Light-diffusing glass for skylights enhances natural light distribution while reducing glare and hotspots. Laminated glass offers superior safety and UV protection by holding shattered pieces together during impact.
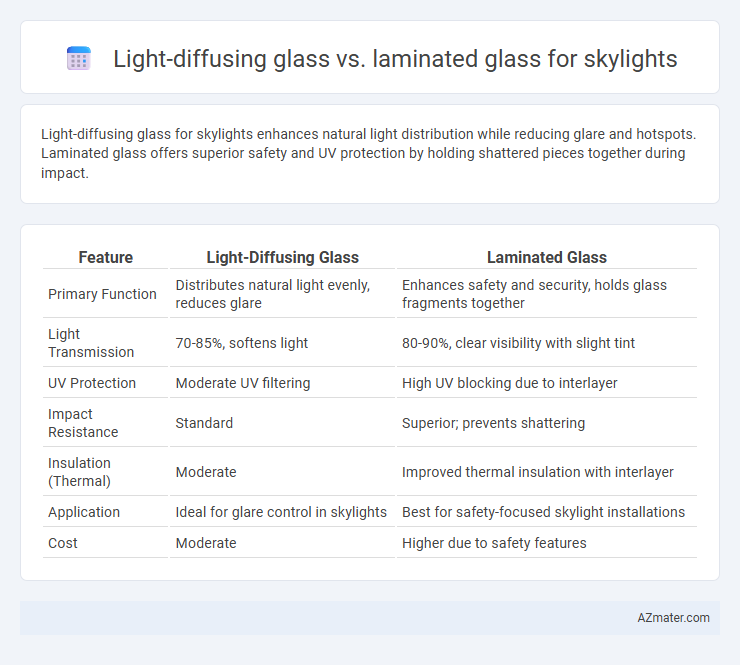
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Light-Diffusing Glass | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Distributes natural light evenly, reduces glare | Enhances safety and security, holds glass fragments together |
| Light Transmission | 70-85%, softens light | 80-90%, clear visibility with slight tint |
| UV Protection | Moderate UV filtering | High UV blocking due to interlayer |
| Impact Resistance | Standard | Superior; prevents shattering |
| Insulation (Thermal) | Moderate | Improved thermal insulation with interlayer |
| Application | Ideal for glare control in skylights | Best for safety-focused skylight installations |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher due to safety features |
Introduction to Skylight Glass Options
Skylight glass options include light-diffusing glass, which evenly disperses natural light to reduce glare and enhance indoor illumination, and laminated glass, known for its superior safety and impact resistance due to its interlayer that holds shards in place upon breakage. Light-diffusing glass improves energy efficiency by softening sunlight and reducing heat gain, while laminated glass provides enhanced UV protection and sound insulation, making it a durable choice for skylights in various climates. Selecting between these types depends on priorities like light quality, safety standards, and thermal performance for optimal skylight functionality.
What is Light-Diffusing Glass?
Light-diffusing glass is designed to scatter natural light evenly, reducing glare and enhancing privacy without compromising brightness, making it ideal for skylights in residential and commercial spaces. Unlike laminated glass, which consists of two or more layers bonded with an interlayer to improve safety and sound insulation, light-diffusing glass utilizes micro-etched or patterned surfaces to disperse incoming light uniformly. This specialized glass enhances visual comfort by softening sunlight and minimizing harsh shadows, optimizing daylighting in interior environments.
Understanding Laminated Glass
Laminated glass for skylights consists of two or more layers of glass bonded together with a durable interlayer, providing enhanced safety and impact resistance compared to light-diffusing glass. This construction reduces the risk of shattering upon impact, ensuring that broken glass remains adhered to the interlayer, which is especially important for overhead installations prone to falling debris or weather events. Laminated glass also offers superior UV protection and noise reduction, making it a practical choice for skylights where both safety and comfort are priorities.
Key Differences in Structure and Composition
Light-diffusing glass for skylights features a textured or coated surface designed to scatter sunlight evenly, reducing glare and enhancing natural light distribution. Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer, typically polyvinyl butyral (PVB), providing superior impact resistance and safety by holding shattered fragments in place. The fundamental difference lies in light diffusion properties versus structural safety, with light-diffusing glass optimizing illumination and laminated glass ensuring durability and protection.
Daylight Distribution: Light-Diffusing vs Laminated Glass
Light-diffusing glass enhances daylight distribution by scattering incoming sunlight evenly across indoor spaces, reducing glare and creating a soft, uniform illumination ideal for skylights. Laminated glass, while primarily designed for safety and sound insulation, transmits clearer, more direct light but can cause hotspots or shadows without diffusion properties. Choosing light-diffusing glass improves visual comfort and energy efficiency by maximizing natural light spread throughout the room under skylights.
Safety and Security Comparisons
Light-diffusing glass for skylights enhances safety by reducing glare and evenly distributing natural light, minimizing eye strain and preventing hotspots that can cause thermal stress. Laminated glass excels in security, as its interlayer holds shattered pieces together, preventing glass from falling and reducing the risk of injury or unauthorized entry. Both glass types meet safety standards, but laminated glass offers superior impact resistance and intrusion protection, making it the preferred choice for enhanced skylight security.
Energy Efficiency and UV Protection
Light-diffusing glass for skylights enhances natural light distribution while reducing glare and heat gain, improving overall energy efficiency by minimizing reliance on artificial lighting and cooling systems. Laminated glass offers superior UV protection by incorporating a plastic interlayer that blocks up to 99% of harmful ultraviolet rays, preventing interior fading and damage while maintaining structural safety. Both materials contribute to energy performance, but laminated glass excels in UV shielding, making it ideal for protecting furnishings and improving durability.
Aesthetic Impact on Interior Spaces
Light-diffusing glass enhances interior spaces by scattering sunlight evenly, reducing glare and creating a soft, natural illumination that highlights architectural details with subtle brilliance. Laminated glass offers a sleek, transparent aesthetic while providing safety and UV protection, maintaining clear outdoor views and preserving natural color vibrancy inside. Choosing between these options impacts the ambiance: light-diffusing glass fosters a gentle, tranquil atmosphere, whereas laminated glass supports a bright, open feel with uncompromised clarity.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Light-diffusing glass for skylights requires precise installation to ensure even distribution of natural light and often demands professional handling to avoid damage to its textured surface. Laminated glass, known for its safety and durability, involves more complex installation due to its layered construction but offers enhanced resistance to impact and UV rays, reducing long-term maintenance needs. Maintenance for light-diffusing glass typically focuses on cleaning without damaging the diffusing layer, whereas laminated glass maintenance centers on inspecting the seal integrity to prevent moisture ingress and delamination.
Choosing the Right Skylight Glass for Your Needs
Light-diffusing glass for skylights enhances natural light distribution by scattering sunlight evenly, reducing glare and creating a soft, comfortable indoor ambiance. Laminated glass offers superior safety and security with its multiple layers bonded by an interlayer that holds shards together upon impact, also providing effective sound insulation and UV protection. Selecting between light-diffusing and laminated glass depends on prioritizing natural light quality versus safety and durability requirements in your skylight installation.
Infographic: Light-diffusing glass vs Laminated glass for Skylight
 azmater.com
azmater.com