Fire-retardant foam offers enhanced safety by resisting ignition and slowing flame spread, making it ideal for sensitive or high-risk packaging needs. Polyethylene foam provides excellent cushioning and moisture resistance at a lower cost, suitable for general-purpose protective packaging.
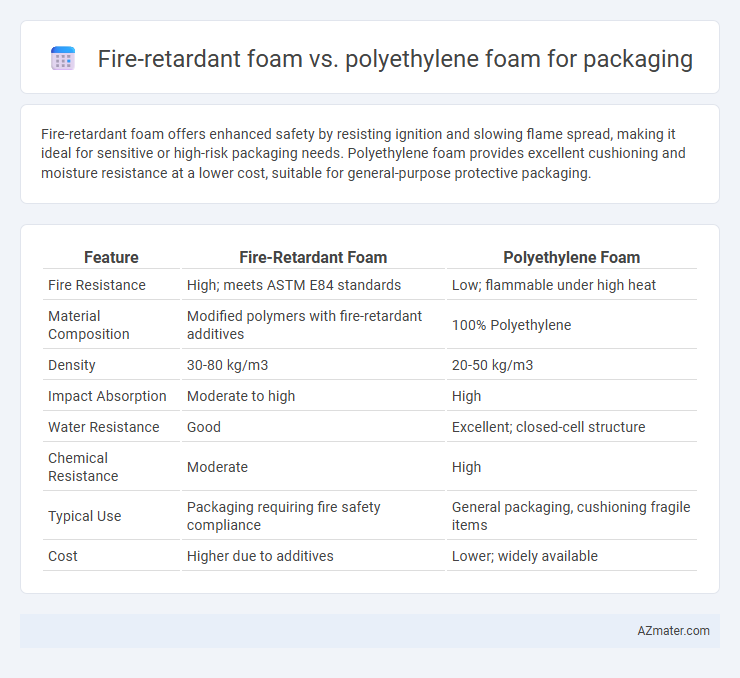
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Fire-Retardant Foam | Polyethylene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Fire Resistance | High; meets ASTM E84 standards | Low; flammable under high heat |
| Material Composition | Modified polymers with fire-retardant additives | 100% Polyethylene |
| Density | 30-80 kg/m3 | 20-50 kg/m3 |
| Impact Absorption | Moderate to high | High |
| Water Resistance | Good | Excellent; closed-cell structure |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Typical Use | Packaging requiring fire safety compliance | General packaging, cushioning fragile items |
| Cost | Higher due to additives | Lower; widely available |
Introduction to Packaging Foams
Fire-retardant foam and polyethylene foam serve distinct roles in packaging, with fire-retardant foam designed to resist ignition and slow flame spread, ensuring enhanced safety for sensitive or hazardous goods during transport. Polyethylene foam offers excellent cushioning, shock absorption, and moisture resistance, making it ideal for protecting delicate items from physical damage and environmental factors. Selecting between these foams depends on the specific protective requirements, where fire-retardant properties prioritize safety and polyethylene prioritizes impact and moisture protection.
What is Fire-Retardant Foam?
Fire-retardant foam is a specially formulated cushioning material designed to resist ignition and slow the spread of fire, making it ideal for packaging sensitive or flammable products. Unlike polyethylene foam, which primarily offers shock absorption and thermal insulation, fire-retardant foam contains chemical additives that enhance its flame-resistant properties. This foam complies with stringent fire safety standards such as UL 94, ensuring greater protection during transportation and storage of hazardous or high-value goods.
Understanding Polyethylene Foam
Polyethylene foam offers exceptional cushioning, impact resistance, and moisture resistance, making it a preferred choice for packaging fragile items. Unlike fire-retardant foam, polyethylene foam is lightweight, closed-cell, and chemically inert, ensuring durability and longevity during transportation and storage. Understanding its thermal properties and flexibility helps optimize packaging solutions for various industries, balancing protection with cost efficiency.
Key Differences Between Fire-Retardant and Polyethylene Foam
Fire-retardant foam contains specialized chemical additives designed to inhibit ignition and slow the spread of flames, enhancing safety in packaging applications where fire risk is a concern. Polyethylene foam, composed of closed-cell polyethylene, provides excellent cushioning, moisture resistance, and lightweight protection but lacks inherent flame-resistant properties. Choosing between fire-retardant and polyethylene foam depends on balancing fire safety requirements against cushioning performance and environmental exposure in the packaging environment.
Fire Safety and Flammability Ratings
Fire-retardant foam offers superior fire safety with enhanced resistance to ignition and slower flame spread, meeting stringent flammability ratings such as UL 94 V-0 or Class A standards. Polyethylene foam, while lightweight and cushioning, typically has higher flammability and lower fire resistance, often requiring additional treatments to comply with fire safety regulations. Choosing fire-retardant foam ensures compliance with safety codes, reducing fire hazards in packaging applications sensitive to heat and flames.
Durability and Impact Resistance Comparison
Fire-retardant foam offers enhanced safety features by resisting ignition and slowing flame spread, making it ideal for packaging sensitive or flammable items. Polyethylene foam provides superior impact resistance due to its closed-cell structure, absorbing shocks and vibrations effectively during transit. In terms of durability, polyethylene foam exhibits greater resilience against wear, moisture, and repeated compressions, whereas fire-retardant foam may have a shorter lifespan under heavy mechanical stress.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Fire-retardant foam often contains chemical additives that can hinder recyclability and contribute to environmental pollution, posing challenges for sustainable disposal. Polyethylene foam, especially when produced from recycled materials, offers better environmental performance due to its higher recyclability and lower toxicity. Choosing polyethylene foam can reduce the ecological footprint of packaging by supporting circular economy practices and minimizing hazardous waste generation.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Fire-retardant foam typically incurs higher costs than polyethylene foam due to specialized chemicals enhancing its flame resistance, impacting overall packaging budgets. Polyethylene foam offers a more economically efficient solution for general-purpose packaging with lower material and production expenses. Evaluating long-term cost savings from fire safety compliance may justify the premium price of fire-retardant foam in regulated industries.
Common Applications in Packaging Solutions
Fire-retardant foam is widely used in packaging applications that require enhanced fire safety, such as electronics, aerospace components, and hazardous materials, ensuring compliance with strict fire regulations. Polyethylene foam, known for its lightweight and cushioning properties, is commonly applied in packaging delicate consumer goods, automotive parts, and medical devices to provide impact resistance and vibration dampening. Both materials serve critical roles in protecting products during transportation and storage, with selection driven by specific safety and durability requirements.
Choosing the Best Foam for Your Packaging Needs
Fire-retardant foam offers enhanced safety by resisting flames and reducing combustion risks, making it ideal for packaging sensitive electronic devices or hazardous materials. Polyethylene foam provides excellent cushioning, moisture resistance, and shock absorption, suitable for lightweight and general-purpose packaging applications. Selecting the best foam depends on balancing fire safety requirements with physical protection needs, ensuring optimal preservation and compliance for your products.
Infographic: Fire-retardant foam vs Polyethylene foam for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com