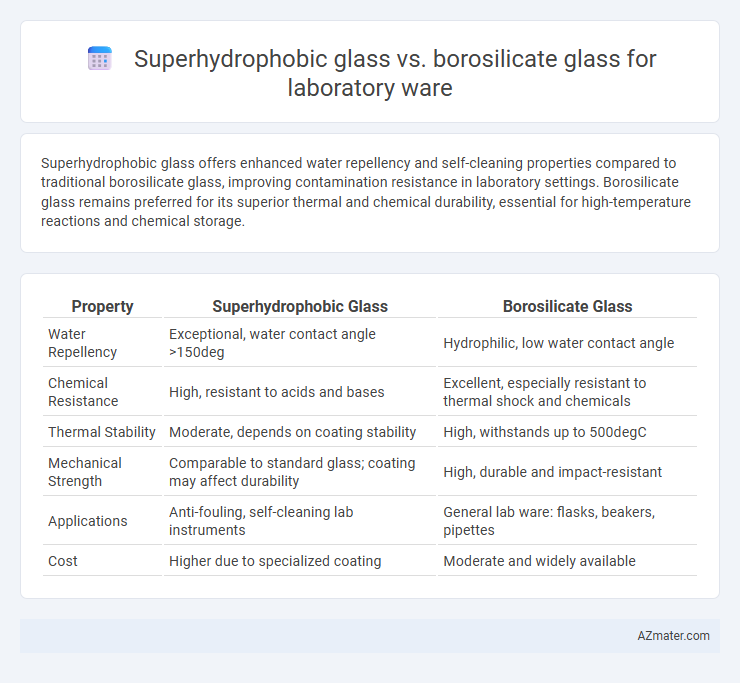
Superhydrophobic glass offers enhanced water repellency and self-cleaning properties compared to traditional borosilicate glass, improving contamination resistance in laboratory settings. Borosilicate glass remains preferred for its superior thermal and chemical durability, essential for high-temperature reactions and chemical storage.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Superhydrophobic Glass | Borosilicate Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Water Repellency | Exceptional, water contact angle >150deg | Hydrophilic, low water contact angle |
| Chemical Resistance | High, resistant to acids and bases | Excellent, especially resistant to thermal shock and chemicals |
| Thermal Stability | Moderate, depends on coating stability | High, withstands up to 500degC |
| Mechanical Strength | Comparable to standard glass; coating may affect durability | High, durable and impact-resistant |
| Applications | Anti-fouling, self-cleaning lab instruments | General lab ware: flasks, beakers, pipettes |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized coating | Moderate and widely available |
Introduction to Laboratory Glassware Materials
Superhydrophobic glass offers enhanced water repellency and self-cleaning properties compared to traditional borosilicate glass, making it ideal for applications requiring reduced contamination and easier maintenance. Borosilicate glass, known for its thermal resistance and chemical durability, remains the standard for laboratory glassware due to its ability to withstand high temperatures and corrosive chemicals. Selecting between superhydrophobic and borosilicate glass depends on experimental needs, balancing hydrophobic performance with thermal and chemical stability.
Defining Superhydrophobic Glass: Properties and Technology
Superhydrophobic glass exhibits an ultrahigh water contact angle typically above 150deg, achieved through nanoscale surface textures combined with low surface energy coatings such as fluorinated silanes. This advanced material repels water and organic liquids, significantly reducing sample adhesion and contamination risks in laboratory ware applications. In contrast, borosilicate glass offers excellent chemical resistance and thermal stability but lacks inherent water-repellent properties crucial for minimizing cross-contamination in sensitive experiments.
Overview of Borosilicate Glass: Composition and Features
Borosilicate glass, primarily composed of silica (SiO2) and boron trioxide (B2O3), is renowned for its low thermal expansion coefficient and high chemical resistance, making it ideal for laboratory ware. This glass withstands rapid temperature changes without cracking and resists corrosion from acids and alkalis, ensuring durability in rigorous lab environments. Borosilicate glass also offers excellent optical clarity and mechanical strength, preferred for precise scientific applications compared to superhydrophobic glass, which mainly enhances surface water repellency.
