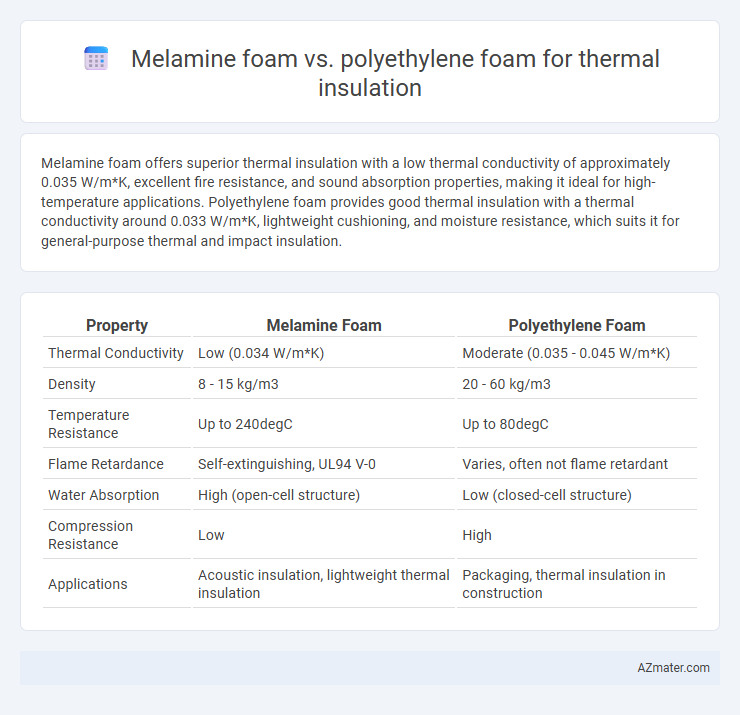
Melamine foam offers superior thermal insulation with a low thermal conductivity of approximately 0.035 W/m*K, excellent fire resistance, and sound absorption properties, making it ideal for high-temperature applications. Polyethylene foam provides good thermal insulation with a thermal conductivity around 0.033 W/m*K, lightweight cushioning, and moisture resistance, which suits it for general-purpose thermal and impact insulation.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Melamine Foam | Polyethylene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | Low (0.034 W/m*K) | Moderate (0.035 - 0.045 W/m*K) |
| Density | 8 - 15 kg/m3 | 20 - 60 kg/m3 |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 240degC | Up to 80degC |
| Flame Retardance | Self-extinguishing, UL94 V-0 | Varies, often not flame retardant |
| Water Absorption | High (open-cell structure) | Low (closed-cell structure) |
| Compression Resistance | Low | High |
| Applications | Acoustic insulation, lightweight thermal insulation | Packaging, thermal insulation in construction |
Introduction to Melamine Foam and Polyethylene Foam
Melamine foam is a lightweight, rigid, open-cell material known for its excellent thermal insulation and sound absorption properties, often used in building insulation and HVAC systems due to its fire resistance and low thermal conductivity. Polyethylene foam, a closed-cell foam, provides effective thermal insulation with superior moisture resistance and cushioning, commonly used in packaging, pipe insulation, and sports equipment. Both foams differ significantly in structure and application, with melamine foam excelling in fire-retardant environments and polyethylene foam favored for moisture protection and impact absorption.
Key Properties of Melamine Foam
Melamine foam offers superior thermal insulation due to its low thermal conductivity of around 0.035 W/mK and excellent fire resistance with self-extinguishing properties. Its open-cell structure provides effective sound absorption and breathability, making it ideal for temperature regulation in buildings and HVAC systems. Compared to polyethylene foam, melamine foam is lighter, more dimensionally stable, and resistant to mold, chemicals, and aging, enhancing long-term insulation performance in harsh environments.
