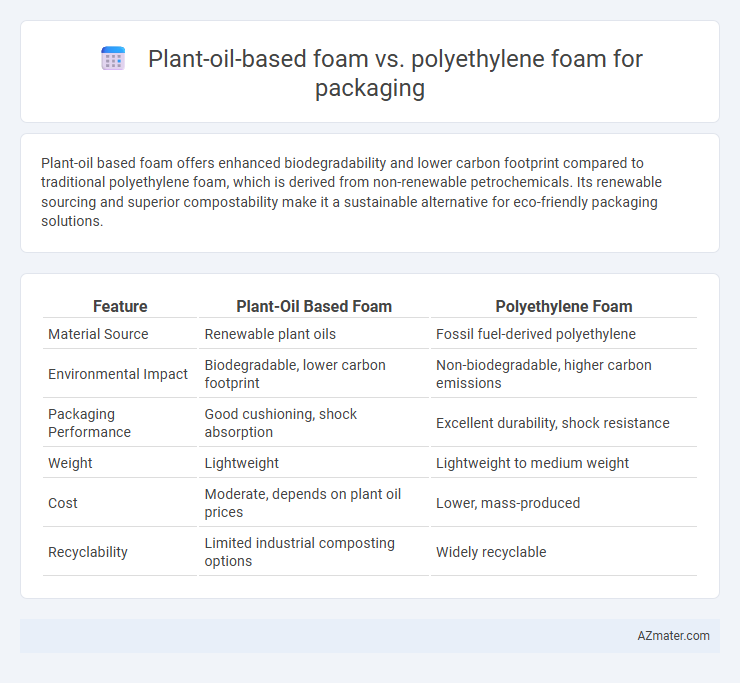
Plant-oil based foam offers enhanced biodegradability and lower carbon footprint compared to traditional polyethylene foam, which is derived from non-renewable petrochemicals. Its renewable sourcing and superior compostability make it a sustainable alternative for eco-friendly packaging solutions.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Plant-Oil Based Foam | Polyethylene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Renewable plant oils | Fossil fuel-derived polyethylene |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, lower carbon footprint | Non-biodegradable, higher carbon emissions |
| Packaging Performance | Good cushioning, shock absorption | Excellent durability, shock resistance |
| Weight | Lightweight | Lightweight to medium weight |
| Cost | Moderate, depends on plant oil prices | Lower, mass-produced |
| Recyclability | Limited industrial composting options | Widely recyclable |
Introduction to Packaging Foams
Plant-oil based foam offers a sustainable alternative to traditional polyethylene foam by utilizing renewable biomass resources, significantly reducing carbon footprint and reliance on fossil fuels. Polyethylene foam, derived from petrochemicals, provides excellent cushioning, durability, and moisture resistance crucial for packaging fragile items during transportation. Both foams serve to protect products, but plant-oil based foam emphasizes biodegradability and environmental impact, aligning with growing eco-conscious packaging demands.
What is Plant-Oil Based Foam?
Plant-oil based foam is a sustainable packaging material derived from renewable plant oils such as soybean, castor, or palm oil, offering an eco-friendly alternative to traditional petroleum-based polyethylene foam. It provides comparable cushioning and protective properties while being biodegradable and reducing carbon footprint during production and disposal. The foam's cellular structure is engineered to maintain durability, shock absorption, and insulation, making it suitable for shipping fragile goods.
Understanding Polyethylene Foam
Polyethylene foam, a widely used packaging material, offers excellent cushioning and impact resistance due to its closed-cell structure and lightweight nature. Its chemical stability and moisture resistance make it ideal for protecting sensitive electronic components and fragile goods during shipping. Compared to plant-oil based foams, polyethylene foam provides superior durability, longer shelf life, and consistent performance across various environmental conditions.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Plant-oil based foam offers a significantly lower environmental impact compared to polyethylene foam, as it is derived from renewable resources and is biodegradable, reducing landfill accumulation and pollution. Polyethylene foam, a petrochemical product, contributes to long-term environmental hazards due to its slow degradation and reliance on fossil fuels. Life cycle assessments show plant-oil based foam reduces carbon footprint and energy consumption, making it a more sustainable choice for eco-friendly packaging solutions.
Performance and Durability Differences
Plant-oil based foam offers enhanced biodegradability and better resistance to compression set compared to traditional polyethylene foam, which provides superior tensile strength and impact absorption. The durability of plant-oil foams tends to decline under prolonged UV exposure, whereas polyethylene foam maintains structural integrity longer in outdoor environments. Performance-wise, plant-oil foam excels in eco-friendly applications demanding moderate cushioning, while polyethylene foam is preferred for heavy-duty packaging requiring consistent protection and longevity.
Cost Analysis: Plant-Oil vs Polyethylene Foam
Plant-oil based foam typically incurs higher production costs due to raw material prices and processing complexities compared to polyethylene foam, which benefits from established manufacturing economies of scale. Polyethylene foam offers a cost-effective solution with lower material and production expenses, making it widely favored in large-scale packaging applications. Despite its higher initial costs, plant-oil based foam may provide long-term economic benefits through potential environmental incentives and increasing regulatory pressures on petrochemical-derived products.
Biodegradability and End-of-Life Options
Plant-oil based foam offers superior biodegradability compared to traditional polyethylene foam, breaking down naturally within months under composting conditions. Polyethylene foam, derived from petrochemicals, is resistant to degradation, often persisting in landfills for hundreds of years and contributing to plastic pollution. End-of-life options for plant-oil based foam include industrial composting and sometimes home composting, while polyethylene foam primarily requires recycling, which is limited and not widely available.
Applications in Modern Packaging
Plant-oil based foam offers sustainable alternatives for modern packaging, excelling in eco-friendly food containers, cushioning materials, and biodegradable protective wraps due to its renewable origin and compostability. Polyethylene foam remains dominant in packaging for electronics, fragile goods, and insulation because of its durability, water resistance, and excellent shock absorption properties. Brands prioritizing sustainability increasingly adopt plant-oil based foam in consumer goods packaging, while polyethylene foam continues to serve high-performance industrial and commercial packaging needs.
Health and Safety Considerations
Plant-oil based foam offers a significant health advantage over polyethylene foam by being free from harmful chemicals such as volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and toxic additives, reducing indoor air pollution and respiratory risks. Biodegradability in plant-oil foams minimizes environmental exposure to persistent microplastics, decreasing long-term ecological hazards and potential human health impacts. Polyethylene foam, derived from petrochemicals, poses greater fire hazards and chemical leaching risks during use and disposal, necessitating stricter safety protocols in handling and waste management.
Future Trends in Packaging Materials
Plant-oil based foam, derived from renewable resources such as soybean and castor oils, offers biodegradable and eco-friendly alternatives to traditional polyethylene foam used in packaging. Future trends indicate a growing shift towards sustainable packaging materials driven by increasing regulatory pressure and consumer demand for environmentally responsible products. Innovations in plant-oil based foam formulations aim to enhance mechanical properties and thermal insulation, positioning them as viable replacements for polyethylene foam in various packaging applications.
Infographic: Plant-oil based foam vs Polyethylene foam for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com