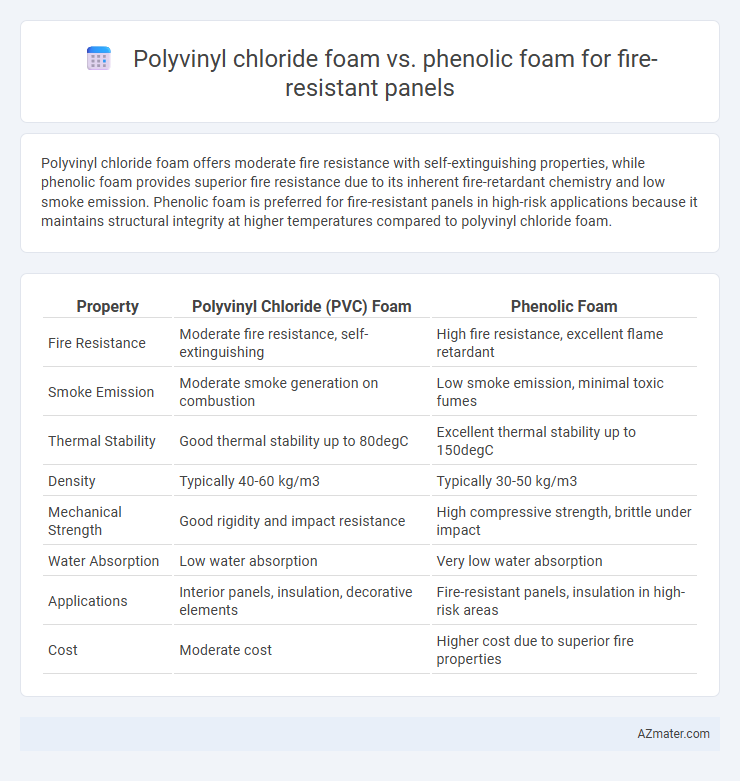
Polyvinyl chloride foam offers moderate fire resistance with self-extinguishing properties, while phenolic foam provides superior fire resistance due to its inherent fire-retardant chemistry and low smoke emission. Phenolic foam is preferred for fire-resistant panels in high-risk applications because it maintains structural integrity at higher temperatures compared to polyvinyl chloride foam.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Foam | Phenolic Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Fire Resistance | Moderate fire resistance, self-extinguishing | High fire resistance, excellent flame retardant |
| Smoke Emission | Moderate smoke generation on combustion | Low smoke emission, minimal toxic fumes |
| Thermal Stability | Good thermal stability up to 80degC | Excellent thermal stability up to 150degC |
| Density | Typically 40-60 kg/m3 | Typically 30-50 kg/m3 |
| Mechanical Strength | Good rigidity and impact resistance | High compressive strength, brittle under impact |
| Water Absorption | Low water absorption | Very low water absorption |
| Applications | Interior panels, insulation, decorative elements | Fire-resistant panels, insulation in high-risk areas |
| Cost | Moderate cost | Higher cost due to superior fire properties |
Introduction to Fire Resistant Panels
Fire resistant panels commonly utilize Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam and Phenolic foam for their exceptional fire retardant properties and thermal insulation performance. Polyvinyl chloride foam offers high durability, self-extinguishing capabilities, and low smoke emissions, making it ideal for fire resistant cladding and partition systems. Phenolic foam provides superior fire resistance with low heat release rates and excellent structural stability under high temperatures, widely applied in industrial and commercial fire barrier panels.
Overview of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Foam
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) foam is a lightweight, closed-cell material known for its excellent fire resistance and low smoke emission, making it ideal for fire-resistant panels. It offers good thermal insulation properties, mechanical strength, and chemical stability, enhancing panel durability in various applications. PVC foam's resistance to flame propagation and its ability to self-extinguish contribute significantly to meeting stringent fire safety standards in construction and industrial uses.
Overview of Phenolic Foam
Phenolic foam is a high-performance insulating material known for its superior fire resistance, low smoke emission, and excellent thermal insulation properties, making it ideal for fire-resistant panels. Its closed-cell structure enhances durability and prevents moisture absorption, contributing to long-term structural stability in harsh environments. Compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam, phenolic foam offers enhanced fire retardancy and low toxicity during combustion, aligning with stringent safety standards in construction and industrial applications.
Fire Resistance Properties: PVC Foam vs Phenolic Foam
Phenolic foam exhibits superior fire resistance compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam, offering higher ignition temperatures and lower smoke emission during combustion. PVC foam tends to melt and produces toxic gases when exposed to high heat, whereas phenolic foam chars and acts as a barrier to flame propagation. Fire-resistant panels utilizing phenolic foam provide enhanced safety in building applications due to their excellent flame retardancy and minimal heat release.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam exhibits moderate thermal insulation with a thermal conductivity typically around 0.038-0.045 W/m*K, making it effective for fire-resistant panels requiring lightweight and moisture resistance. Phenolic foam outperforms PVC foam in thermal performance, boasting lower thermal conductivity values approximately 0.020-0.025 W/m*K and superior fire retardant characteristics due to its char-forming nature and self-extinguishing properties. The enhanced thermal resistance of phenolic foam contributes to better energy efficiency and fire safety in panel applications subjected to high-temperature environments.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Analysis
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam exhibits superior mechanical strength with high impact resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for fire-resistant panels subjected to dynamic loads. Phenolic foam offers excellent thermal stability and inherent fire resistance but tends to be more brittle, resulting in lower impact strength compared to PVC foam. Durability analysis reveals PVC foam maintains structural integrity longer under cyclic stress and environmental exposure, whereas phenolic foam can degrade faster due to its rigid cellular structure despite better fire retardant properties.
Smoke and Toxicity in Fire Scenarios
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam emits hydrogen chloride gas and dense black smoke when exposed to fire, which increases toxicity and poses significant inhalation hazards in fire scenarios. Phenolic foam produces significantly lower smoke density and releases less toxic gases due to its inherent char-forming properties that act as a thermal barrier. The superior fire resistance, lower smoke generation, and reduced toxicity make phenolic foam a safer choice for fire-resistant panel applications compared to PVC foam.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam panels typically offer a more cost-effective solution compared to phenolic foam due to lower raw material and manufacturing expenses, making them widely available in the construction market. Phenolic foam, while pricier, provides superior fire resistance and smoke suppression, which can justify its higher capital investment in safety-critical applications. Availability of phenolic foam is generally more limited and subject to supplier constraints, whereas PVC foam panels benefit from broader distribution and easier procurement globally.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam and phenolic foam differ significantly in environmental impact and sustainability for fire-resistant panels. PVC foam, derived from non-renewable fossil fuels, poses challenges due to toxic chlorine emissions during production and disposal, whereas phenolic foam often boasts lower smoke toxicity and better fire resistance with reduced environmental pollutants. Phenolic foam generally exhibits a smaller carbon footprint and enhanced recyclability, positioning it as a more sustainable choice in fire-resistant panel applications.
Choosing the Right Foam for Fire Resistant Panels
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers excellent fire resistance with self-extinguishing properties and low smoke emission, making it ideal for fire resistant panels in commercial and industrial applications. Phenolic foam provides superior thermal insulation and high fire retardancy, maintaining structural integrity at elevated temperatures but often comes at a higher cost and increased brittleness. Choosing the right foam depends on balancing factors such as fire performance standards (e.g., ASTM E84, UL 94 ratings), mechanical durability, thermal insulation needs, and budget constraints specific to the project's fire safety requirements.
Infographic: Polyvinyl chloride foam vs Phenolic foam for Fire resistant panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com