Essential Characteristics of Polyethylene Foam
Polyethylene foam offers superior thermal insulation due to its closed-cell structure, providing excellent resistance to moisture and vapor absorption. Its high compressive strength and lightweight nature make it ideal for applications requiring durability and ease of installation. The material's low thermal conductivity contributes to effective heat retention and energy efficiency compared to melamine foam.
Thermal Insulation Performance Comparison
Melamine foam exhibits superior thermal insulation properties due to its low thermal conductivity, typically around 0.034 W/m*K, making it highly effective in reducing heat transfer compared to polyethylene foam, which generally has a higher thermal conductivity near 0.035-0.040 W/m*K. The open-cell structure of melamine foam enhances its ability to trap air and provide better insulation, while polyethylene foam's closed-cell configuration offers moisture resistance but slightly less thermal performance. For applications requiring maximum insulation efficiency, melamine foam outperforms polyethylene foam by maintaining lower heat flow and enhancing energy savings.
Fire Resistance: Melamine vs Polyethylene Foam
Melamine foam exhibits superior fire resistance compared to polyethylene foam, as it is inherently flame retardant and self-extinguishing, making it ideal for thermal insulation in fire-sensitive environments. Polyethylene foam, on the other hand, is combustible and tends to melt and emit toxic fumes when exposed to high temperatures, limiting its use in applications requiring stringent fire safety standards. Melamine foam's low flame spread, minimal smoke production, and high thermal stability enhance building fire safety, whereas polyethylene foam requires additional fire retardant treatments to meet similar regulations.
Sound Absorption Capabilities
Melamine foam exhibits superior sound absorption capabilities compared to polyethylene foam due to its open-cell structure, which effectively traps and dissipates sound waves. Polyethylene foam, with a closed-cell structure, provides limited sound absorption but excels in thermal insulation and impact resistance. Melamine foam's lightweight and flexible properties make it ideal for acoustic panels and noise control in environments requiring both sound damping and thermal insulation.
Durability and Longevity
Melamine foam offers superior fire resistance and maintains structural integrity at higher temperatures, enhancing its durability in thermal insulation applications. Polyethylene foam provides excellent moisture resistance and flexibility, contributing to its longevity but may degrade faster under UV exposure and high heat. When selecting between the two, melamine foam generally outperforms polyethylene foam in long-term thermal insulation durability due to its inherent fire retardant properties and thermal stability.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Melamine foam offers lightweight, flexible installation with excellent fire resistance and minimal odor, making it ideal for complex or confined spaces, while polyethylene foam requires precise cutting and secure sealing to prevent thermal bridging and moisture ingress. Melamine foam's non-toxic properties reduce maintenance efforts and do not degrade when exposed to moisture, whereas polyethylene foam may require periodic inspection for compression or damage due to its susceptibility to UV and chemical exposure. Installation of melamine foam typically demands specialized adhesives or mechanical fastening compatible with its open-cell structure, contrasting with polyethylene foam's compatibility with tape and standard fasteners, influencing long-term upkeep strategies.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Melamine foam offers superior thermal insulation with low density and exceptional fire resistance, but it is derived from synthetic resins that pose recycling challenges and contribute to environmental pollution. Polyethylene foam, while less effective in thermal insulation, is more easily recyclable and can be produced from bio-based sources, enhancing its sustainability profile. Choosing between these materials requires balancing thermal performance with environmental impact, favoring polyethylene foam for lower ecological footprint and melamine foam for advanced insulation needs.
Choosing the Right Foam for Thermal Insulation Applications
Melamine foam offers excellent thermal insulation with a low thermal conductivity of approximately 0.035 W/m*K, making it ideal for high-temperature applications and sound absorption. Polyethylene foam has a higher thermal conductivity around 0.04 to 0.05 W/m*K but provides superior moisture resistance and flexibility, suitable for lightweight insulation needs in damp environments. Choosing the right foam depends on the specific thermal performance requirements, environmental conditions, and mechanical properties needed for the application.
Infographic: Melamine foam vs Polyethylene foam for Thermal insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com