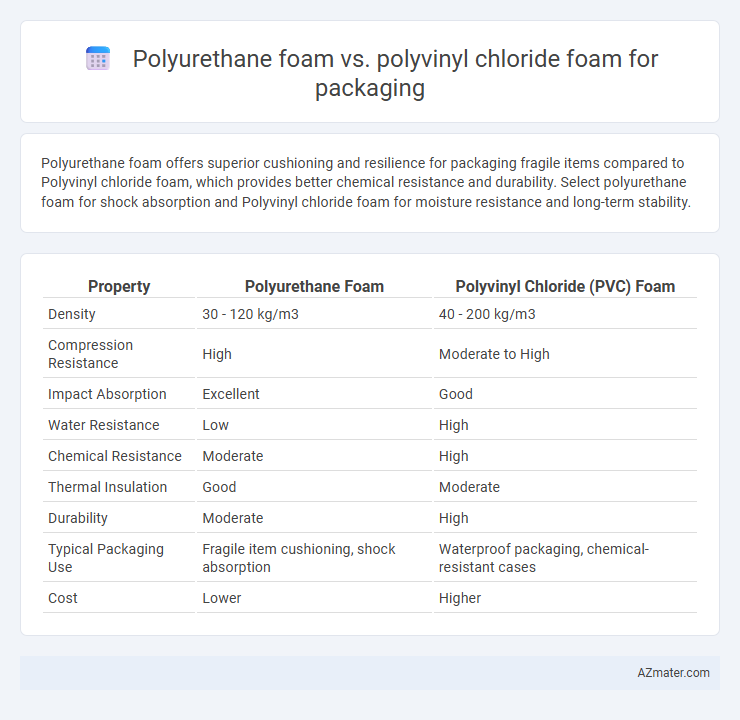
Polyurethane foam offers superior cushioning and resilience for packaging fragile items compared to Polyvinyl chloride foam, which provides better chemical resistance and durability. Select polyurethane foam for shock absorption and Polyvinyl chloride foam for moisture resistance and long-term stability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyurethane Foam | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 30 - 120 kg/m3 | 40 - 200 kg/m3 |
| Compression Resistance | High | Moderate to High |
| Impact Absorption | Excellent | Good |
| Water Resistance | Low | High |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Thermal Insulation | Good | Moderate |
| Durability | Moderate | High |
| Typical Packaging Use | Fragile item cushioning, shock absorption | Waterproof packaging, chemical-resistant cases |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Packaging Foams
Polyurethane foam and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam are widely used materials in packaging due to their excellent cushioning and protective properties. Polyurethane foam offers high flexibility, shock absorption, and lightweight characteristics, making it ideal for delicate and high-value products. PVC foam provides superior chemical resistance, rigidity, and durability, suitable for packaging items requiring more structural support and protection against environmental factors.
Overview of Polyurethane Foam
Polyurethane foam is a versatile cushioning material widely used in packaging due to its excellent shock absorption, lightweight nature, and high resilience. Its closed-cell structure provides superior resistance to moisture and chemicals, making it ideal for protecting delicate electronics and fragile items during shipping. Compared to polyvinyl chloride foam, polyurethane foam offers enhanced durability and flexibility, ensuring optimal protection and secure packaging solutions.
Overview of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Foam
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) foam is a closed-cell, lightweight material known for its excellent chemical resistance, durability, and rigidity, making it ideal for protective packaging applications. Its low water absorption and resistance to environmental factors ensure long-lasting protection for delicate goods during shipping and storage. PVC foam also offers superior impact resistance and cushioning compared to many other packaging foams, enhancing product safety.
Physical Properties Comparison
Polyurethane foam exhibits higher resilience and superior cushioning properties compared to polyvinyl chloride foam, making it ideal for protecting delicate items during shipping. Polyvinyl chloride foam offers greater rigidity and chemical resistance, providing enhanced structural support and durability under harsh environmental conditions. The density of polyurethane foam typically ranges from 20 to 60 kg/m3, whereas PVC foam density varies from 40 to 200 kg/m3, influencing their respective compressive strength and impact absorption capabilities.
Cushioning and Shock Absorption
Polyurethane foam offers superior cushioning and shock absorption due to its open-cell structure, which effectively disperses impact forces, making it ideal for packaging fragile items. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam, with its closed-cell structure, provides good resistance to compression and moisture, but generally absorbs shocks less efficiently than polyurethane foam. For packaging applications requiring maximum protection against impact, polyurethane foam is typically preferred over PVC foam.
Durability and Longevity
Polyurethane foam offers superior cushioning and resilience, providing excellent durability for packaging fragile items over extended periods. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam is more resistant to chemical exposure and moisture, enhancing longevity in harsh environments but may degrade faster under continuous mechanical stress. Choosing between polyurethane and PVC foam depends on the packaging requirements for impact absorption versus environmental resistance and lifespan.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyurethane foam and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam differ significantly in environmental impact and sustainability for packaging use. Polyurethane foam is typically more eco-friendly due to its potential for recyclability and lower toxic emissions during production, whereas PVC foam is associated with persistent organic pollutants and challenges in recyclability, contributing to long-term environmental pollution. Sustainable packaging choices increasingly favor polyurethane foam because of its better biodegradability profile and less harmful chemical additives compared to PVC foam.
Cost Analysis and Economic Factors
Polyurethane foam offers superior cushioning properties at a generally higher material cost compared to Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam, which is more cost-effective and commonly used for lightweight packaging applications. The economic factors influencing the choice include production volume, where large-scale manufacturing can offset Polyurethane foam's initial expense through reduced product damage and returns. PVC foam's lower density and cheaper raw materials provide savings in shipping and handling, making it preferable for budget-sensitive operations prioritizing minimal protective demands.
Application Suitability in Packaging
Polyurethane foam and Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam both serve critical roles in packaging applications, with polyurethane foam excelling in cushioning fragile items due to its high resilience and superior shock absorption properties. PVC foam offers enhanced chemical resistance and durability, making it suitable for packaging exposed to harsh environmental conditions or requiring moisture barriers. Selection between these foams depends on packaging demands, such as the need for impact protection versus environmental resilience.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Foam for Packaging
Polyurethane foam offers superior cushioning and flexibility, making it ideal for protecting fragile items during shipping. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam provides excellent durability and resistance to chemicals, water, and temperature variations, suitable for heavier or industrial packaging applications. Selecting the right foam depends on the specific requirements of shock absorption, environmental exposure, and product sensitivity in packaging needs.
Infographic: Polyurethane foam vs Polyvinyl chloride foam for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com