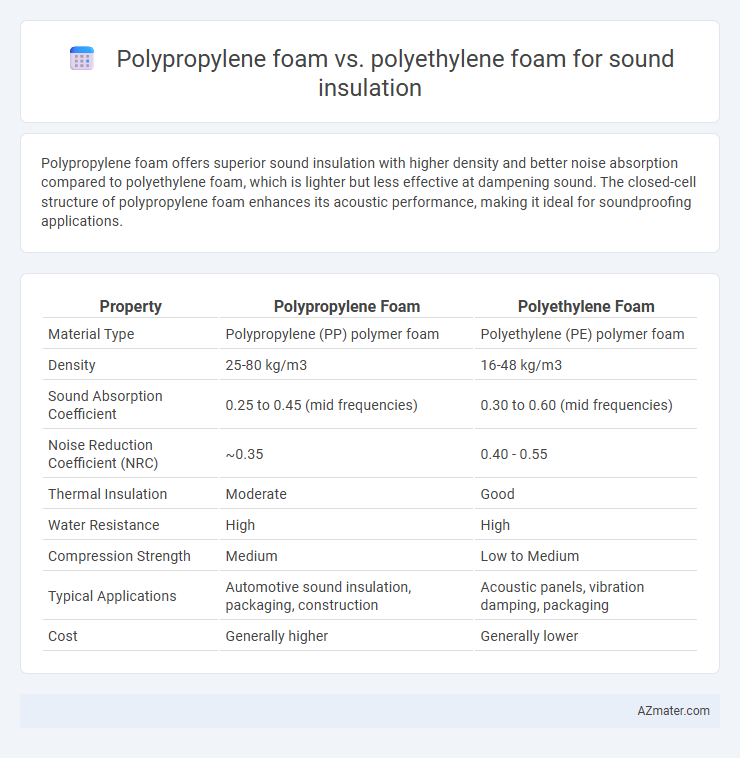
Polypropylene foam offers superior sound insulation with higher density and better noise absorption compared to polyethylene foam, which is lighter but less effective at dampening sound. The closed-cell structure of polypropylene foam enhances its acoustic performance, making it ideal for soundproofing applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polypropylene Foam | Polyethylene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Polypropylene (PP) polymer foam | Polyethylene (PE) polymer foam |
| Density | 25-80 kg/m3 | 16-48 kg/m3 |
| Sound Absorption Coefficient | 0.25 to 0.45 (mid frequencies) | 0.30 to 0.60 (mid frequencies) |
| Noise Reduction Coefficient (NRC) | ~0.35 | 0.40 - 0.55 |
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate | Good |
| Water Resistance | High | High |
| Compression Strength | Medium | Low to Medium |
| Typical Applications | Automotive sound insulation, packaging, construction | Acoustic panels, vibration damping, packaging |
| Cost | Generally higher | Generally lower |
Introduction to Acoustic Foam Materials
Polypropylene foam and polyethylene foam are widely used acoustic foam materials for sound insulation due to their lightweight and cellular structure. Polypropylene foam offers excellent noise reduction with high tensile strength and thermal stability, making it suitable for industrial and automotive soundproofing applications. Polyethylene foam provides superior impact absorption and moisture resistance, often favored in packaging and construction for both sound dampening and vibration control.
Understanding Polypropylene Foam Properties
Polypropylene foam exhibits higher stiffness, excellent chemical resistance, and superior thermal stability compared to polyethylene foam, making it more durable for sound insulation applications. Its open-cell structure enhances sound absorption by trapping and dissipating acoustic energy effectively, while polyethylene foam, typically closed-cell, provides better impact resistance but less acoustic performance. Polypropylene foam's lightweight and moisture-resistant properties contribute to long-term sound insulation efficiency in diverse environments.
Overview of Polyethylene Foam Characteristics
Polyethylene foam is a closed-cell, lightweight material known for its excellent sound absorption and impact resistance, making it highly effective for sound insulation applications. Its thermal stability and moisture resistance contribute to long-lasting performance in diverse environments, ensuring consistent acoustic dampening. Compared to polypropylene foam, polyethylene foam generally offers better cushioning and noise reduction due to its higher density and closed-cell structure.
Sound Insulation Performance Comparison
Polyethylene foam generally provides superior sound insulation compared to polypropylene foam due to its higher density and cellular structure, which better absorbs and dampens airborne noise. Polypropylene foam often exhibits greater durability and chemical resistance but typically has lower sound absorption coefficients, making it less effective for reducing sound transmission in applications requiring optimal acoustic performance. For environments prioritizing sound insulation, polyethylene foam's combination of density and flexibility results in more efficient noise reduction across a broader range of frequencies.
Density and Thickness Impacts on Sound Absorption
Polypropylene foam and polyethylene foam differ significantly in density and thickness, which directly affect their sound insulation properties. Higher density polypropylene foam typically offers improved sound absorption by reducing sound wave transmission, while polyethylene foam's lower density requires increased thickness to achieve comparable acoustic performance. Optimizing foam thickness in polyethylene materials compensates for its lower density, enhancing sound absorption especially in mid to high-frequency ranges.
Durability and Longevity in Acoustic Applications
Polypropylene foam offers superior durability and resistance to wear, making it ideal for long-term acoustic insulation in environments exposed to mechanical stress and moisture. Polyethylene foam provides excellent cushioning but tends to degrade faster under UV exposure and heavy compression, reducing its lifespan in soundproofing applications. For sustained acoustic performance, polypropylene foam maintains structural integrity and acoustic properties longer than polyethylene foam.
Moisture and Chemical Resistance Differences
Polyethylene foam exhibits superior moisture resistance compared to polypropylene foam due to its closed-cell structure, making it less prone to water absorption and ideal for damp environments in sound insulation applications. Polypropylene foam, while offering lightweight and decent acoustic properties, is more susceptible to chemical degradation and moisture penetration, which can compromise its insulating performance over time. Chemical resistance in polyethylene foam is generally higher, providing better durability and longevity in environments exposed to oils, solvents, and other chemicals during soundproofing installations.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
Polyethylene foam offers better cost-effectiveness for sound insulation due to its widespread availability and lower material price compared to polypropylene foam. Polypropylene foam provides superior sound absorption qualities but tends to be more expensive and less readily available in standard market quantities. For large-scale projects requiring economical sound insulation, polyethylene foam is often the preferred choice due to its balance of performance, cost, and accessibility.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polypropylene foam offers superior sound insulation properties with a lower environmental impact due to its higher thermal stability and resistance to chemical degradation, enhancing its longevity and reducing landfill waste. Polyethylene foam, while effective in sound absorption, is less environmentally friendly because it tends to degrade faster, releasing pollutants and microplastics, complicating recycling processes. Both materials are recyclable, but polypropylene's chemical structure allows for more efficient recycling and repurposing, contributing to a more sustainable lifecycle in sound insulation applications.
Choosing the Best Foam for Sound Insulation Needs
Polyethylene foam offers superior sound absorption due to its closed-cell structure that effectively reduces airborne noise and vibrations, making it ideal for sound insulation. Polypropylene foam, while lightweight and resistant to chemicals, generally provides less acoustic dampening compared to polyethylene foam. Selecting the best foam depends on balancing soundproofing effectiveness with factors like density, durability, and environmental resistance for specific insulation requirements.
Infographic: Polypropylene foam vs Polyethylene foam for Sound insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com