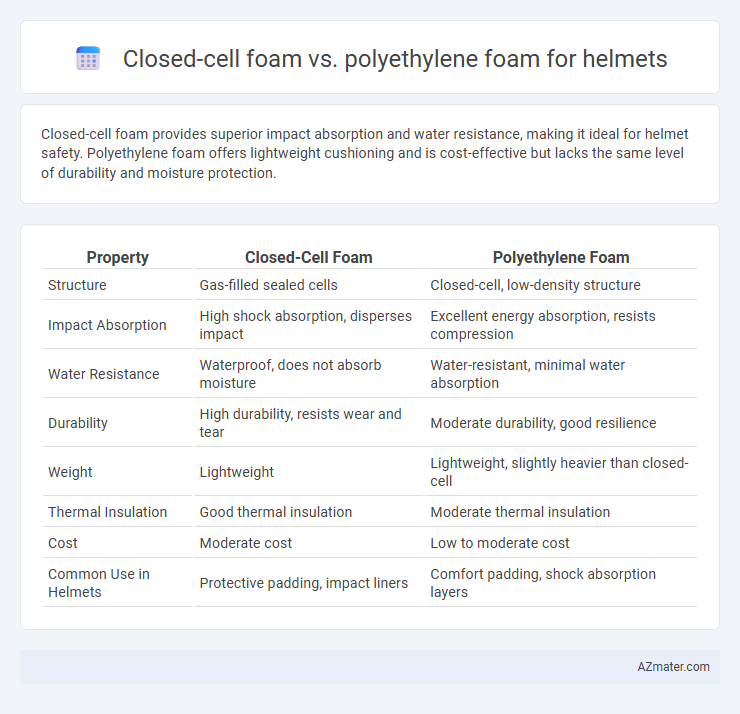
Closed-cell foam provides superior impact absorption and water resistance, making it ideal for helmet safety. Polyethylene foam offers lightweight cushioning and is cost-effective but lacks the same level of durability and moisture protection.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Closed-Cell Foam | Polyethylene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Gas-filled sealed cells | Closed-cell, low-density structure |
| Impact Absorption | High shock absorption, disperses impact | Excellent energy absorption, resists compression |
| Water Resistance | Waterproof, does not absorb moisture | Water-resistant, minimal water absorption |
| Durability | High durability, resists wear and tear | Moderate durability, good resilience |
| Weight | Lightweight | Lightweight, slightly heavier than closed-cell |
| Thermal Insulation | Good thermal insulation | Moderate thermal insulation |
| Cost | Moderate cost | Low to moderate cost |
| Common Use in Helmets | Protective padding, impact liners | Comfort padding, shock absorption layers |
Overview of Helmet Foam Materials
Closed-cell foam offers superior impact absorption and water resistance, making it a popular choice for helmet liners where durability and protection are critical. Polyethylene foam provides excellent lightweight cushioning with moderate shock attenuation, ideal for helmets prioritizing comfort and breathability. Both materials contribute to enhanced helmet safety standards by balancing energy absorption and wearer comfort.
What is Closed-Cell Foam?
Closed-cell foam is a dense, impermeable material characterized by tightly packed cells that prevent air and moisture penetration, making it highly effective for impact absorption in helmets. Unlike polyethylene foam, closed-cell foam offers superior resistance to water, chemicals, and environmental factors, enhancing helmet durability and safety in various conditions. Its rigid structure provides enhanced cushioning and energy dispersion, crucial for protecting the head during collisions and falls.
What is Polyethylene Foam?
Polyethylene foam is a lightweight, closed-cell foam known for its excellent impact absorption properties and durability, making it ideal for helmet padding. It offers superior resistance to water, chemicals, and abrasion compared to open-cell foams, enhancing helmet longevity and safety. Its high energy return and cushioning capabilities contribute to effective shock dispersion during impact in protective gear.
Key Properties: Closed-Cell vs Polyethylene Foam
Closed-cell foam offers superior impact absorption and water resistance, making it ideal for helmet safety and durability. Polyethylene foam provides excellent shock attenuation with lightweight properties but tends to absorb more moisture than closed-cell foam. Both materials feature high compressive strength, yet closed-cell foam's closed structure ensures enhanced insulation and longevity in helmet applications.
Impact Absorption Capabilities
Closed-cell foam exhibits superior impact absorption capabilities for helmets due to its dense structure that effectively disperses energy upon impact, reducing force transmission to the head. Polyethylene foam, while lightweight and resilient, offers moderate impact absorption but may compress more under repeated impacts, decreasing its protective performance over time. Helmets utilizing closed-cell foam typically provide enhanced shock attenuation and increased durability, making them preferable for high-impact safety applications.
Comfort and Fit Differences
Closed-cell foam offers superior impact absorption and moisture resistance, enhancing helmet comfort by maintaining dryness and reducing pressure points. Polyethylene foam provides a lightweight, flexible fit but may absorb sweat, potentially causing discomfort during extended use. The choice between the two influences helmet ergonomics, with closed-cell foam better suited for long-term wear and polyethylene foam favored for its adaptability to head shape.
Durability and Longevity
Closed-cell foam offers superior durability and longevity for helmets due to its dense structure that resists water absorption, compression, and environmental wear, maintaining protective performance over time. Polyethylene foam, while lightweight and impact-absorbing, tends to degrade faster under repeated stress and exposure to moisture, reducing its effective lifespan. Choosing closed-cell foam ensures enhanced helmet resilience in harsh conditions, extending service life and consistent safety.
Weight Considerations for Helmets
Closed-cell foam offers superior impact absorption while maintaining a lightweight profile, making it ideal for helmet construction where minimal weight is critical. Polyethylene foam, although providing good cushioning, tends to be denser and heavier, potentially increasing helmet weight and affecting wearer comfort during extended use. Choosing closed-cell foam can significantly enhance helmet performance by reducing overall mass without compromising safety standards.
Cost Comparison
Closed-cell foam typically offers higher durability and better impact absorption but comes at a higher price point compared to polyethylene foam. Polyethylene foam is more cost-effective, providing adequate protection for budget-conscious helmet manufacturing while maintaining lightweight properties. When evaluating overall cost, closed-cell foam's longevity may justify its initial investment despite polyethylene foam's lower upfront expenses.
Best Applications: Choosing the Right Foam for Helmets
Closed-cell foam offers superior moisture resistance and impact absorption, making it ideal for helmets used in high-impact sports and outdoor activities. Polyethylene foam provides excellent shock absorption and lightweight cushioning, suited for helmets in cycling and recreational use where ventilation and comfort are priorities. Selecting the right foam depends on balancing durability, weight, and protection level specific to the helmet's intended environment and activity.
Infographic: Closed-cell foam vs Polyethylene foam for Helmets
 azmater.com
azmater.com