Chemical Resistance: Superhydrophobic vs Borosilicate Glass
Superhydrophobic glass offers excellent chemical resistance due to its ultra-repellent surface that minimizes reagent adhesion and corrosion. Borosilicate glass is widely recognized for its high chemical durability, resisting acids, bases, and organic solvents, making it a standard choice for laboratory ware. While superhydrophobic coatings enhance surface protection, borosilicate glass inherently provides robust chemical stability under diverse laboratory conditions.
Thermal Stability: Performance Under Extreme Temperatures
Superhydrophobic glass maintains excellent thermal stability at temperatures up to 200degC, preventing water adhesion and ensuring easy cleaning, making it suitable for routine laboratory applications with moderate heat exposure. Borosilicate glass withstands extreme thermal shocks and sustained temperatures up to 500degC due to its low coefficient of thermal expansion, making it ideal for high-temperature reactions and steam sterilization processes. In applications requiring both high thermal resistance and anti-wetting properties, combining superhydrophobic coatings with borosilicate substrates offers enhanced performance and durability under extreme laboratory conditions.
Wetting Behavior and Liquid Interaction
Superhydrophobic glass exhibits extreme water repellency with contact angles above 150deg, significantly reducing liquid adhesion compared to borosilicate glass, which typically has contact angles around 30-40deg. This hydrophobic surface minimizes wetting and reduces residue buildup, enhancing sample recovery and cleanliness in laboratory ware applications. Borosilicate glass, valued for its chemical resistance and thermal stability, interacts more readily with aqueous solutions, leading to greater liquid retention and potential contamination risks during experiments.
Durability and Mechanical Strength Comparison
Superhydrophobic glass exhibits enhanced durability due to its water-repellent surface, reducing contamination and chemical degradation over time, while borosilicate glass is renowned for its exceptional thermal resistance and mechanical strength, making it highly resistant to thermal shock and mechanical stress. In mechanical strength tests, borosilicate glass outperforms superhydrophobic glass, which may have a delicate nano-structured coating prone to abrasion under harsh laboratory conditions. For laboratory ware requiring repeated thermal cycling and mechanical handling, borosilicate glass remains the preferred choice due to its proven robustness and longevity.
Cleaning and Maintenance Considerations
Superhydrophobic glass significantly reduces water and chemical residue adherence, facilitating easier cleaning and minimizing contamination risks in laboratory ware compared to borosilicate glass. Borosilicate glass, known for its thermal and chemical resistance, requires more rigorous cleaning protocols involving solvents and detergents to remove stains and residues. Choosing superhydrophobic glass can lower maintenance time and chemical use, enhancing laboratory efficiency and prolonging the lifespan of glassware.
Cost Analysis and Accessibility
Superhydrophobic glass offers advanced water-repellent properties ideal for reducing contamination in laboratory ware but comes at a significantly higher cost compared to borosilicate glass, which is widely recognized for its chemical durability and thermal resistance at a lower price point. Borosilicate glass is more accessible globally due to established manufacturing processes and widespread distribution, making it the preferred choice for routine laboratory applications. The premium price and specialized production of superhydrophobic coatings limit their current accessibility primarily to high-tech or specialized research environments.
Applications in Laboratory Settings: Choosing the Right Glassware
Superhydrophobic glass offers superior water and chemical repellency, making it ideal for applications requiring minimal sample adhesion and easy cleaning, such as microfluidics and analytical chemistry. Borosilicate glass, known for its excellent thermal resistance and chemical durability, remains preferred for high-temperature reactions, autoclaving, and general laboratory use where robustness is essential. Selecting the right glassware depends on the specific laboratory task: superhydrophobic glass enhances precision in fluid handling, while borosilicate glass ensures reliability under harsh chemical and thermal conditions.
Infographic: Superhydrophobic glass vs Borosilicate glass for Laboratory ware
 azmater.com
azmater.com