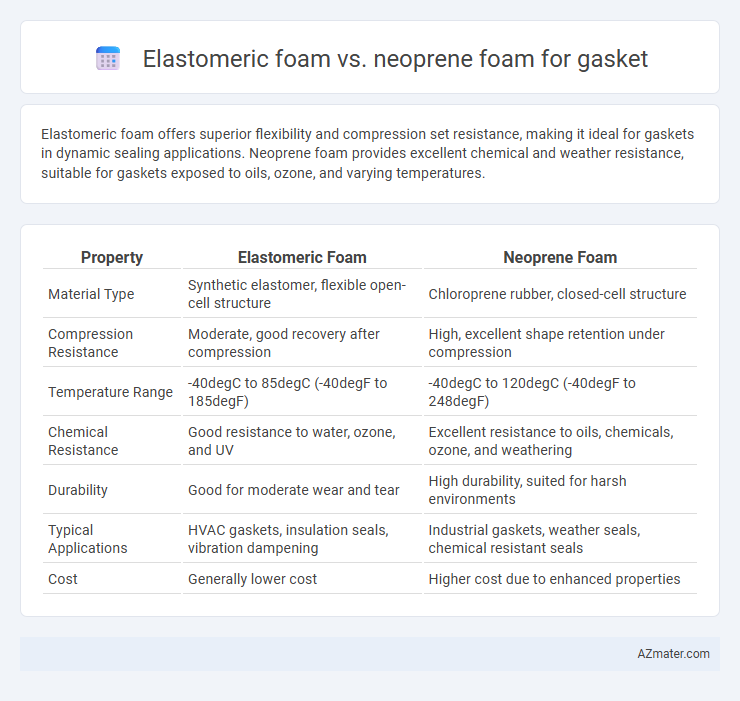
Elastomeric foam offers superior flexibility and compression set resistance, making it ideal for gaskets in dynamic sealing applications. Neoprene foam provides excellent chemical and weather resistance, suitable for gaskets exposed to oils, ozone, and varying temperatures.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Elastomeric Foam | Neoprene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic elastomer, flexible open-cell structure | Chloroprene rubber, closed-cell structure |
| Compression Resistance | Moderate, good recovery after compression | High, excellent shape retention under compression |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 85degC (-40degF to 185degF) | -40degC to 120degC (-40degF to 248degF) |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to water, ozone, and UV | Excellent resistance to oils, chemicals, ozone, and weathering |
| Durability | Good for moderate wear and tear | High durability, suited for harsh environments |
| Typical Applications | HVAC gaskets, insulation seals, vibration dampening | Industrial gaskets, weather seals, chemical resistant seals |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to enhanced properties |
Introduction to Gasket Materials
Elastomeric foam and neoprene foam are widely used gasket materials due to their flexibility, durability, and sealing properties. Elastomeric foam offers excellent compression and recovery characteristics, making it ideal for applications requiring cushioning and airtight seals. Neoprene foam provides superior resistance to weathering, oils, and chemicals, ensuring long-term performance in harsh environments.
Overview of Elastomeric Foam
Elastomeric foam is a flexible, closed-cell material widely used in gaskets for its excellent thermal insulation, moisture resistance, and compressibility. It provides superior sealing performance in HVAC systems, plumbing, and automotive applications by effectively reducing vibration and preventing air or fluid leaks. Compared to neoprene foam, elastomeric foam offers enhanced durability and environmental resistance, making it ideal for long-term sealing solutions.
Understanding Neoprene Foam
Neoprene foam, a synthetic rubber known for its excellent chemical stability and flexibility, outperforms elastomeric foam in gasket applications exposed to oils, fuels, and weathering. Its closed-cell structure provides superior resistance to water absorption, making it ideal for outdoor and marine environments. Unlike generic elastomeric foams, neoprene foam maintains durability and cushioning even under fluctuating temperatures and harsh conditions.
Key Physical Properties Comparison
Elastomeric foam offers superior flexibility and thermal insulation with excellent resistance to ozone and weathering, making it ideal for dynamic sealing applications in gaskets. Neoprene foam provides enhanced chemical resistance, moderate compression set, and good durability under varying temperature ranges, suited for harsh environments requiring robust mechanical strength. Key physical properties comparison highlights elastomeric foam's lower density and higher elongation at break, while neoprene foam excels with better tensile strength and resilience to oils and solvents.
Chemical Resistance: Elastomeric vs Neoprene
Elastomeric foam exhibits superior chemical resistance against hydrocarbons, alcohols, and mild acids, making it ideal for gaskets in automotive and industrial applications exposed to such substances. Neoprene foam demonstrates strong resistance to oils, ozone, and weathering but may degrade faster when exposed to strong solvents and certain chemicals. For gasket applications requiring sustained chemical stability and durability, elastomeric foam generally provides a more reliable performance profile compared to neoprene foam.
Thermal Performance in Gasket Applications
Elastomeric foam offers superior thermal insulation with low thermal conductivity, making it effective for maintaining temperature stability in gasket applications. Neoprene foam provides moderate thermal resistance but excels more in chemical and weather resistance rather than high-temperature insulation. Selecting elastomeric foam enhances energy efficiency and thermal protection in gaskets used in HVAC and refrigeration systems.
Durability and Longevity Analysis
Elastomeric foam gaskets exhibit superior resistance to compression set, ozone, and UV exposure, resulting in enhanced durability and extended service life compared to neoprene foam variants. Neoprene foam, while offering good chemical and weather resistance, tends to degrade faster under prolonged exposure to oils, solvents, and extreme temperatures, shortening its functional lifespan in gasket applications. The intrinsic closed-cell structure of elastomeric foam improves its longevity by minimizing moisture absorption and maintaining elasticity over time, critical factors for reliable sealing performance.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Elastomeric foam offers a cost-effective solution with widespread availability, making it ideal for large-scale gasket production where budget constraints are critical. Neoprene foam typically entails higher material costs and can be less readily available due to specialized manufacturing processes, impacting lead times. Evaluating project budgets and supply chain reliability is essential when choosing between elastomeric and neoprene foam for gasket applications.
Typical Applications and Industry Uses
Elastomeric foam gaskets are widely used in HVAC systems, refrigeration, and automotive sealing due to their excellent flexibility, thermal insulation, and resistance to water and air infiltration. Neoprene foam gaskets find extensive application in marine, electrical, and industrial machinery sectors, offering superior chemical resistance, weather durability, and moderate oil and solvent resistance. Both materials serve critical roles in sealing, cushioning, and vibration dampening across construction, automotive, and electronic industries, with selection driven by environment-specific exposure and performance requirements.
How to Choose the Right Foam for Your Gasket
Selecting the right foam for your gasket depends on the application's temperature range, chemical exposure, and required flexibility. Elastomeric foam offers superior cushioning and excellent resistance to weathering and ozone, making it ideal for outdoor or dynamic seals, while neoprene foam provides better resistance to oils, solvents, and moderate temperatures, suited for industrial environments. Assessing the environmental and mechanical stresses ensures optimal sealing performance and longevity when choosing between elastomeric and neoprene foam gaskets.
Infographic: Elastomeric foam vs Neoprene foam for Gasket
 azmater.com
azmater.com