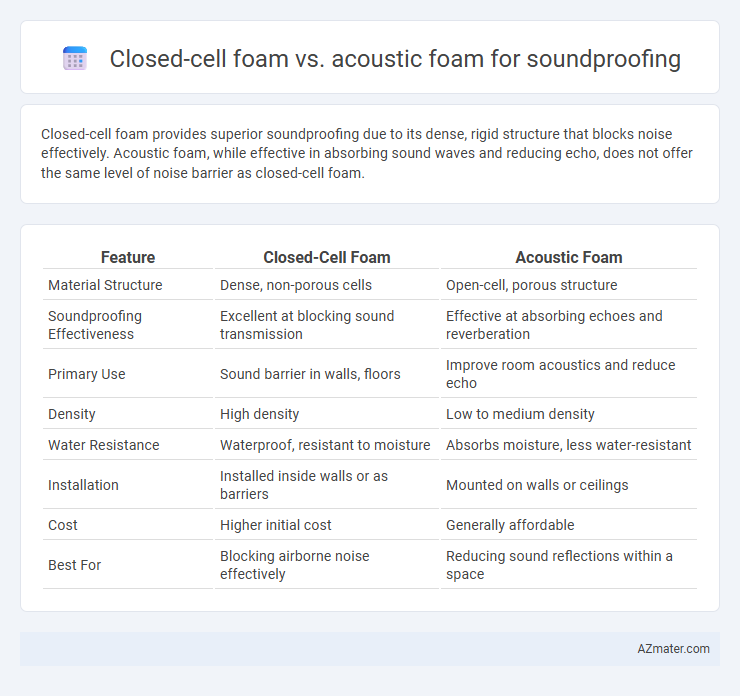
Closed-cell foam provides superior soundproofing due to its dense, rigid structure that blocks noise effectively. Acoustic foam, while effective in absorbing sound waves and reducing echo, does not offer the same level of noise barrier as closed-cell foam.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Closed-Cell Foam | Acoustic Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Structure | Dense, non-porous cells | Open-cell, porous structure |
| Soundproofing Effectiveness | Excellent at blocking sound transmission | Effective at absorbing echoes and reverberation |
| Primary Use | Sound barrier in walls, floors | Improve room acoustics and reduce echo |
| Density | High density | Low to medium density |
| Water Resistance | Waterproof, resistant to moisture | Absorbs moisture, less water-resistant |
| Installation | Installed inside walls or as barriers | Mounted on walls or ceilings |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Generally affordable |
| Best For | Blocking airborne noise effectively | Reducing sound reflections within a space |
Introduction to Soundproofing Materials
Closed-cell foam offers superior density and moisture resistance, making it effective for blocking sound transmission through walls and floors. Acoustic foam, designed with an open-cell structure, primarily absorbs sound waves to reduce echoes and improve room acoustics rather than blocking noise. Selecting between these materials depends on whether the goal is sound absorption or sound insulation in soundproofing applications.
What is Closed-Cell Foam?
Closed-cell foam is a dense, rigid material composed of tightly packed foam cells that are completely enclosed, making it highly resistant to air and moisture infiltration. This structure provides excellent thermal insulation and soundproofing qualities by effectively blocking and absorbing sound waves, making it ideal for reducing noise transmission in walls, ceilings, and floors. Compared to traditional acoustic foam, closed-cell foam offers superior durability, water resistance, and impact absorption, enhancing its effectiveness in soundproofing applications in environments with moisture or structural stress.
What is Acoustic Foam?
Acoustic foam is a specialized material designed to absorb sound waves, reducing echoes and reverberation within a room to improve sound quality. Unlike closed-cell foam, which is dense and primarily used for insulation and moisture resistance, acoustic foam features an open-cell structure that traps and dissipates sound energy. Its effectiveness in soundproofing stems from its ability to convert sound waves into small amounts of heat, making it a preferred choice for studios, theaters, and other environments requiring controlled acoustics.
Soundproofing Mechanisms: Absorption vs. Blocking
Closed-cell foam primarily functions by blocking sound transmission through its dense, impermeable structure that reflects and inhibits airborne noise, making it highly effective for soundproofing applications requiring noise isolation. Acoustic foam, on the other hand, emphasizes sound absorption by trapping sound waves within its porous, open-cell design, reducing echo and reverberation inside rooms without significantly blocking sound from passing through walls. The key difference lies in closed-cell foam's density and impermeability for sound blocking, while acoustic foam's open-cell morphology enhances sound wave absorption and acoustic treatment.
Performance Comparison: Closed-Cell Foam vs Acoustic Foam
Closed-cell foam offers superior soundproofing due to its dense, airtight structure that effectively blocks airborne noise and vibration, making it ideal for high-performance sound isolation. Acoustic foam, typically open-cell, excels in sound absorption by reducing echo and reverberation within rooms, but it lacks the mass to prevent sound transmission through walls. For optimal soundproofing, closed-cell foam delivers better noise barrier properties, while acoustic foam improves sound quality by minimizing reflections.
Applications and Use Cases
Closed-cell foam excels in applications requiring moisture resistance and structural support, making it ideal for insulation in walls, roofs, and outdoor environments. Acoustic foam specializes in sound absorption, effectively reducing echo and reverberation in recording studios, home theaters, and office spaces. Both materials serve distinct purposes: closed-cell foam enhances thermal insulation and durability, while acoustic foam improves sound clarity and noise control.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Closed-cell foam offers superior water resistance and durability, making it suitable for environments with high moisture and easier to maintain with minimal upkeep. Acoustic foam primarily focuses on sound absorption and often requires more frequent cleaning and replacement due to dust accumulation and wear. Installation of closed-cell foam typically demands specialized tools and adhesives for a tight seal, whereas acoustic foam panels are easier to install using simple mounting methods like adhesive strips or hooks.
Cost Analysis and Budget Considerations
Closed-cell foam generally costs more upfront than acoustic foam due to its denser structure and superior sound insulation properties, making it a premium choice for effective soundproofing. Acoustic foam, being lighter and less dense, offers a more budget-friendly solution ideal for moderate sound absorption but may require thicker or more panels to achieve similar results. When balancing cost and performance, consider long-term durability and installation expenses, as closed-cell foam can provide better value in high-demand environments despite higher initial investment.
Durability and Longevity
Closed-cell foam offers superior durability and longevity compared to acoustic foam due to its dense, rigid structure that resists moisture, compression, and wear over time. Acoustic foam, while effective for sound absorption, typically has a more open-cell design that can degrade faster under environmental stress and frequent use. For long-term soundproofing solutions, closed-cell foam provides enhanced resistance to physical damage and maintains its acoustic properties much longer.
Which Foam is Best for Your Soundproofing Needs?
Closed-cell foam offers superior soundproofing due to its dense, airtight structure that effectively blocks and absorbs low-frequency sounds, making it ideal for preventing sound transmission. Acoustic foam, with its open-cell design, excels at reducing echo and improving room acoustics by absorbing mid to high-frequency sounds but provides less sound isolation compared to closed-cell foam. For best soundproofing results, choose closed-cell foam if blocking noise is the priority, or acoustic foam for enhancing sound quality within a space.
Infographic: Closed-cell foam vs Acoustic foam for Soundproofing
 azmater.com
azmater.com