Silica glass offers superior thermal resistance and clarity compared to laminated glass, which provides enhanced impact absorption and safety due to its layered plastic interlayer. Windshields typically use laminated glass for its shatterproof properties, while silica glass is preferred in high-temperature applications like scientific instruments.
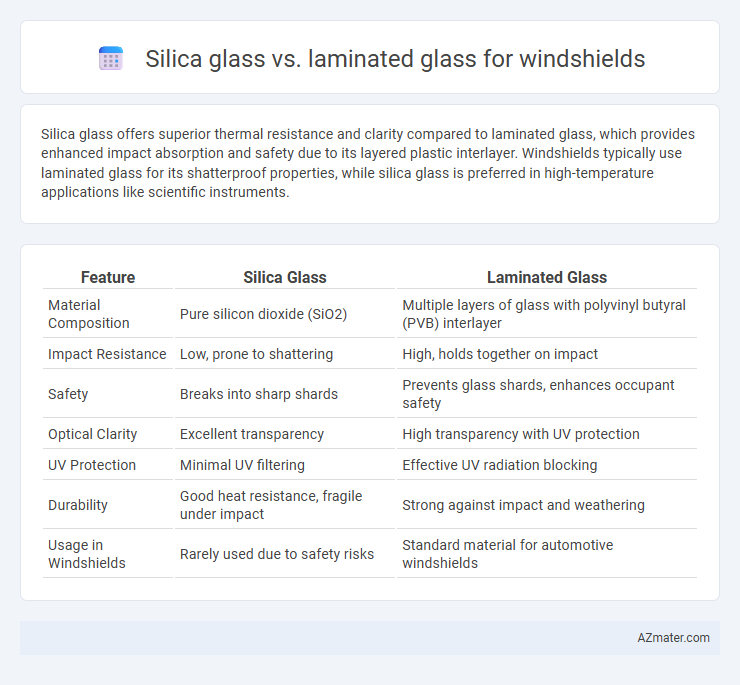
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Silica Glass | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Pure silicon dioxide (SiO2) | Multiple layers of glass with polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer |
| Impact Resistance | Low, prone to shattering | High, holds together on impact |
| Safety | Breaks into sharp shards | Prevents glass shards, enhances occupant safety |
| Optical Clarity | Excellent transparency | High transparency with UV protection |
| UV Protection | Minimal UV filtering | Effective UV radiation blocking |
| Durability | Good heat resistance, fragile under impact | Strong against impact and weathering |
| Usage in Windshields | Rarely used due to safety risks | Standard material for automotive windshields |
Introduction to Windshield Glass Types
Silica glass, known for its high thermal resistance and clarity, is less commonly used for windshields due to its brittleness and lower impact resistance. Laminated glass, composed of two glass layers bonded with a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer, provides superior safety by preventing shattering upon impact. The laminated glass type is widely preferred in automotive windshields for its durability, impact resistance, and ability to maintain visibility after damage.
What is Silica Glass?
Silica glass, also known as fused silica or quartz glass, is a high-purity glass made primarily from silicon dioxide (SiO2) and is renowned for its exceptional thermal stability, optical clarity, and chemical resistance. Unlike laminated glass used in windshields, which consists of multiple layers of glass and plastic for impact resistance and safety, silica glass offers superior hardness and transparency but lacks the flexibility and impact absorption required for automotive applications. Silica glass's high melting point and low thermal expansion make it ideal for specialized optical and industrial uses rather than windshield manufacturing.
What is Laminated Glass?
Laminated glass consists of two or more layers of glass bonded together with an interlayer, typically made of polyvinyl butyral (PVB), which enhances safety by holding the glass fragments in place upon impact. Unlike silica glass, laminated glass offers superior impact resistance and prevents shattering, making it the preferred choice for windshields in vehicles. Its structural integrity improves occupant protection and reduces the risk of injury during collisions or accidents.
Manufacturing Process: Silica vs Laminated Glass
Silica glass, also known as tempered or toughened glass, undergoes a rapid heating and cooling process to increase strength and resistance to impact, making it less prone to shattering but prone to breaking into small blunt pieces. Laminated glass manufacturing involves sandwiching a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) or ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) layer between two glass sheets, followed by heat and pressure treatment to bond the layers, providing enhanced safety by holding shards together upon impact. The intricate lamination process results in superior durability and sound insulation properties compared to silica glass, which is primarily focused on thermal strengthening.
Safety Performance Comparison
Silica glass, known for its high thermal resistance and durability, offers superior clarity but lacks the shatter-resistant properties essential for windshield safety. Laminated glass combines layers of glass with a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer, which prevents shards from scattering upon impact, significantly reducing injury risk during collisions. The safety performance of laminated glass exceeds that of silica glass by providing enhanced impact absorption, structural integrity, and occupant protection in automotive applications.
Impact Resistance and Durability
Silica glass boasts superior hardness and scratch resistance but falls short in impact resistance compared to laminated glass, which features a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer that prevents shattering upon impact. Laminated glass excels in durability by maintaining structural integrity and reducing the risk of injury during collisions, making it the preferred choice for vehicle windshields. The combination of impact absorption and long-term resistance to environmental stressors ensures laminated glass outperforms silica glass in automotive safety applications.
Optical Clarity Differences
Silica glass offers superior optical clarity with minimal distortion and high light transmission, making it ideal for precise visibility requirements in windshields. Laminated glass, composed of two glass layers with an interlayer, provides effective UV filtering and enhanced impact resistance but can exhibit slight optical distortion due to the interlayer's refractive properties. The choice between silica glass and laminated glass for windshields hinges on balancing ultimate clarity against safety and durability features.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Silica glass, known for its high thermal resistance and durability, generally incurs a higher upfront cost compared to laminated glass used in windshields. Laminated glass, composed of two glass layers with a plastic interlayer, offers enhanced safety and impact resistance at a more affordable price point, making it a cost-effective choice for mass production and replacement. Economic considerations favor laminated glass for its balance of performance, repairability, and overall value, which reduces long-term maintenance expenses.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Silica glass used in windshields offers higher purity and easier recyclability due to its simpler composition, reducing environmental impact through efficient material recovery. Laminated glass, composed of multiple layers including polyvinyl butyral (PVB), presents challenges in recycling because separating these layers requires energy-intensive processes, increasing its ecological footprint. Choosing silica glass enhances sustainability by minimizing waste and supporting circular economy practices in automotive glass recycling.
Which Glass is Better for Windshields?
Silica glass offers superior heat resistance and optical clarity, making it ideal for vehicle windshields subjected to extreme temperature variations. Laminated glass, composed of two glass layers with a plastic interlayer, provides enhanced safety by preventing shattering upon impact and better sound insulation. For windshields, laminated glass is generally better due to its combination of strength, safety features, and durability.
Infographic: Silica glass vs Laminated glass for Windshield
 azmater.com
azmater.com