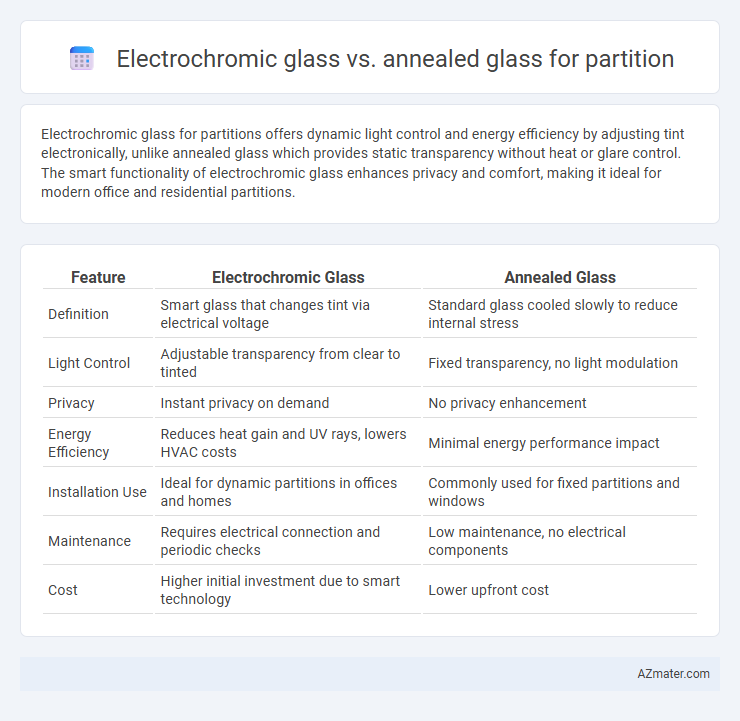
Electrochromic glass for partitions offers dynamic light control and energy efficiency by adjusting tint electronically, unlike annealed glass which provides static transparency without heat or glare control. The smart functionality of electrochromic glass enhances privacy and comfort, making it ideal for modern office and residential partitions.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Electrochromic Glass | Annealed Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Smart glass that changes tint via electrical voltage | Standard glass cooled slowly to reduce internal stress |
| Light Control | Adjustable transparency from clear to tinted | Fixed transparency, no light modulation |
| Privacy | Instant privacy on demand | No privacy enhancement |
| Energy Efficiency | Reduces heat gain and UV rays, lowers HVAC costs | Minimal energy performance impact |
| Installation Use | Ideal for dynamic partitions in offices and homes | Commonly used for fixed partitions and windows |
| Maintenance | Requires electrical connection and periodic checks | Low maintenance, no electrical components |
| Cost | Higher initial investment due to smart technology | Lower upfront cost |
Introduction to Partition Glass Types
Electrochromic glass offers dynamic light control by changing opacity with electrical voltage, enhancing privacy and energy efficiency in partitions. Annealed glass, commonly used for partitions, is a standard, heat-treated glass known for its clarity and affordability but lacks smart functionality. Choosing between electrochromic and annealed glass depends on the need for adaptive shading versus simple, cost-effective partition solutions.
What is Electrochromic Glass?
Electrochromic glass is a smart glass technology that changes its opacity or tint when an electrical voltage is applied, allowing users to control light transmission and privacy in real-time. Unlike annealed glass, which is standard, non-tinted glass that provides no control over light or glare, electrochromic glass enhances energy efficiency, reduces UV exposure, and offers dynamic privacy solutions for partitions. This glass integrates a thin electrochromic layer between panes, making it ideal for modern offices and homes seeking adaptable and sustainable design.
What is Annealed Glass?
Annealed glass is a standard type of glass that has been slowly cooled after formation to relieve internal stresses, ensuring increased durability and easier cutting or shaping for partitions. Unlike electrochromic glass, which can change transparency with an electrical signal to control light and privacy, annealed glass remains permanently transparent and is often used in partitions for its cost-effectiveness and consistent clarity. The choice between annealed and electrochromic glass depends on functional needs, with annealed glass favored for static visibility and electrochromic glass for dynamic light control.
Key Differences: Electrochromic vs Annealed Glass
Electrochromic glass offers dynamic light control by changing opacity through electrical voltage, enhancing privacy and energy efficiency in partitions, whereas annealed glass remains static with no tint or light modulation. Electrochromic glass integrates smart technology for adjustable transparency, ideal for modern offices seeking adjustable ambiance, while annealed glass provides basic durability and clarity without added functionality. The cost and installation complexity of electrochromic glass are higher compared to the simpler, more affordable annealed glass used primarily for basic partitioning needs.
Light Control and Privacy Features
Electrochromic glass offers dynamic light control by adjusting opacity on demand, providing customizable privacy and glare reduction ideal for office partitions. Annealed glass, being static and transparent, lacks adjustable privacy features, relying on films or blinds for light management. The electrochromic option enhances energy efficiency and occupant comfort through smart tinting, whereas annealed glass prioritizes cost-effectiveness but limits light modulation capabilities.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Electrochromic glass significantly enhances energy efficiency in partitions by dynamically controlling solar heat gain and reducing HVAC loads, unlike annealed glass which lacks this adaptive capability. The smart tinting feature of electrochromic glass minimizes glare and heat transmission, leading to lower energy consumption and improved occupant comfort. Conversely, annealed glass provides basic insulation but cannot actively modulate light or thermal properties, resulting in higher energy costs over time.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Electrochromic glass partitions require specialized electrical wiring and integration with control systems during installation, increasing complexity compared to the straightforward mounting process of annealed glass. Maintenance of electrochromic glass involves periodic checks of the electronic components and software updates, whereas annealed glass demands minimal upkeep, primarily regular cleaning and inspections for physical damage. The advanced functionality of electrochromic glass offers dynamic light control but necessitates more technical expertise for both installation and ongoing maintenance compared to the simple, passive nature of annealed glass.
Cost Analysis: Upfront and Long-Term
Electrochromic glass commands a higher upfront cost due to its advanced technology integrating smart tinting capabilities, while annealed glass remains more budget-friendly with basic static properties. Long-term savings with electrochromic glass arise from energy efficiency, reducing HVAC expenses by controlling solar heat gain and glare, whereas annealed glass may lead to increased energy costs due to poor thermal regulation. Maintenance costs for electrochromic glass can be higher, but its potential for dynamic light management offers a cost-benefit balance not achievable with traditional annealed glass partitions.
Design Flexibility and Aesthetic Impact
Electrochromic glass offers dynamic light control and privacy through adjustable tinting, enhancing design flexibility compared to static annealed glass partitions. The sleek, modern appearance of electrochromic glass creates a high-tech aesthetic impact that transforms interior environments, while annealed glass provides a traditional clear and consistent look. Architects and designers favor electrochromic glass for its ability to integrate seamlessly into smart building systems, delivering both visual appeal and functional adaptability.
Best Applications for Each Glass Type in Partitions
Electrochromic glass excels in office partitions where dynamic privacy control and natural light management are essential, making it ideal for conference rooms, executive offices, and healthcare facilities. Annealed glass is best suited for fixed partitions in commercial and residential interiors where cost-efficiency, structural stability, and basic light transmission are required without the need for switchable opacity. Each glass type provides unique benefits aligned with specific partition applications, optimizing both functionality and aesthetics.
Infographic: Electrochromic glass vs Annealed glass for Partition
 azmater.com
azmater.com