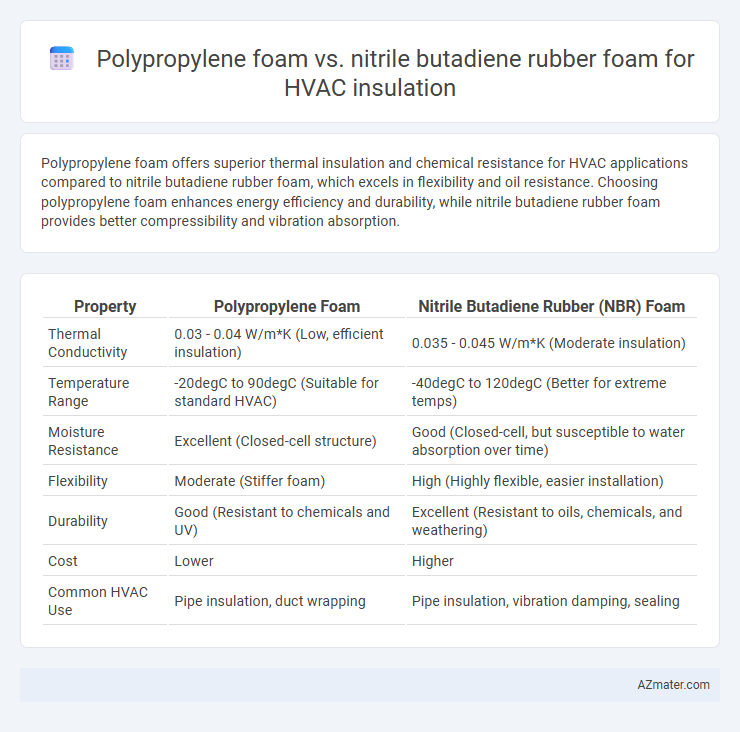
Polypropylene foam offers superior thermal insulation and chemical resistance for HVAC applications compared to nitrile butadiene rubber foam, which excels in flexibility and oil resistance. Choosing polypropylene foam enhances energy efficiency and durability, while nitrile butadiene rubber foam provides better compressibility and vibration absorption.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polypropylene Foam | Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.03 - 0.04 W/m*K (Low, efficient insulation) | 0.035 - 0.045 W/m*K (Moderate insulation) |
| Temperature Range | -20degC to 90degC (Suitable for standard HVAC) | -40degC to 120degC (Better for extreme temps) |
| Moisture Resistance | Excellent (Closed-cell structure) | Good (Closed-cell, but susceptible to water absorption over time) |
| Flexibility | Moderate (Stiffer foam) | High (Highly flexible, easier installation) |
| Durability | Good (Resistant to chemicals and UV) | Excellent (Resistant to oils, chemicals, and weathering) |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Common HVAC Use | Pipe insulation, duct wrapping | Pipe insulation, vibration damping, sealing |
Introduction to HVAC Insulation Materials
Polypropylene foam and nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) foam are widely used HVAC insulation materials due to their thermal resistance and durability. Polypropylene foam offers low thermal conductivity and is lightweight, making it ideal for reducing energy loss in ductwork and pipes. NBR foam provides excellent flexibility, moisture resistance, and sound absorption, enhancing HVAC system efficiency and longevity in diverse environmental conditions.
Overview of Polypropylene (PP) Foam
Polypropylene (PP) foam is a lightweight, closed-cell material with excellent thermal insulation properties and high resistance to moisture, chemicals, and heat, making it ideal for HVAC insulation. Its high tensile strength and dimensional stability contribute to long-term durability and energy efficiency in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems. Compared to Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) foam, PP foam offers superior resistance to water absorption and chemical degradation, enhancing performance in demanding environments.
Overview of Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) Foam
Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) foam is a synthetic rubber material widely used for HVAC insulation due to its excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals, as well as its superior thermal insulation properties. It exhibits high flexibility, durability, and resistance to temperature variations, making it ideal for preventing condensation and heat loss in HVAC systems. Compared to polypropylene foam, NBR foam offers enhanced mechanical strength and better performance in environments exposed to aggressive substances.
Thermal Insulation Performance
Polypropylene foam exhibits superior thermal insulation performance for HVAC applications due to its closed-cell structure, which reduces heat transfer and provides excellent resistance to moisture absorption. Nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) foam offers good thermal insulation but generally has higher thermal conductivity compared to polypropylene foam, making it less effective in minimizing energy loss. Polypropylene foam's lower density and enhanced insulating properties make it a preferred choice in energy-efficient HVAC insulation systems.
Moisture and Vapor Resistance
Polypropylene foam exhibits superior moisture resistance and low vapor permeability, making it highly effective in preventing condensation and mold growth in HVAC insulation. Nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) foam offers good vapor resistance but tends to absorb more moisture over time compared to polypropylene, which can reduce its insulating efficiency. Selecting polypropylene foam enhances long-term durability and energy efficiency by maintaining consistent thermal performance under high humidity conditions.
Durability and Mechanical Strength
Polypropylene foam exhibits superior durability and mechanical strength for HVAC insulation due to its high resistance to compression and excellent impact absorption, maintaining integrity under fluctuating temperatures and humidity. Nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) foam offers good flexibility and moderate mechanical strength but tends to degrade faster under prolonged exposure to oils, chemicals, and UV radiation compared to polypropylene foam. When prioritizing long-term performance in HVAC systems, polypropylene foam provides greater resilience and sustained mechanical properties essential for insulation applications.
Fire Resistance and Safety Aspects
Polypropylene foam offers superior fire resistance with a higher ignition point and lower smoke emission compared to nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) foam, enhancing safety in HVAC insulation applications. NBR foam, while providing excellent flexibility and chemical resistance, tends to have lower thermal stability and emits more toxic gases during combustion, posing greater health risks in fire scenarios. Choosing polypropylene foam improves overall fire safety by minimizing flame spread and toxic smoke, crucial for maintaining safe indoor air quality and complying with stringent building codes.
Installation and Flexibility in HVAC Systems
Polypropylene foam offers lightweight and rigid properties that simplify installation in HVAC systems, enabling quick shaping and cutting for precise duct insulation. Nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) foam provides superior flexibility and resilience, allowing it to conform easily to complex shapes and tight spaces, which enhances sealing and minimizes air leaks. While polypropylene foam supports ease of handling during installation, NBR foam's elasticity ensures long-term durability and adaptability under various thermal expansion conditions in HVAC applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polypropylene foam exhibits a lower environmental footprint due to its recyclability and lower greenhouse gas emissions during production compared to nitrile butadiene rubber foam, which relies on synthetic rubber derived from petroleum with higher carbon intensity. Polypropylene's closed-cell structure enhances thermal insulation efficiency, reducing energy consumption and supporting sustainable building goals, while nitrile foam's durability offers long-term use but can present challenges in end-of-life disposal due to limited recycling options. Choosing polypropylene foam aligns better with circular economy principles and reduced ecological impact in HVAC insulation applications.
Cost Comparison and Application Recommendations
Polypropylene foam offers a lower cost solution for HVAC insulation compared to nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) foam, making it ideal for budget-sensitive projects. NBR foam provides superior durability and resistance to oils and chemicals, which is crucial for applications requiring enhanced thermal insulation and long-term performance. For general HVAC insulation, polypropylene foam is recommended, while NBR foam suits environments with exposure to harsh conditions or higher mechanical stress.
Infographic: Polypropylene foam vs Nitrile butadiene rubber foam for HVAC insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com