Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers lightweight cushioning and excellent flexibility for shoe soles, while polyurethane (PU) foam provides superior durability and abrasion resistance. EVA is preferred for comfort and shock absorption, whereas PU is ideal for long-lasting wear and structural support.
Table of Comparison
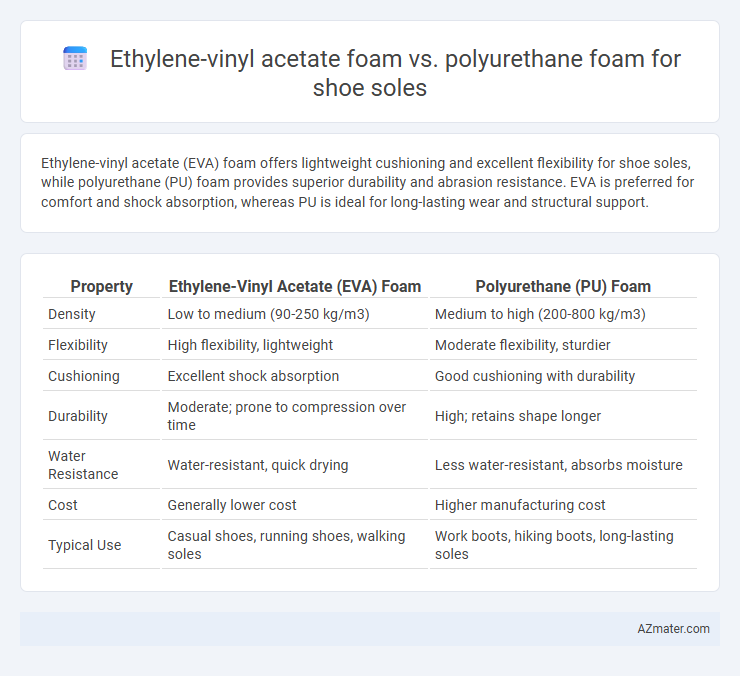
| Property | Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA) Foam | Polyurethane (PU) Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Density | Low to medium (90-250 kg/m3) | Medium to high (200-800 kg/m3) |
| Flexibility | High flexibility, lightweight | Moderate flexibility, sturdier |
| Cushioning | Excellent shock absorption | Good cushioning with durability |
| Durability | Moderate; prone to compression over time | High; retains shape longer |
| Water Resistance | Water-resistant, quick drying | Less water-resistant, absorbs moisture |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher manufacturing cost |
| Typical Use | Casual shoes, running shoes, walking soles | Work boots, hiking boots, long-lasting soles |
Introduction to Shoe Sole Materials
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam and polyurethane (PU) foam are among the most commonly used materials for shoe soles due to their unique properties tailored to footwear performance. EVA foam offers exceptional cushioning, lightweight construction, and excellent flexibility, making it ideal for athletic and casual shoes. PU foam provides superior durability, high resilience, and enhanced shock absorption, making it a preferred choice for work boots and high-performance footwear.
What is Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA) Foam?
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam is a polymer material widely used in shoe soles for its lightweight, flexible, and shock-absorbing properties. Compared to polyurethane foam, EVA offers excellent cushioning and resilience while maintaining superior water resistance and UV stability, making it ideal for athletic and casual footwear. Its ability to compress and return to its original shape enhances comfort and durability in various walking and running conditions.
What is Polyurethane (PU) Foam?
Polyurethane (PU) foam is a versatile polymer material widely used in shoe soles for its excellent durability, cushioning, and flexibility. Compared to Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam, PU foam offers superior abrasion resistance and enhanced load-bearing capacity, making it ideal for high-performance footwear. Its ability to absorb impact and retain shape ensures long-lasting comfort and support in various shoe sole applications.
Cushioning and Comfort: EVA vs PU Foam
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam provides excellent cushioning with lightweight flexibility, making it ideal for shock absorption and long-lasting comfort in shoe soles. Polyurethane (PU) foam offers superior durability and higher density support, resulting in enhanced resilience and consistent cushioning under pressure. EVA is preferred for its softness and flexibility, while PU is favored for its durability and firm comfort in high-impact footwear applications.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam exhibits superior durability and resistance to compression set compared to polyurethane (PU) foam, making it more suitable for shoe soles subjected to frequent impact and flexing. EVA's lightweight and closed-cell structure provide enhanced shock absorption while maintaining structural integrity over extended use, whereas PU foam tends to degrade faster under repeated stress due to its open-cell design. Longevity tests indicate EVA soles retain cushioning and resilience longer than PU, especially in moist or outdoor conditions where PU foam is prone to hydrolytic breakdown.
Weight and Flexibility Differences
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam is significantly lighter than polyurethane (PU) foam, making it ideal for lightweight shoe sole applications. EVA offers superior flexibility and cushioning due to its closed-cell structure, enhancing comfort and shock absorption during movement. In contrast, PU foam, while denser and heavier, provides greater durability and resistance to compression but sacrifices some flexibility compared to EVA.
Shock Absorption and Energy Return
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers excellent shock absorption due to its low density and flexible cushioning properties, making it highly effective in reducing impact forces during walking or running. Polyurethane (PU) foam provides superior energy return with a denser and more resilient structure, enhancing propulsion and overall performance in shoe soles. EVA remains lighter and more durable in moist conditions, while PU foam delivers firmer support and better long-term rebound, influencing choice based on specific footwear requirements.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers lower raw material and production costs compared to polyurethane (PU) foam, making it a cost-effective choice for mass-produced shoe soles. EVA foam's straightforward manufacturing process involves simpler molding and foaming techniques, reducing cycle times and energy consumption in comparison to the more complex chemical reactions and curing needed for PU foam. Manufacturers prioritize EVA foam when aiming for economical scalability and faster production without significantly compromising cushioning and flexibility.
Environmental Impact: EVA vs PU
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam is considered more environmentally friendly than polyurethane (PU) foam due to its lower CO2 emissions during production and higher potential for recycling and biodegradability. PU foam production involves toxic chemicals such as isocyanates, which can contribute to air and water pollution, making it less sustainable. EVA's reduced reliance on petroleum-based materials and its capacity for closed-loop recycling make it a preferable choice for eco-conscious shoe sole manufacturing.
Best Applications: Choosing the Right Foam for Your Shoes
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers superior cushioning, flexibility, and lightweight properties, making it ideal for running shoes, casual footwear, and insoles requiring shock absorption and comfort. Polyurethane (PU) foam provides enhanced durability, higher density, and excellent abrasion resistance, suitable for work boots, hiking shoes, and footwear demanding long-lasting support and resilience. Selecting EVA foam optimizes comfort and flexibility, while PU foam ensures structural strength and wear resistance in shoe soles.
Infographic: Ethylene-vinyl acetate foam vs Polyurethane foam for Shoe sole
 azmater.com
azmater.com