Reticulated foam offers superior breathability and cushioning for delicate packaging, while polyethylene foam provides excellent impact resistance and moisture barrier properties. Choosing between reticulated foam and polyethylene foam depends on protection requirements, with reticulated foam ideal for ventilation-sensitive items and polyethylene foam best for shock absorption and water resistance.
Table of Comparison
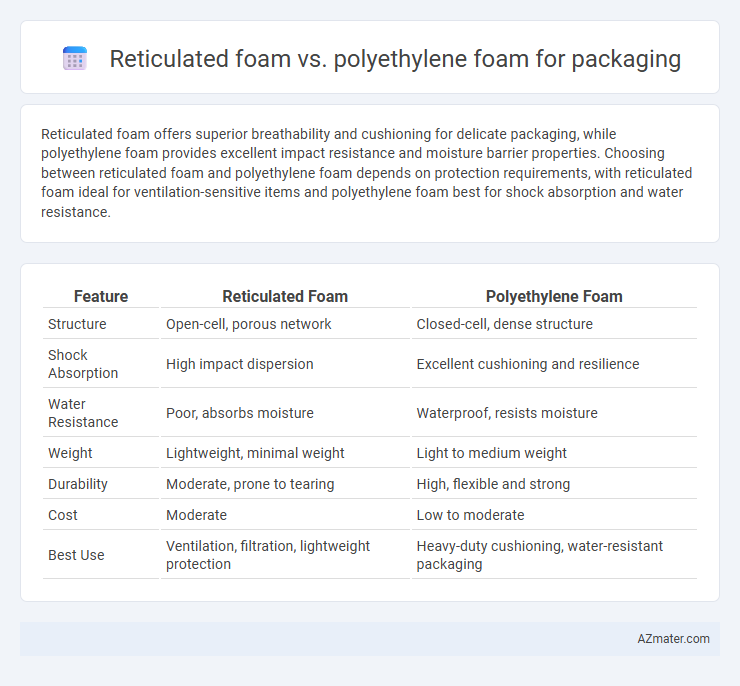
| Feature | Reticulated Foam | Polyethylene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Open-cell, porous network | Closed-cell, dense structure |
| Shock Absorption | High impact dispersion | Excellent cushioning and resilience |
| Water Resistance | Poor, absorbs moisture | Waterproof, resists moisture |
| Weight | Lightweight, minimal weight | Light to medium weight |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to tearing | High, flexible and strong |
| Cost | Moderate | Low to moderate |
| Best Use | Ventilation, filtration, lightweight protection | Heavy-duty cushioning, water-resistant packaging |
Introduction to Packaging Foams
Reticulated foam offers an open-cell structure ideal for cushioning and protecting delicate items by absorbing shocks and vibrations effectively, while polyethylene foam features a closed-cell design that provides excellent water resistance and durability for heavy-duty packaging. Packaging foams are essential in safeguarding products during transportation by minimizing impact damage and ensuring stability within shipping containers. Selecting the appropriate foam depends on factors like product fragility, environmental exposure, and required cushioning performance.
What is Reticulated Foam?
Reticulated foam is a highly porous, open-cell material commonly used in packaging for its excellent cushioning and breathability properties. Unlike polyethylene foam, which has a closed-cell structure providing water resistance and impact absorption, reticulated foam allows air and liquids to pass through, making it ideal for applications requiring ventilation or filtration. Its durable, lightweight composition ensures protection of delicate items while minimizing moisture buildup during transportation and storage.
What is Polyethylene Foam?
Polyethylene foam is a closed-cell, lightweight material known for its excellent cushioning, impact resistance, and moisture barrier properties, making it ideal for packaging applications. It provides superior protection for fragile items by absorbing shocks and vibrations during transportation. Compared to reticulated foam, polyethylene foam offers greater durability and water resistance, ensuring reliable performance in various shipping and storage environments.
Key Differences Between Reticulated and Polyethylene Foam
Reticulated foam features an open-cell structure that allows excellent airflow and drainage, making it ideal for applications requiring cushioning with ventilation, while polyethylene foam is closed-cell, providing superior water resistance and higher impact absorption for protective packaging. Reticulated foam is lightweight and highly porous, enhancing filtration and shock absorption capacities, whereas polyethylene foam offers greater durability, chemical resistance, and insulation properties. These structural characteristics define their distinct uses in packaging, with reticulated foam suited for fragile, moisture-sensitive items and polyethylene foam preferred for heavy-duty, moisture-prone environments.
Shock Absorption and Cushioning Comparison
Reticulated foam provides superior shock absorption due to its open-cell structure, allowing it to deform and recover quickly under impact, making it ideal for sensitive and high-precision packaging applications. Polyethylene foam, with its closed-cell composition, offers excellent cushioning and resistance to compression, maintaining shape and providing consistent protection against repetitive impacts. While reticulated foam excels in ventilation and drainage, polyethylene foam is generally more durable and water-resistant, enhancing overall packaging performance in various industrial and shipping environments.
Durability and Longevity: Reticulated vs Polyethylene
Reticulated foam offers high durability due to its open-cell structure, allowing excellent airflow and resistance to compression over time, making it ideal for packaging delicate items needing breathability. Polyethylene foam exhibits superior longevity with closed-cell construction, providing excellent moisture resistance, impact absorption, and permanent resilience under repeated stress, which extends its protective life in harsh shipping conditions. Choosing between reticulated and polyethylene foam depends on whether ventilation or long-term durability against environmental factors is prioritized in packaging applications.
Moisture and Chemical Resistance Properties
Reticulated foam exhibits high permeability and lower resistance to moisture, making it less suitable for environments with high humidity or exposure to liquids during packaging. Polyethylene foam offers superior moisture resistance due to its closed-cell structure, effectively protecting packaged items from water and chemical damage. Its chemical resistance extends to oils, solvents, and acids, ensuring enhanced durability compared to reticulated foam in aggressive packaging conditions.
Applications in Packaging: Use Cases
Reticulated foam offers superior airflow and drainage properties, making it ideal for packaging delicate electronics and medical instruments that require cushioning with breathability. Polyethylene foam provides excellent shock absorption and water resistance, commonly used for heavy-duty packaging of automotive parts and industrial equipment. Both foams protect goods during transit, with reticulated foam suited for lightweight, fragile items and polyethylene foam preferred for robust, impact-prone products.
Cost Considerations for Packaging Foams
Reticulated foam generally costs more than polyethylene foam due to its open-cell structure and enhanced filtration capabilities, which require more complex manufacturing processes. Polyethylene foam offers a more economical solution for packaging, providing good impact resistance and cushioning at a lower price point. When budgeting for packaging foams, it is essential to balance cost efficiency with the specific protection needs, as reticulated foam is better suited for specialized or delicate items despite its higher cost.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Packaging Needs
Reticulated foam offers high porosity and breathability, making it ideal for packaging delicate or moisture-sensitive items, while polyethylene foam provides excellent cushioning and impact resistance, suitable for heavy or fragile products. Choosing the right foam depends on your product's specific protection needs, weight, and environmental exposure, with reticulated foam favored for ventilation and filtration, and polyethylene foam preferred for shock absorption and durability. Evaluate factors such as foam density, compressibility, and chemical resistance to ensure optimal packaging performance and product safety.
Infographic: Reticulated foam vs Polyethylene foam for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com