, also known as lead crystal, contains lead oxide which enhances brilliance and weight but poses potential lead exposure risks, especially if acidic or alcoholic drinks are stored for prolonged periods. Regulatory guidelines recommend limiting the use of lead crystal for drinking vessels to minimize lead leaching and ensure consumer health safety.
Cost and Accessibility
Water glass offers a cost-effective and widely accessible option for crystal glassware, utilizing sodium silicate that is abundant and inexpensive to produce. Lead glass, containing lead oxide, is generally more expensive due to its complex manufacturing process and higher material costs, but it provides superior brilliance and weight. While water glass is favored for budget-friendly and durable tableware, lead glass remains a premium choice for luxury crystal pieces with enhanced optical properties.
Best Uses for Water Glass and Lead Glass
Water glass, known for its high durability and resistance to thermal shock, is ideal for everyday glassware and practical kitchen items where strength and temperature changes are common. Lead glass, with its higher refractive index and brilliance, excels in luxury crystal glassware such as decorative pieces, fine wine glasses, and high-end chandeliers, showcasing clarity and sparkle. The choice depends on whether durability or aesthetic brilliance is the priority, with water glass favoring functional use and lead glass emphasizing elegance.
Choosing the Right Crystal Glassware for You
Water glass crystal glassware contains a high silica content and fewer lead oxides, making it more durable and chip-resistant, ideal for everyday use. Lead glass crystal offers a higher refractive index due to its lead oxide content, delivering exceptional brilliance and clarity suited for formal settings and luxury collections. When choosing the right crystal glassware, consider durability needs versus aesthetic preferences to select water glass for practical durability or lead glass for superior sparkle and elegance.
Infographic: Water glass vs Lead glass for Crystal glassware
 azmater.com
azmater.com