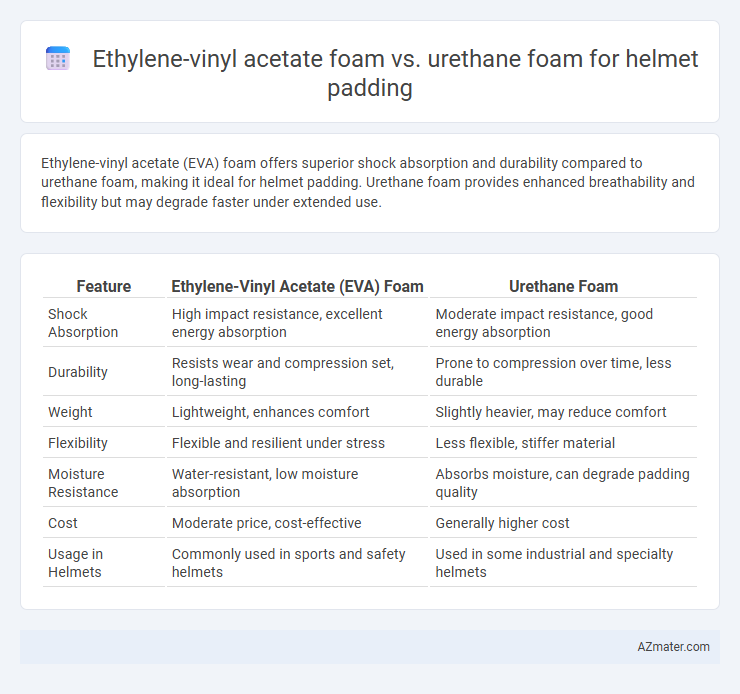
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers superior shock absorption and durability compared to urethane foam, making it ideal for helmet padding. Urethane foam provides enhanced breathability and flexibility but may degrade faster under extended use.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA) Foam | Urethane Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Shock Absorption | High impact resistance, excellent energy absorption | Moderate impact resistance, good energy absorption |
| Durability | Resists wear and compression set, long-lasting | Prone to compression over time, less durable |
| Weight | Lightweight, enhances comfort | Slightly heavier, may reduce comfort |
| Flexibility | Flexible and resilient under stress | Less flexible, stiffer material |
| Moisture Resistance | Water-resistant, low moisture absorption | Absorbs moisture, can degrade padding quality |
| Cost | Moderate price, cost-effective | Generally higher cost |
| Usage in Helmets | Commonly used in sports and safety helmets | Used in some industrial and specialty helmets |
Introduction to Helmet Padding Materials
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers lightweight, flexible cushioning with excellent shock absorption and durability, making it ideal for helmet padding to enhance impact protection. Urethane foam provides superior energy dispersion and comfort due to its open-cell structure, which improves ventilation and moisture management in helmets. Choosing between EVA and urethane foam depends on the desired balance of impact resistance, breathability, and long-term durability for specific helmet applications.
What is Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA) Foam?
Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA) foam is a soft, flexible, and lightweight material commonly used for helmet padding due to its excellent shock absorption and durability. Compared to urethane foam, EVA offers superior resistance to cracking, UV radiation, and moisture, making it ideal for prolonged outdoor use in helmets. Its closed-cell structure provides enhanced cushioning and impact protection, ensuring improved comfort and safety for the wearer.
Key Characteristics of Urethane Foam
Urethane foam used for helmet padding is highly durable, providing excellent impact absorption and resilience under repeated compression, which enhances long-term protection. It features superior cushioning properties with a flexible, open-cell structure that allows for effective ventilation and moisture management. Compared to ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam, urethane foam offers enhanced conformability to head contours and superior energy dispersion, making it a preferred choice for high-performance helmet applications.
Impact Absorption: EVA Foam vs Urethane Foam
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers superior impact absorption compared to urethane foam due to its closed-cell structure, which efficiently disperses impact forces and enhances shock attenuation. EVA foam's resilience and ability to recover its shape quickly make it ideal for helmet padding, providing consistent protection during multiple impacts. Urethane foam, while softer and more breathable, generally compresses more under impact, resulting in less effective energy absorption and potentially reduced helmet safety performance.
Comfort and Fit: Comparing Both Foams
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers superior shock absorption and flexibility, enhancing comfort by conforming closely to the head's shape for a secure fit in helmet padding. Urethane foam provides excellent cushioning and durability but tends to be denser, which can sacrifice some breathability and adaptability to individual head contours. Choosing EVA foam often results in a lighter, more comfortable helmet with better long-term fit retention, while urethane foam excels in impact resistance but may feel less tailored over extended wear.
Durability and Longevity of Helmet Padding
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam exhibits superior durability and resistance to compression set compared to urethane foam, making it more effective in maintaining helmet padding shape over time. Urethane foam tends to degrade faster with repeated impact and exposure to sweat, resulting in reduced longevity and cushioning performance. EVA foam's enhanced resilience and moisture resistance contribute to extended helmet lifespan and sustained protective qualities.
Weight Considerations: EVA vs Urethane
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers a lightweight solution for helmet padding, typically weighing less than urethane foam of equivalent thickness, which enhances overall comfort and reduces fatigue during extended wear. Urethane foam, while slightly denser, provides more resilient cushioning and impact absorption but adds extra weight, potentially affecting helmet balance and user endurance. Selecting EVA foam for helmet padding prioritizes weight reduction without significant compromise in protective performance, making it ideal for applications where minimizing helmet load is critical.
Cost Effectiveness of EVA and Urethane Foams
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers a lower cost per unit volume compared to urethane foam, making it a more cost-effective option for helmet padding in mass production. EVA foam also provides durable shock absorption and resilience over time, reducing the frequency of replacements and maintenance expenses. Urethane foam, while offering superior cushioning and comfort, typically incurs higher material and manufacturing costs, impacting overall budget efficiency for helmet manufacturers.
Safety Standards and Testing Performance
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam and urethane foam are widely used in helmet padding, with EVA foam often preferred for its superior shock absorption and impact resistance, meeting stringent safety standards such as ASTM F1447 and CPSC certification. Urethane foam, while offering good flexibility and comfort, may exhibit less consistent energy dissipation during impact testing, affecting its performance under high-velocity impacts. Comparative evaluations through EN 1078 and SNELL tests highlight EVA foam's enhanced durability and resilience, making it a reliable choice for helmets requiring high safety performance.
Choosing the Best Foam for Helmet Padding
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers superior shock absorption and durability, making it ideal for helmet padding designed to reduce impact forces effectively. Urethane foam provides excellent comfort and cushioning due to its softer texture but may degrade faster under repeated stress and environmental exposure. Selecting the best foam depends on balancing EVA's resilience for long-term protection with urethane's enhanced comfort for sustained wear.
Infographic: Ethylene-vinyl acetate foam vs Urethane foam for Helmet padding
 azmater.com
azmater.com