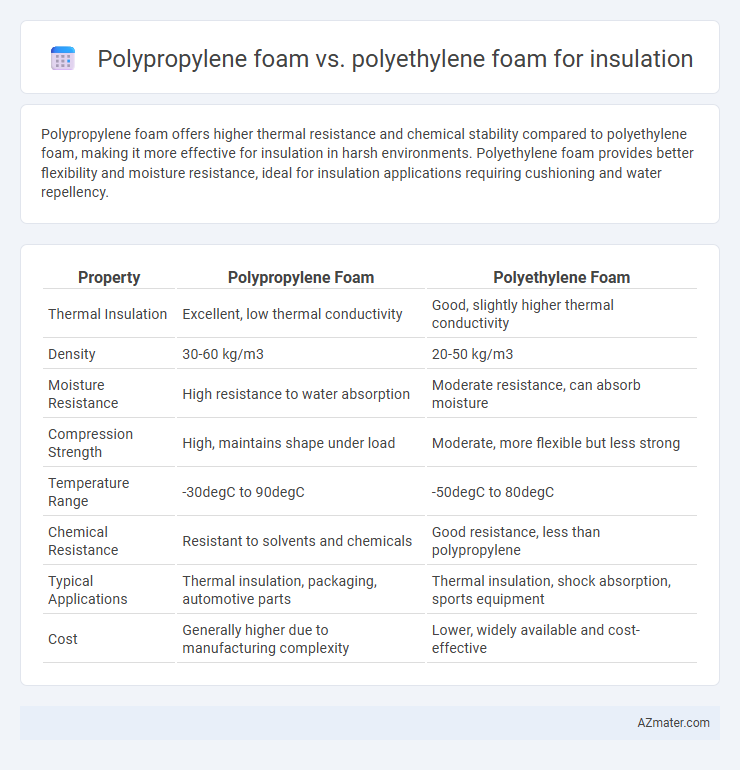
Polypropylene foam offers higher thermal resistance and chemical stability compared to polyethylene foam, making it more effective for insulation in harsh environments. Polyethylene foam provides better flexibility and moisture resistance, ideal for insulation applications requiring cushioning and water repellency.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polypropylene Foam | Polyethylene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent, low thermal conductivity | Good, slightly higher thermal conductivity |
| Density | 30-60 kg/m3 | 20-50 kg/m3 |
| Moisture Resistance | High resistance to water absorption | Moderate resistance, can absorb moisture |
| Compression Strength | High, maintains shape under load | Moderate, more flexible but less strong |
| Temperature Range | -30degC to 90degC | -50degC to 80degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to solvents and chemicals | Good resistance, less than polypropylene |
| Typical Applications | Thermal insulation, packaging, automotive parts | Thermal insulation, shock absorption, sports equipment |
| Cost | Generally higher due to manufacturing complexity | Lower, widely available and cost-effective |
Introduction: Understanding Foam Insulation Materials
Polypropylene foam offers excellent thermal resistance and rigidity, making it highly effective for insulation in automotive and construction applications. Polyethylene foam provides superior cushioning and moisture resistance, ideal for packaging and soundproofing purposes. Comparing their density, thermal conductivity, and moisture absorption reveals polypropylene foam's advantage in structural insulation and polyethylene foam's strength in moisture-prone environments.
What is Polypropylene Foam?
Polypropylene foam is a closed-cell, lightweight plastic material characterized by high stiffness, excellent chemical resistance, and superior thermal insulation properties, making it ideal for energy-efficient building applications. It offers low thermal conductivity and superior moisture resistance compared to polyethylene foam, enhancing its durability in humid or wet environments. Polypropylene foam's cellular structure and mechanical strength provide effective thermal barriers while maintaining flexibility and impact absorption in insulation systems.
What is Polyethylene Foam?
Polyethylene foam is a closed-cell, lightweight material known for its excellent thermal insulation, moisture resistance, and cushioning properties. It provides superior shock absorption and durability, making it ideal for insulation in construction, packaging, and automotive industries. Compared to polypropylene foam, polyethylene foam offers better flexibility and chemical resistance, enhancing its performance in various insulation applications.
Thermal Insulation Properties Compared
Polypropylene foam exhibits a lower thermal conductivity, typically around 0.035 W/m*K, making it highly effective for thermal insulation applications compared to polyethylene foam, which has a thermal conductivity closer to 0.038 W/m*K. The closed-cell structure of polypropylene foam enhances its resistance to heat transfer and moisture absorption, providing superior thermal insulation performance. Polyethylene foam, while slightly less efficient thermally, offers greater flexibility and impact resistance, but for strict insulation needs, polypropylene foam remains the preferred choice due to its optimized thermal barriers.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polypropylene foam exhibits higher mechanical strength and superior durability compared to polyethylene foam, making it ideal for applications requiring long-lasting insulation under stress. Its closed-cell structure enhances impact resistance and compressive strength, sustaining performance over extended periods. Polyethylene foam, while flexible and resilient, generally offers lower load-bearing capacity and quicker degradation when exposed to environmental factors.
Moisture Resistance and Water Absorption
Polypropylene foam demonstrates superior moisture resistance compared to polyethylene foam due to its closed-cell structure, reducing water absorption significantly and preventing material degradation. Polyethylene foam, while effective as an insulator, tends to absorb more water in prolonged exposure, which can compromise its insulation properties and structural integrity. For insulation applications in high-humidity environments, polypropylene foam offers enhanced durability and maintains thermal performance by minimizing moisture infiltration.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polypropylene foam offers a lower environmental impact due to its higher recyclability rate and ability to be reprocessed multiple times without significant degradation. Polyethylene foam, while widely used for insulation, presents challenges in recycling because of its mixed polymer structures and slower biodegradation. Choosing polypropylene foam supports sustainable construction practices by reducing landfill waste and promoting circular economy principles.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
Polypropylene foam offers superior thermal insulation properties but tends to be more expensive and less widely available compared to polyethylene foam, which is known for its cost-effectiveness and broad market presence. Polyethylene foam's affordability and extensive distribution make it a preferred choice for large-scale insulation projects, despite its slightly lower insulation performance. Evaluating project budget and regional supply chains is crucial for selecting between polypropylene and polyethylene foam insulation materials.
Typical Applications in Insulation Projects
Polypropylene foam is commonly used in thermal insulation for automotive parts, building panels, and packaging due to its excellent rigidity, chemical resistance, and durability. Polyethylene foam is favored for pipe insulation, HVAC systems, and vibration dampening because of its flexibility, moisture resistance, and superior cushioning properties. Both materials provide effective insulation, but polypropylene foam excels in structural applications while polyethylene foam is preferred for impact absorption and moisture barriers.
Choosing the Right Foam: Key Considerations
Polypropylene foam offers higher thermal resistance and chemical stability, making it ideal for industrial insulation requiring durability and temperature control. Polyethylene foam provides excellent cushioning and moisture resistance, suitable for residential insulation and applications where impact absorption is critical. Key considerations include the foam's density, thermal conductivity, environmental exposure, and budget constraints to ensure optimal insulation performance.
Infographic: Polypropylene foam vs Polyethylene foam for Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com