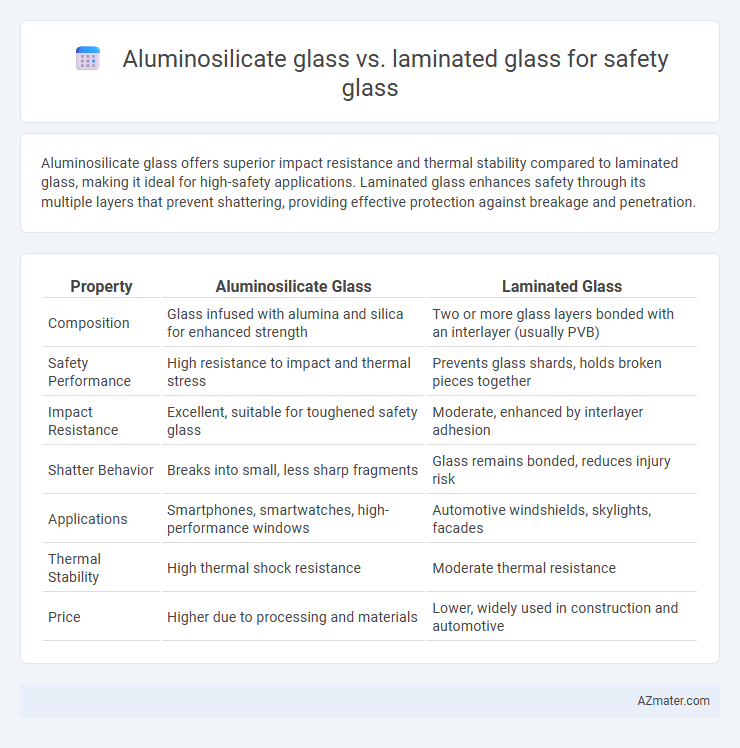
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior impact resistance and thermal stability compared to laminated glass, making it ideal for high-safety applications. Laminated glass enhances safety through its multiple layers that prevent shattering, providing effective protection against breakage and penetration.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Aluminosilicate Glass | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Glass infused with alumina and silica for enhanced strength | Two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer (usually PVB) |
| Safety Performance | High resistance to impact and thermal stress | Prevents glass shards, holds broken pieces together |
| Impact Resistance | Excellent, suitable for toughened safety glass | Moderate, enhanced by interlayer adhesion |
| Shatter Behavior | Breaks into small, less sharp fragments | Glass remains bonded, reduces injury risk |
| Applications | Smartphones, smartwatches, high-performance windows | Automotive windshields, skylights, facades |
| Thermal Stability | High thermal shock resistance | Moderate thermal resistance |
| Price | Higher due to processing and materials | Lower, widely used in construction and automotive |
Introduction to Safety Glass Types
Aluminosilicate glass offers high thermal resistance and mechanical strength, making it ideal for safety applications requiring durability and heat tolerance. Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded by an interlayer, providing enhanced impact resistance and preventing shattering upon breakage. Both types are essential in safety glass solutions, with aluminosilicate glass favored for tough environments and laminated glass commonly used in automotive and architectural glazing for occupant protection.
Overview of Aluminosilicate Glass
Aluminosilicate glass exhibits superior strength and thermal resistance compared to traditional laminated glass, making it ideal for high-performance safety glass applications in automotive and electronic devices. Its enhanced chemical durability and ability to withstand extreme temperature variations reduce the risk of shattering upon impact, providing improved protection. Unlike laminated glass, which relies on interlayers to hold fragments, aluminosilicate glass offers inherent toughness due to its specialized composition of aluminum, silicon, and oxygen.
Overview of Laminated Glass
Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded by an interlayer, typically polyvinyl butyral (PVB), which enhances impact resistance and prevents shattering upon breakage. This composition offers superior safety benefits compared to aluminosilicate glass by holding glass fragments in place, reducing injury risk during collisions or accidents. Widely used in automotive windshields and architectural applications, laminated glass also provides improved sound insulation and UV protection.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Aluminosilicate glass consists primarily of aluminum oxide and silicon dioxide, offering enhanced thermal and chemical resistance, and is manufactured through a fusion process involving molten glass cooled rapidly to form a tough structure. Laminated glass is composed of two or more layers of glass bonded with an interlayer, typically polyvinyl butyral (PVB) or ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), produced by assembling the layers and applying heat and pressure for lamination, resulting in a safety glass that holds together upon impact. The manufacturing of aluminosilicate glass involves precise chemical formulations and thermal treatments to optimize strength and durability, while laminated glass production focuses on mechanical bonding and impact resistance through layered construction.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Aluminosilicate glass exhibits superior mechanical strength and higher resistance to impact and thermal stress compared to laminated glass, making it ideal for applications requiring enhanced durability. Laminated glass, consisting of multiple glass layers bonded with interlayers, provides excellent impact resistance but typically demonstrates lower tensile strength and is more prone to fracture under high mechanical loads. In safety-critical environments, aluminosilicate glass's enhanced structural integrity offers better performance for resisting mechanical forces and ensuring long-term safety.
Impact and Shatter Resistance
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior impact resistance due to its high mechanical strength and thermal stability, making it less likely to crack under sudden force. Laminated glass, composed of multiple glass layers bonded with a plastic interlayer, excels in shatter resistance by holding fragments together upon impact, preventing dangerous shards. For safety glass applications requiring both impact absorption and containment of broken pieces, laminated glass provides enhanced protection despite aluminosilicate glass's higher durability.
Optical Clarity and Light Transmission
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior optical clarity with minimal distortion and high light transmission rates, typically above 90%, making it ideal for applications requiring clear visibility. Laminated glass, composed of two or more layers of glass bonded with an interlayer, slightly reduces light transmission due to the interlayer but enhances safety by holding shards together upon impact. Choosing between the two depends on whether optical performance or structural safety is the priority, with aluminosilicate glass excelling in clarity and laminated glass prioritizing impact resistance.
Applications in Safety and Security
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and enhanced chemical durability, making it ideal for high-security environments such as bulletproof windows and electronic device screens where impact resistance is critical. Laminated glass consists of multiple glass layers bonded with a plastic interlayer, providing effective shatter resistance and preventing glass fragments from dispersing, widely used in automotive windshields, skylights, and storefronts for safety and intrusion protection. Both types contribute significantly to safety glass applications, with aluminosilicate glass favored for extreme stress conditions and laminated glass prioritized for impact containment and human injury reduction.
Cost and Availability
Aluminosilicate glass generally costs more than laminated glass due to its enhanced thermal and chemical durability, making it preferable for high-performance safety applications. Laminated glass is widely available and more cost-effective, featuring layers of glass bonded with interlayers that absorb impact and prevent shattering. Cost-efficiency and accessibility make laminated glass the predominant choice for everyday safety glass, while aluminosilicate glass suits specialized environments requiring higher strength and resistance.
Choosing the Right Glass for Safety Needs
Aluminosilicate glass offers high resistance to thermal stress and impact, making it ideal for environments requiring enhanced durability and safety, such as electronics and automotive applications. Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded with a plastic interlayer, providing superior shatter resistance and maintaining integrity upon impact, crucial for preventing injury in architectural and automotive safety glazing. Selecting between aluminosilicate and laminated glass depends on the specific safety needs, including impact resistance, structural integrity, and application environment.
Infographic: Aluminosilicate glass vs Laminated glass for Safety glass
 azmater.com
azmater.com